Society shapes the values, norms, and behaviors that guide human interactions and cultural development. Understanding societal dynamics helps you navigate complex social structures and fosters a sense of belonging. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how society influences every aspect of your daily life.
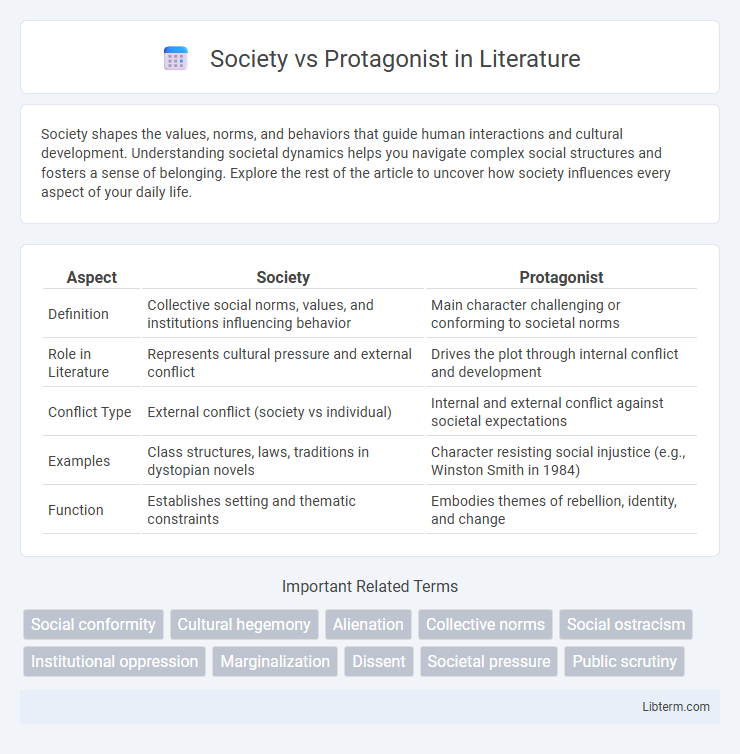
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Society | Protagonist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective social norms, values, and institutions influencing behavior | Main character challenging or conforming to societal norms |
| Role in Literature | Represents cultural pressure and external conflict | Drives the plot through internal conflict and development |
| Conflict Type | External conflict (society vs individual) | Internal and external conflict against societal expectations |
| Examples | Class structures, laws, traditions in dystopian novels | Character resisting social injustice (e.g., Winston Smith in 1984) |
| Function | Establishes setting and thematic constraints | Embodies themes of rebellion, identity, and change |
Introduction: Framing Society vs Protagonist
Conflict between society and protagonist explores the tension where individual beliefs clash with collective norms or institutional rules, highlighting struggles for identity, freedom, or justice. This dynamic often reveals societal constraints that challenge the protagonist's values, motivations, or goals, creating a narrative tension central to thematic development. Understanding this opposition illuminates how cultural, social, or political forces shape character arcs and plot progression.
Defining the Role of Society in Fiction
Society in fiction functions as a complex network of cultural norms, laws, and collective values that shape the protagonist's challenges and growth. It often embodies external conflicts, forcing the protagonist to confront social expectations, prejudices, or institutional barriers. This dynamic highlights themes of conformity, rebellion, and identity, defining the protagonist's journey within a broader communal context.
Protagonist as the Catalyst for Change
The protagonist acts as the catalyst for change by challenging societal norms and confronting established conventions that resist progress. Through decisive actions and unwavering conviction, the protagonist exposes systemic flaws and inspires collective reflection. Their journey underscores the transformative power individuals hold to reshape cultural and institutional paradigms.
Common Themes in Society vs Protagonist Conflicts
Society vs Protagonist conflicts often explore themes of individuality versus conformity, highlighting the protagonist's struggle to maintain personal identity against societal norms and expectations. These conflicts delve into issues of injustice, as protagonists challenge oppressive systems or cultural traditions that marginalize or suppress dissenting voices. Themes of rebellion, alienation, and the quest for freedom underscore the tension between the individual and collective values imposed by society.
Historical Contexts Influencing the Struggle
Historical contexts such as oppressive regimes, cultural revolutions, and social inequalities shape the conflict between society and protagonist, highlighting systemic challenges faced by individuals. Protagonists often embody resistance against prevailing norms dictated by political ideologies, economic pressures, or social hierarchies. These struggles reflect broader historical tensions where personal agency confronts collective doctrines, driving narratives of change and rebellion.
Literary Examples: Society Opposing the Individual
In George Orwell's *1984*, the totalitarian regime exemplifies society's oppressive power against the individual, enforcing conformity and punishing dissent relentlessly. Similarly, in Ray Bradbury's *Fahrenheit 451*, the government bans books to suppress individual thought, demonstrating societal control over personal freedom. These works highlight the conflict where society's demands for uniformity clash with the protagonist's desire for autonomy and truth.
Character Development Through Societal Opposition
Character development intensifies when the protagonist faces societal opposition, revealing inner resilience and adaptability. Conflicts arising from cultural norms, laws, or social expectations force protagonists to challenge their beliefs and evolve. This tension between individual values and collective pressures enriches character complexity and drives narrative depth.
Narrative Techniques for Highlighting the Conflict
Narrative techniques like internal monologues and unreliable narration effectively highlight the conflict between society and the protagonist by revealing personal dilemmas and societal pressures. Symbolism and setting often emphasize the protagonist's alienation, portraying society as an oppressive force. Through fragmented timelines and shifting perspectives, authors deepen the tension, showcasing the protagonist's struggle against societal norms.
Social Commentary and Authorial Purpose
The conflict between society and the protagonist illuminates critical social issues such as conformity, injustice, and resistance to oppression. Authors use this tension to critique prevailing cultural norms and power structures, urging readers to question societal values and embrace individual autonomy. This dynamic also reflects broader themes of alienation and the struggle for identity within rigid social frameworks.
Conclusion: Enduring Relevance in Modern Storytelling
The conflict between society and protagonist remains a central theme in contemporary storytelling, reflecting ongoing tensions between individual desires and collective norms. Modern narratives often explore this dynamic to critique social structures and highlight personal identity struggles. This enduring relevance underscores the universal appeal of challenging societal expectations through compelling character journeys.
Society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com