Escapism offers a mental refuge from daily stress, allowing your mind to wander through books, movies, or immersive experiences. While it provides valuable emotional relief, excessive escapism can hinder personal growth and problem-solving abilities. Discover how to balance escapism and reality effectively by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
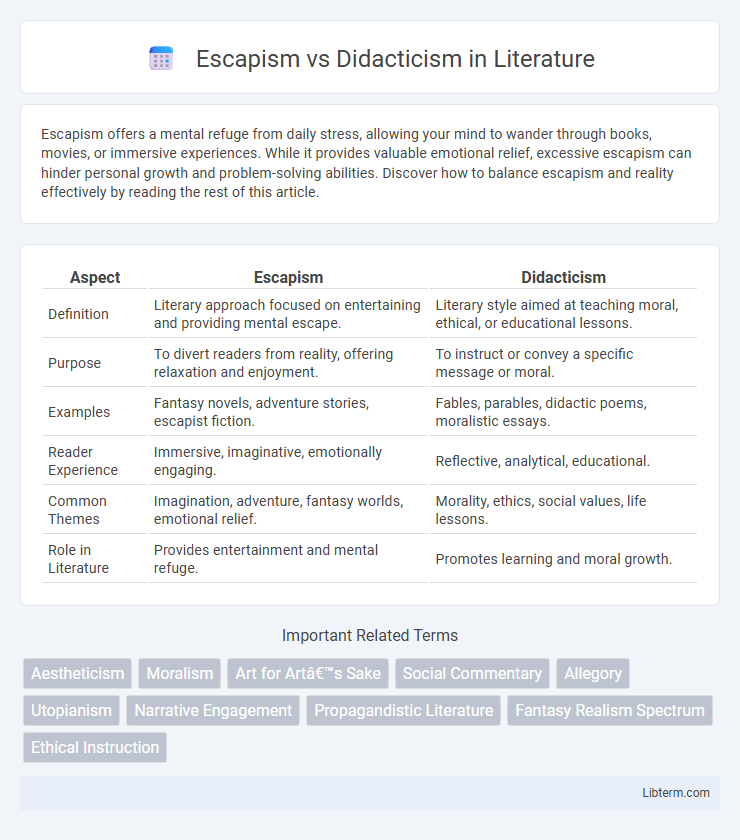
| Aspect | Escapism | Didacticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary approach focused on entertaining and providing mental escape. | Literary style aimed at teaching moral, ethical, or educational lessons. |
| Purpose | To divert readers from reality, offering relaxation and enjoyment. | To instruct or convey a specific message or moral. |
| Examples | Fantasy novels, adventure stories, escapist fiction. | Fables, parables, didactic poems, moralistic essays. |
| Reader Experience | Immersive, imaginative, emotionally engaging. | Reflective, analytical, educational. |
| Common Themes | Imagination, adventure, fantasy worlds, emotional relief. | Morality, ethics, social values, life lessons. |
| Role in Literature | Provides entertainment and mental refuge. | Promotes learning and moral growth. |
Defining Escapism and Didacticism
Escapism is a literary or artistic approach that immerses the audience in imaginative worlds or experiences to provide relief from reality, emphasizing entertainment and emotional engagement. Didacticism, by contrast, aims to instruct or convey moral, ethical, or educational lessons through its content, prioritizing clarity and purpose over entertainment. Both forms influence how narratives shape audience perception, with escapism fostering emotional escape and didacticism promoting reflection and understanding.
Historical Roots of Escapism in Art and Literature
Escapism in art and literature traces its roots to ancient civilizations where storytelling and visual art provided respite from harsh realities, exemplified by epic poems like Homer's "Odyssey" offering immersive journeys beyond everyday life. During the Renaissance, escapism flourished as artists and writers crafted imaginative worlds that captivated audiences while subtly reflecting societal ideals. This historical foundation underscores escapism's enduring role in shaping creative expression as a means to temporarily transcend physical and social constraints.
The Purpose of Didacticism: Teaching Through Stories
Didacticism serves the primary purpose of teaching moral, ethical, or practical lessons through storytelling, aiming to educate readers while engaging them emotionally and intellectually. Stories imbued with didactic intent often use clear, structured narratives and symbolic characters to communicate values and guide behavior, making complex ideas accessible through relatable examples. This educational approach contrasts with escapism by prioritizing cognitive and moral development over solely providing entertainment or immersive fantasy.
Escapist Works: Notable Examples in Modern Media
Escapist works in modern media, such as the "Harry Potter" series by J.K. Rowling and the Marvel Cinematic Universe, provide immersive experiences that transport audiences into fantastical worlds. Video games like "The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild" and streaming series like "Stranger Things" exemplify escapism by offering narratives that prioritize adventure and creativity over moral instruction. These media focus on engaging viewers' imagination and emotions, providing relief from everyday realities through escapist storytelling.
Didactic Narratives: Influential Works and Authors
Didactic narratives aim to educate and impart moral lessons, with influential works such as John Bunyan's "The Pilgrim's Progress" exemplifying this style through allegorical storytelling. Authors like George Orwell in "Animal Farm" and Harriet Beecher Stowe in "Uncle Tom's Cabin" use didacticism to address social and political issues, embedding ethical messages within compelling narratives. This literary approach prioritizes instruction and reflection, shaping readers' values and perspectives through carefully crafted themes and character development.
Psychological Impact: Why Readers Seek Escape or Guidance
Escapism offers readers psychological relief by providing immersive experiences that reduce stress and anxiety, allowing temporary detachment from real-life problems. Didacticism appeals to those seeking personal growth and moral guidance, fostering critical thinking and self-reflection. The psychological impact of escapism satisfies emotional needs for comfort, while didacticism addresses intellectual and ethical development.
Escapism vs Didacticism in Contemporary Culture
Escapism in contemporary culture offers immersive experiences through virtual reality, video games, and streaming platforms, allowing audiences to temporarily disconnect from reality. Didacticism, by contrast, remains prevalent in modern media that emphasizes moral lessons, social critiques, and educational content, shaping public discourse and awareness. The tension between escapist entertainment and didactic messaging reflects ongoing debates about the role of culture in providing relief versus fostering social responsibility.
Criticisms and Controversies Surrounding Both Approaches
Escapism is often criticized for promoting avoidance of reality and encouraging passive consumption of content, potentially leading to disengagement from societal issues. Didacticism faces controversy for its tendency to prioritize moral or educational messages over artistic expression, which can result in overly preachy or simplistic narratives. Both approaches spark debate regarding the balance between entertainment and purpose, with critics arguing that excessive focus on either can undermine the complexity and authenticity of storytelling.
Blending Escapism and Didacticism: Striking a Balance
Blending escapism and didacticism involves crafting narratives that both entertain and educate, ensuring readers remain engaged while absorbing meaningful lessons. Effective works balance imaginative storytelling with clear moral or informational content, enhancing retention and emotional impact. This approach maximizes literary value by appealing to diverse audiences seeking enjoyment and insight simultaneously.
The Future of Storytelling: Shifting Trends and Preferences
Escapism and didacticism represent two dominant approaches in storytelling, with current trends showing a nuanced blend that caters to evolving audience preferences for immersive experiences infused with meaningful insights. The future of storytelling emphasizes interactive narratives and transmedia platforms, allowing users to escape into richly detailed worlds while simultaneously engaging with educational or thought-provoking content. Advances in virtual reality and AI-driven personalization enhance the balance between entertainment and instruction, reshaping how stories influence cultural and social discourse.
Escapism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com