An autobiography offers an intimate glimpse into the author's life, capturing pivotal moments, personal growth, and unique experiences that define their journey. By sharing authentic stories and reflections, it allows readers to connect on a deeper emotional level and gain insights into different perspectives. Discover how crafting an autobiography can inspire your own storytelling and enrich your understanding of life's narrative in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
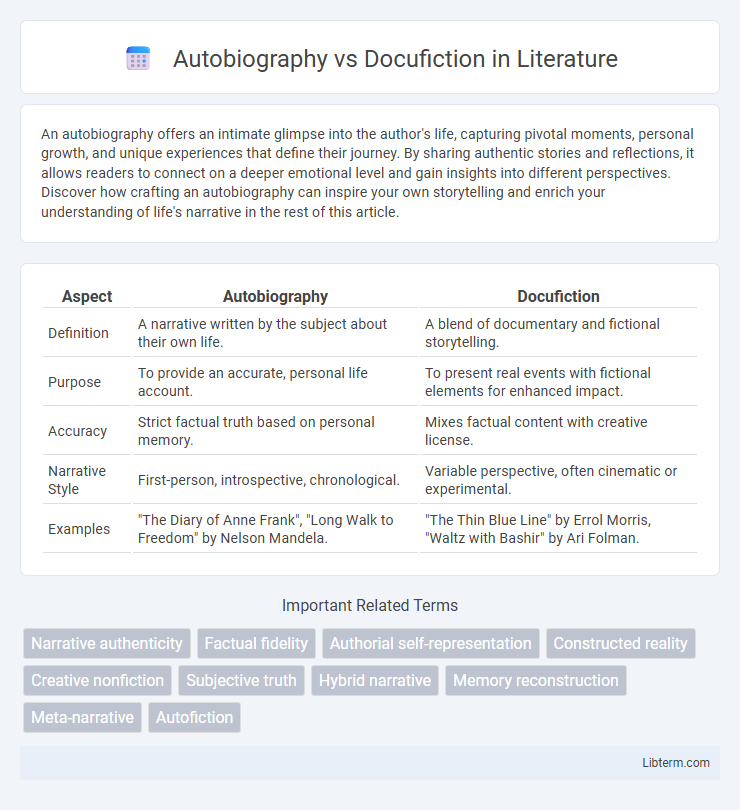
| Aspect | Autobiography | Docufiction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A narrative written by the subject about their own life. | A blend of documentary and fictional storytelling. |
| Purpose | To provide an accurate, personal life account. | To present real events with fictional elements for enhanced impact. |
| Accuracy | Strict factual truth based on personal memory. | Mixes factual content with creative license. |
| Narrative Style | First-person, introspective, chronological. | Variable perspective, often cinematic or experimental. |
| Examples | "The Diary of Anne Frank", "Long Walk to Freedom" by Nelson Mandela. | "The Thin Blue Line" by Errol Morris, "Waltz with Bashir" by Ari Folman. |
Understanding Autobiography: Definition and Key Features
An autobiography is a self-written account of the author's life, emphasizing personal experiences, memories, and reflections presented in a chronological or thematic structure. Key features include authenticity, first-person narration, and a focus on factual events while capturing the author's inner thoughts and emotions. Unlike docufiction, which blends factual documentary elements with fictional storytelling, autobiographies prioritize truthful representation and introspective insight.
What is Docufiction? Exploring Its Core Elements
Docufiction is a hybrid genre that blends documentary and fictional storytelling to create a narrative grounded in real events while incorporating imaginative elements. Core elements include a factual basis supported by real footage or interviews, combined with dramatized scenes or fictionalized dialogues to enhance emotional engagement and thematic depth. This approach allows filmmakers to explore subjective truths and perspectives that pure documentaries might not capture, offering a nuanced representation of reality.
Historical Origins of Autobiography and Docufiction
The historical origins of autobiography trace back to ancient texts such as Saint Augustine's "Confessions" in the 4th century, pioneering self-reflective narrative as a literary form. Docufiction emerged in the 20th century, blending documentary and fictional elements to present historical events with creative narrative techniques, as seen in early films like Robert Flaherty's "Nanook of the North" (1922). Both genres evolved to explore personal and collective histories, with autobiography emphasizing individual experience and docufiction merging factual storytelling with dramatic interpretation.
Major Differences Between Autobiography and Docufiction
Autobiography is a factual narrative written by an individual about their own life, emphasizing real events and personal experiences with authenticity and chronological accuracy. Docufiction blends documentary and fictional elements to present a story that may include dramatized scenes, imaginative interpretations, or invented dialogue, often prioritizing thematic truth over literal fact. The major difference lies in autobiography's commitment to factual accuracy, while docufiction employs creative license to enhance storytelling and engage viewers emotionally.
Narrative Voice: Fact vs. Creative Interpretation
Autobiography employs a first-person narrative voice rooted in factual recounting, emphasizing authenticity and personal experience. Docufiction blends documentary elements with fictionalized storytelling, allowing creative interpretation through a hybrid narrative voice. This hybrid approach balances objective facts with imaginative reconstruction to engage audiences emotionally and intellectually.
Blurring Boundaries: Truth, Memory, and Imagination
Autobiography and docufiction both challenge traditional notions of truth by blending factual memories with imaginative reinterpretations, creating a fluid narrative that resists clear categorization. Autobiographies rely heavily on personal memory as a source of truth, while docufiction incorporates fictional elements to enhance or question reality, emphasizing the subjective nature of human experience. This blurring of boundaries invites readers to reconsider the reliability of memory and the role of creativity in representing lived experiences.
Impact on Readers: Authenticity vs. Artistic License
Autobiography offers readers a direct, authentic glimpse into the author's personal experiences, fostering deep emotional connections through verifiable truths. Docufiction blends factual events with creative storytelling, enhancing engagement but blurring the lines of authenticity and raising questions about accuracy. The impact on readers hinges on their preference for truthful representation versus immersive, artistically crafted narratives that provoke thought beyond mere facts.
Famous Works: Notable Examples of Each Genre
Famous autobiographies such as "The Diary of a Young Girl" by Anne Frank and "Long Walk to Freedom" by Nelson Mandela provide deeply personal and factual narratives. In contrast, docufiction is exemplified by films like "The Blair Witch Project" and "Naked Lunch," which blend documentary realism with fictional elements to create a hybrid storytelling form. These works highlight the distinct narrative strategies used to explore truth and creativity within their respective genres.
Ethical Considerations in Blending Fact and Fiction
Autobiography and docufiction differ significantly in ethical considerations when blending fact and fiction; autobiographies demand strict adherence to truth to maintain credibility and respect for subjects, while docufiction allows artistic license but requires transparency to avoid misleading audiences. Ethical concerns arise around consent, representation accuracy, and the potential distortion of real events, which can impact public perception and personal reputations. Creators must balance creative expression with responsibility by clearly delineating fact from fiction to uphold trust and integrity in storytelling.
Choosing the Right Form: Which Suits Your Story?
Choosing between autobiography and docufiction hinges on the level of factual accuracy and creative freedom you desire. Autobiographies offer a truthful, detailed account rooted in personal experience, making them ideal for authentic storytelling and historical documentation. Docufiction blends reality with fictional elements, allowing for imaginative narratives that explore deeper emotional truths or hypothetical scenarios beyond strict factual constraints.
Autobiography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com