Prescriptivism emphasizes strict rules and guidelines governing language use, aiming to maintain clarity and prevent ambiguity. It often prioritizes traditional grammar, syntax, and vocabulary standards to uphold linguistic correctness. Discover how prescriptivism shapes effective communication by reading the rest of the article.
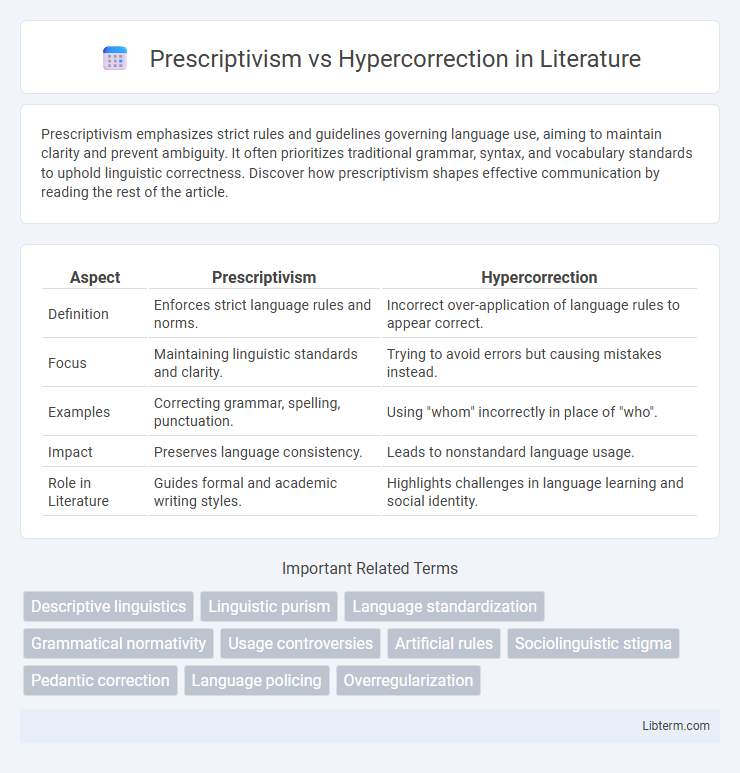
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Prescriptivism | Hypercorrection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enforces strict language rules and norms. | Incorrect over-application of language rules to appear correct. |
| Focus | Maintaining linguistic standards and clarity. | Trying to avoid errors but causing mistakes instead. |
| Examples | Correcting grammar, spelling, punctuation. | Using "whom" incorrectly in place of "who". |
| Impact | Preserves language consistency. | Leads to nonstandard language usage. |
| Role in Literature | Guides formal and academic writing styles. | Highlights challenges in language learning and social identity. |
Understanding Prescriptivism in Language
Prescriptivism in language advocates for established grammatical rules and standardized usage to maintain clarity and consistency in communication. It emphasizes correct forms based on historical norms and authoritative sources, often resisting linguistic change or regional variations. This approach contrasts with hypercorrection, where speakers overapply these prescriptive rules, leading to nonstandard or erroneous language usage.
What is Hypercorrection?
Hypercorrection occurs when language users apply prescriptive grammar rules excessively or incorrectly, leading to errors rather than improvements in speech or writing. This phenomenon often arises from attempts to sound more educated or proper, such as using "whom" in the wrong context or pronouncing words unnaturally. Hypercorrection highlights the tension between prescriptivism, which enforces strict language rules, and natural language evolution.
Origins and Evolution of Prescriptivism
Prescriptivism, rooted in 18th-century grammatical traditions, emerged as a response to the desire for linguistic order and standardized communication, emphasizing fixed rules based on classical languages like Latin and Greek. Its evolution was shaped by educational reforms and the rise of print culture, reinforcing the belief in a "correct" form of language to maintain clarity and social hierarchy. Over time, prescriptivism influenced language policies, but also sparked debates around linguistic authority, leading to phenomena like hypercorrection where speakers apply rules excessively or inaccurately in pursuit of correctness.
Common Examples of Hypercorrection
Common examples of hypercorrection occur when speakers mistakenly apply grammatical rules to sound more prestigious, such as using "whom" incorrectly in place of "who" or pronouncing "r" in non-rhotic accents where it is traditionally silent. Another frequent case involves overgeneralizing irregular verb forms, like saying "breaked" instead of "broke." These errors result from an attempt to conform to prescriptive norms, highlighting the tension between prescriptivism and natural language variation.
Prescriptivism vs Descriptivism: Key Differences
Prescriptivism enforces strict language rules to maintain clarity and correctness, while descriptivism observes and records how language is naturally used by speakers without judgment. Prescriptivists aim to preserve traditional grammar standards, whereas descriptivists accept language evolution and variation as valid. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for linguists in analyzing language norms versus real-world usage.
Causes Behind Hypercorrection
Hypercorrection often arises from individuals attempting to conform to perceived language standards, especially when influenced by social or educational pressures that emphasize prescriptive grammar rules. This phenomenon is prevalent among non-native speakers and language learners aiming to avoid stigmatized errors but inadvertently producing atypical forms. Social factors such as the desire for prestige, identity reinforcement, and anxiety about language correctness significantly contribute to hypercorrection.
Prescriptive Rules: Necessity or Nuisance?
Prescriptive rules in language serve to establish standardized grammar and usage, ensuring clear communication and mutual understanding across diverse speakers. These rules often prevent ambiguity and maintain linguistic consistency, especially in formal contexts such as education and professional writing. However, rigid adherence to prescriptive norms can sometimes hinder natural language evolution and foster hypercorrection, where speakers overapply rules, resulting in errors and social stigma.
Impact of Hypercorrection on Communication
Hypercorrection often leads to misunderstandings and reduced clarity in communication as speakers prioritize perceived correctness over natural language use, causing awkward or incorrect expressions. This linguistic phenomenon can disrupt effective interaction, confusing listeners and diminishing the speaker's credibility. Prescriptivism's rigid rules may fuel hypercorrection, ultimately hindering authentic and fluid conversations.
Social and Cultural Influences on Language Norms
Prescriptivism enforces strict language rules often reflecting dominant social and cultural values that influence perceptions of correctness and prestige. Hypercorrection arises when speakers over-apply these prescriptive norms in an effort to conform, revealing tensions between social identity and linguistic accommodation. Both phenomena highlight how language norms are shaped by socio-cultural power dynamics and the desire for social acceptance.
Striking a Balance: Effective Language Use
Prescriptivism emphasizes strict adherence to grammar rules, while hypercorrection results from overapplying these norms, often leading to errors. Striking a balance involves adopting prescriptive guidelines thoughtfully and recognizing situational language variations. Effective language use respects standard conventions yet remains adaptable to communication context and evolving linguistic trends.
Prescriptivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com