Diachronic analysis examines language development and change over time, revealing how meanings and structures evolve across historical periods. This approach allows linguists to trace the origins and shifts in vocabulary, grammar, and phonetics within different languages. Explore the rest of the article to understand how diachronic analysis can deepen your insight into linguistic evolution.
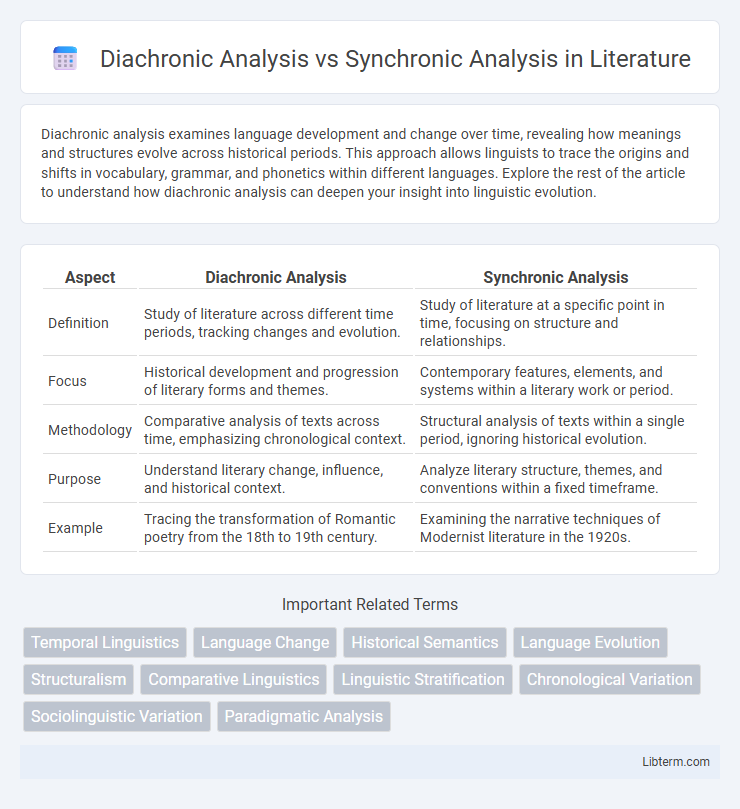
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Diachronic Analysis | Synchronic Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of literature across different time periods, tracking changes and evolution. | Study of literature at a specific point in time, focusing on structure and relationships. |
| Focus | Historical development and progression of literary forms and themes. | Contemporary features, elements, and systems within a literary work or period. |
| Methodology | Comparative analysis of texts across time, emphasizing chronological context. | Structural analysis of texts within a single period, ignoring historical evolution. |
| Purpose | Understand literary change, influence, and historical context. | Analyze literary structure, themes, and conventions within a fixed timeframe. |
| Example | Tracing the transformation of Romantic poetry from the 18th to 19th century. | Examining the narrative techniques of Modernist literature in the 1920s. |
Introduction to Linguistic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines the historical development and evolution of language over time, tracing changes in phonetics, morphology, and syntax through different periods. Synchronic analysis studies a language at a specific point in time, analyzing its structure and usage without considering historical context. Both approaches are fundamental in linguistic analysis, providing complementary insights into language dynamics and its structural variations.
Defining Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines the evolution and historical development of a language, culture, or phenomenon over time, tracking changes and transformations across different periods. This approach contrasts with synchronic analysis, which studies a subject at a specific point in time without considering its historical context. Diachronic analysis is essential for understanding linguistic shifts, cultural progressions, and the dynamic nature of social constructs through temporal progression.
Defining Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis examines a language, culture, or system at a specific point in time, emphasizing its structure and function without considering historical development. This approach prioritizes understanding the current state and relationships within the system, often used in linguistics to analyze phonetics, syntax, or semantics as they coexist. Contrastingly, diachronic analysis studies changes and evolutions over time, tracking historical transformations and development trajectories.
Historical Background of Both Approaches
Diachronic analysis traces the evolution of language, culture, or phenomena over time, rooted in historical linguistics pioneered by scholars like Sir William Jones in the 18th century. Synchronic analysis examines a subject at a specific point in time, popularized by Ferdinand de Saussure's early 20th-century work in structural linguistics. Both approaches have shaped modern humanities and social sciences by providing complementary perspectives on change and stability.
Key Differences Between Diachronic and Synchronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines the evolution and changes in language, culture, or phenomena over time, emphasizing historical development and temporal context. Synchronic analysis focuses on a specific moment or period, analyzing structures and relationships without considering historical progression. Key differences include diachronic's temporal dimension versus synchronic's emphasis on systematic description at a single point in time.
Importance in Linguistic Studies
Diachronic analysis examines language change over time, revealing the evolution of phonetics, grammar, and semantics essential for understanding historical language development. Synchronic analysis studies language at a specific moment, providing a snapshot of structure and usage that informs contemporary linguistic theory and language teaching. Both approaches are crucial in linguistic studies for comprehensively analyzing language dynamics and informing fields such as historical linguistics, sociolinguistics, and language acquisition.
Methodologies Used in Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis employs methodologies such as historical linguistics, comparative philology, and corpus linguistics to trace language evolution across time. Techniques include studying sound changes, morphological developments, and semantic shifts by examining historical texts, inscriptions, and archived recordings. This approach contrasts with synchronic analysis, which focuses on language structure at a specific point.
Methodologies Used in Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis employs methodologies that examine linguistic or cultural phenomena at a specific point in time, emphasizing structure and function rather than historical development. Techniques include descriptive observation, structural analysis, and comparative methods that analyze contemporary patterns and relationships within the system under study. This approach contrasts with diachronic analysis, which tracks changes and evolution across historical timelines.
Applications and Case Studies
Diachronic analysis traces language, culture, or phenomena changes over time, enabling researchers to study historical linguistics, evolution of social norms, and long-term economic trends. Synchronic analysis examines systems or languages at a specific moment, useful in sociolinguistics, structural linguistics, and contemporary market analysis. Case studies in diachronic linguistics include studying the Great Vowel Shift, while synchronic approaches are applied in analyzing modern dialects or real-time network traffic.
Future Perspectives in Linguistic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines language evolution over time, uncovering historical shifts and trends, while synchronic analysis studies language structures at a specific point, enabling detailed understanding of current grammatical and semantic patterns. Future perspectives in linguistic analysis emphasize integrating diachronic data with synchronic frameworks using advanced computational models and big data analytics to predict language changes and enhance natural language processing systems. This interdisciplinary approach promises more dynamic language models that adapt to linguistic innovation and cultural transformations effectively.
Diachronic Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com