Poetic language weaves emotions into vivid imagery, creating powerful connections that resonate deeply within the reader's soul. Crafting verses with rhythmic flow and metaphorical depth enhances the impact of your message, making it unforgettable. Explore the rest of this article to unlock the secrets of mastering your poetic expression.
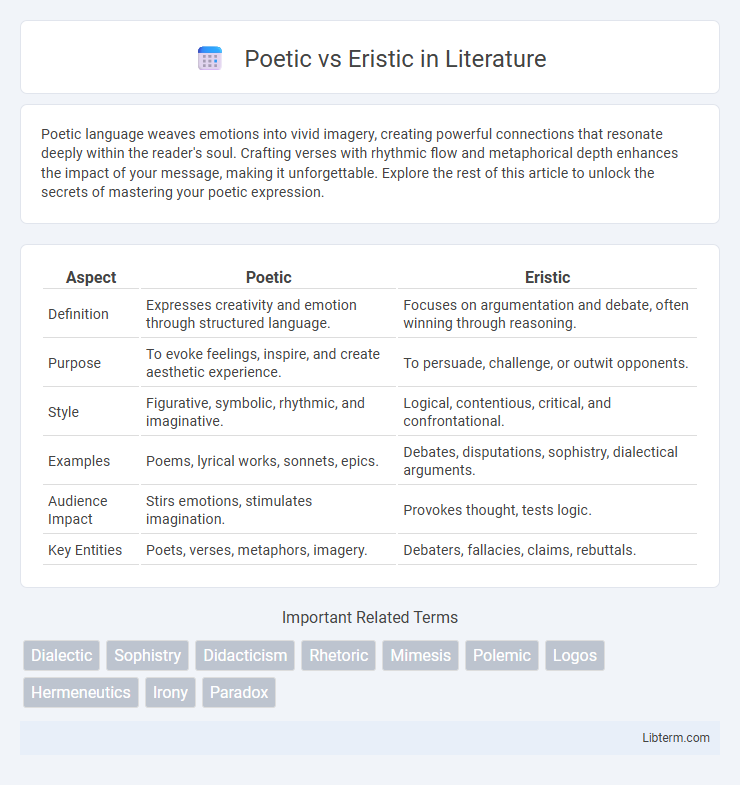
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Poetic | Eristic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expresses creativity and emotion through structured language. | Focuses on argumentation and debate, often winning through reasoning. |
| Purpose | To evoke feelings, inspire, and create aesthetic experience. | To persuade, challenge, or outwit opponents. |
| Style | Figurative, symbolic, rhythmic, and imaginative. | Logical, contentious, critical, and confrontational. |
| Examples | Poems, lyrical works, sonnets, epics. | Debates, disputations, sophistry, dialectical arguments. |
| Audience Impact | Stirs emotions, stimulates imagination. | Provokes thought, tests logic. |
| Key Entities | Poets, verses, metaphors, imagery. | Debaters, fallacies, claims, rebuttals. |
Introduction to Poetic and Eristic Modes
Poetic mode emphasizes creativity, aesthetic expression, and the exploration of emotions through metaphor and symbolism, fostering understanding and appreciation. Eristic mode centers on argumentation, dialectical reasoning, and the pursuit of winning debates, often prioritizing conflict and contradiction over truth. Both modes shape communication by influencing how ideas are conveyed and received in various intellectual and artistic contexts.
Defining Poetic Expression
Poetic expression emphasizes imaginative language, metaphor, and emotional resonance to evoke sensory experience and deeper meaning. It prioritizes aesthetic qualities, rhythm, and symbolism over direct argument or debate found in eristic discourse. Unlike eristic's goal of winning disputes through contentious reasoning, poetic expression creates a space for reflection and subjective interpretation.
Understanding Eristic Argumentation
Eristic argumentation centers on winning debates through persuasive tactics rather than seeking truth, contrasting with poetic discourse that emphasizes creative expression and deeper meaning. Understanding eristic techniques involves recognizing strategies like logical fallacies, rhetorical tricks, and emotional manipulation used to dominate discussions. Mastery of eristic argumentation requires critical awareness to identify when dialogue shifts from genuine inquiry to confrontational contest.
Historical Roots of Poetic and Eristic Traditions
The historical roots of poetic traditions trace back to ancient civilizations where oral storytelling, mythology, and ritualistic performances laid the foundation for artistic expression through structured language and metaphor. In contrast, eristic traditions originate from classical Greek philosophy, where dialectical confrontations emphasized argumentation aimed at victory rather than truth, shaping a confrontational and competitive discourse style. These divergent origins reflect the poetic focus on aesthetic and emotional resonance versus the eristic emphasis on logical debate and rhetorical strategy.
Key Differences: Intention and Outcome
Poetic discourse aims to evoke emotion, inspire creativity, and explore beauty through artistic expression, whereas eristic debate focuses on winning arguments and demonstrating intellectual dominance. The intention behind poetic communication is to enrich human experience and provoke thought, while eristic aims at outsmarting opponents regardless of truth. Consequently, poetic outcomes tend to foster reflection and empathy, whereas eristic often leads to conflict and polarization.
Rhetoric: Persuasion in Poetic and Eristic Styles
Poetic rhetoric emphasizes persuasion through aesthetic and emotive language that evokes shared values and idealized visions, fostering consensus and inspiration. Eristic rhetoric prioritizes argumentative strategies geared toward winning disputes by exploiting logical flaws, contradictions, and emotional provocation. The poetic style cultivates harmony and reflective engagement, while the eristic style advances adversarial debate and strategic dominance in discourse.
The Role of Emotion vs Logic
Poetic expression emphasizes the role of emotion, using vivid imagery and metaphor to evoke feelings and connect with the audience on an intuitive level. Eristic discourse prioritizes logic, employing rigorous argumentation and critical reasoning to challenge and refute opposing views. The tension between poetic passion and eristic reason shapes the dynamics of persuasive communication and debate.
Contexts Where Poetic or Eristic Prevail
Poetic discourse predominates in artistic and literary contexts where expression, metaphor, and emotional resonance shape meaning, such as in poetry, narrative fiction, and speeches. Eristic dialogue is more common in adversarial settings like debates, legal arguments, and political confrontations, prioritizing winning and rhetorical skill over mutual understanding. Contextual cues determine whether communication aims to explore truth aesthetically or to assert dominance through disputation.
Impact on Communication and Discourse
Poetic communication enhances discourse by fostering emotional resonance and imaginative engagement, creating deep connections through metaphor and symbolism. Eristic communication, centered on argumentation and conflict, drives discourse by sharpening critical thinking and exposing opposing viewpoints but can escalate tensions. Balancing poetic expressiveness with eristic rigor enriches dialogue, promoting both creativity and clarity in communication.
Conclusion: Finding Balance Between the Two
Balancing poetic and eristic approaches enhances communication by merging creativity with critical thinking. Poetic expression fosters emotional depth and imaginative insight, while eristic argument sharpens analytical precision and debate skills. Integrating both cultivates a harmonious dialogue that values beauty in language and rigor in reasoning.
Poetic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com