Gothic fiction transports readers into eerie settings filled with dark, mysterious atmospheres and supernatural elements that evoke suspense and terror. This genre often explores themes of decay, madness, and the uncanny, weaving complex characters caught between fear and fascination. Dive deeper into the world of Gothic fiction to uncover its hauntingly captivating stories and timeless appeal.
Table of Comparison
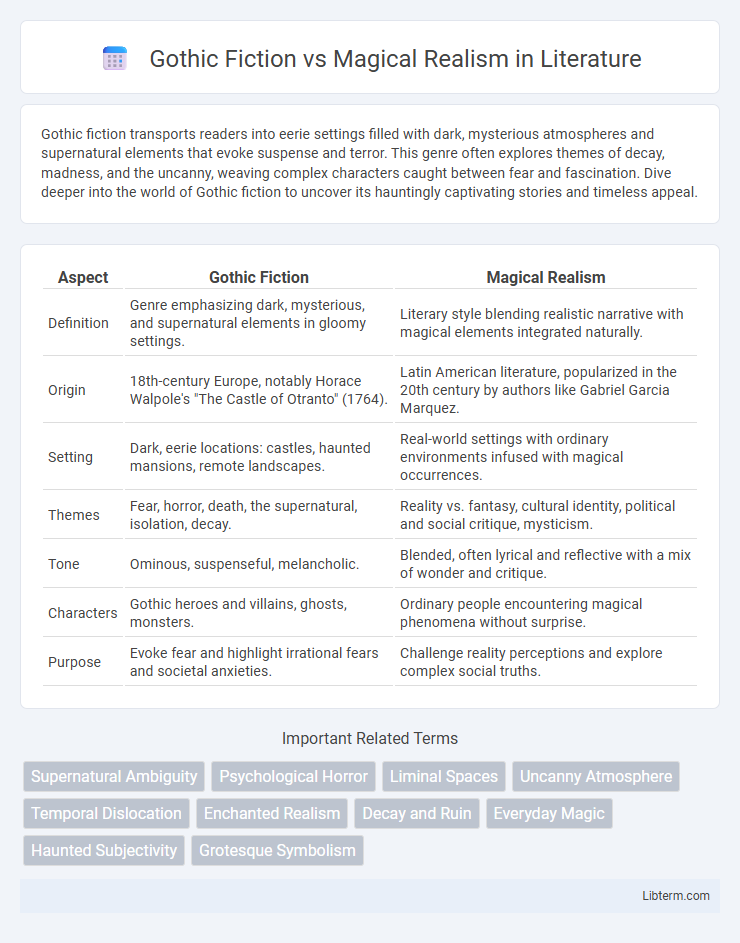
| Aspect | Gothic Fiction | Magical Realism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Genre emphasizing dark, mysterious, and supernatural elements in gloomy settings. | Literary style blending realistic narrative with magical elements integrated naturally. |
| Origin | 18th-century Europe, notably Horace Walpole's "The Castle of Otranto" (1764). | Latin American literature, popularized in the 20th century by authors like Gabriel Garcia Marquez. |
| Setting | Dark, eerie locations: castles, haunted mansions, remote landscapes. | Real-world settings with ordinary environments infused with magical occurrences. |
| Themes | Fear, horror, death, the supernatural, isolation, decay. | Reality vs. fantasy, cultural identity, political and social critique, mysticism. |
| Tone | Ominous, suspenseful, melancholic. | Blended, often lyrical and reflective with a mix of wonder and critique. |
| Characters | Gothic heroes and villains, ghosts, monsters. | Ordinary people encountering magical phenomena without surprise. |
| Purpose | Evoke fear and highlight irrational fears and societal anxieties. | Challenge reality perceptions and explore complex social truths. |
Introduction to Gothic Fiction and Magical Realism
Gothic fiction emerged in the late 18th century, characterized by its dark, eerie settings, supernatural elements, and themes of horror and romance, often exploring human psychology and ancestral curses. Magical realism, originating in Latin American literature in the mid-20th century, blends realistic narratives with fantastical elements, portraying extraordinary occurrences as normal within everyday life. Both genres challenge traditional reality but diverge in tone, with Gothic fiction emphasizing fear and suspense, while magical realism highlights the mystical within the mundane.
Defining the Gothic: Key Elements and Themes
Gothic fiction is characterized by its emphasis on dark, mysterious settings, supernatural elements, and themes of horror, decay, and madness, often set in gloomy castles or haunted locations. It explores human fears through motifs like death, the uncanny, and the sublime, with an atmosphere of suspense and psychological terror. Key elements include the presence of ghosts or monsters, a troubled protagonist, and a narrative that delves into the conflict between reason and emotion.
Magical Realism: Origins and Core Characteristics
Magical Realism originated in Latin America during the mid-20th century, blending realistic narrative with fantastical elements to explore complex social and political realities. Core characteristics include the seamless integration of magical events into everyday life, a focus on myth and folklore, and an ambiguous boundary between reality and fantasy. This genre challenges conventional perceptions of reality by treating supernatural occurrences as routine aspects of the characters' world.
Supernatural vs. Mundane: Contrasts in Narrative Focus
Gothic fiction emphasizes the supernatural through eerie settings, haunted castles, and paranormal phenomena that evoke fear and suspense, while magical realism integrates magical elements seamlessly into everyday, mundane life, blurring the line between reality and fantasy. The supernatural in Gothic narratives often serves as a catalyst for terror or psychological unrest, contrasting with magical realism's subtle, matter-of-fact inclusion of magical happenings that highlight cultural and social realities. This fundamental contrast shapes the narrative focus, with Gothic fiction highlighting darkness and dread, and magical realism emphasizing wonder and nuanced coexistence of the extraordinary within the ordinary.
Atmosphere and Setting: Darkness vs. the Everyday
Gothic fiction immerses readers in dark, eerie atmospheres, often set in decaying castles or haunted landscapes that evoke fear and mystery. In contrast, magical realism blends the supernatural seamlessly into everyday settings, creating a sense of wonder within the familiar and mundane. This juxtaposition highlights Gothic fiction's focus on foreboding environments versus magical realism's subtle enchantment embedded in ordinary life.
Role of Fear and Wonder in Both Genres
Gothic fiction leverages fear as a primary emotional driver, using dark settings, supernatural elements, and themes of horror to evoke suspense and terror. Magical realism blends the ordinary with the fantastical, fostering a sense of wonder by presenting magical elements as natural parts of reality, which challenges perception without eliciting outright fear. Both genres manipulate readers' emotions--Gothic fiction through anxiety and dread, and magical realism through curiosity and amazement--to deepen narrative impact and thematic complexity.
Iconic Works and Authors from Both Traditions
Gothic fiction is exemplified by iconic works such as Mary Shelley's "Frankenstein" and Bram Stoker's "Dracula," where authors employ dark, eerie settings and themes of terror and the supernatural. Magical realism, prominently found in Gabriel Garcia Marquez's "One Hundred Years of Solitude" and Isabel Allende's "The House of the Spirits," blends fantastical elements with realistic narratives rooted in Latin American culture. Both traditions use their respective narrative techniques to explore complex human emotions and social issues through distinctive literary lenses.
Symbolism and Metaphorical Depth
Gothic fiction employs dark, eerie settings and supernatural elements as symbols of human fears, psychological turmoil, and societal decay, emphasizing metaphorical depth through grotesque imagery and haunted landscapes. Magical realism weaves fantastical elements seamlessly into everyday life to symbolize complex cultural, political, and spiritual realities, offering layered metaphorical interpretations that blur the boundaries between reality and imagination. Both genres use symbolism to explore human consciousness and existential themes but differ in tone and narrative integration of the surreal.
Cultural and Historical Influences
Gothic Fiction emerged in the late 18th century, heavily influenced by the Romantic era's emphasis on emotion, the supernatural, and the anxieties of industrialization in Europe, reflecting societal fears through dark, haunted settings and themes of decay. Magical Realism originated in Latin America during the mid-20th century, shaped by postcolonial perspectives and indigenous storytelling traditions, blending fantastical elements with everyday reality to critique political oppression and explore cultural identity. Both genres use supernatural motifs but differ in cultural contexts, with Gothic Fiction rooted in European historical turmoil and Magical Realism shaped by Latin American cultural hybridity and historical struggle.
Lasting Impact on Contemporary Literature
Gothic fiction's haunting atmospheres and exploration of human fears have deeply influenced contemporary horror and psychological thrillers, embedding themes of darkness and the supernatural into modern storytelling. Magical realism's blending of the ordinary with fantastical elements reshaped narrative techniques, fostering a fusion of reality and imagination that continues to inspire diverse genres and global literary voices. Both movements profoundly shaped contemporary literature by expanding the boundaries of narrative style and thematic exploration.
Gothic Fiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com