Strong argumentative writing requires clear claims supported by relevant evidence and logical reasoning to persuade the reader effectively. Developing counterarguments and addressing potential objections enhances your credibility and strengthens your position. Explore the rest of the article to master techniques that will sharpen your argumentative skills and help you present compelling, well-structured arguments.
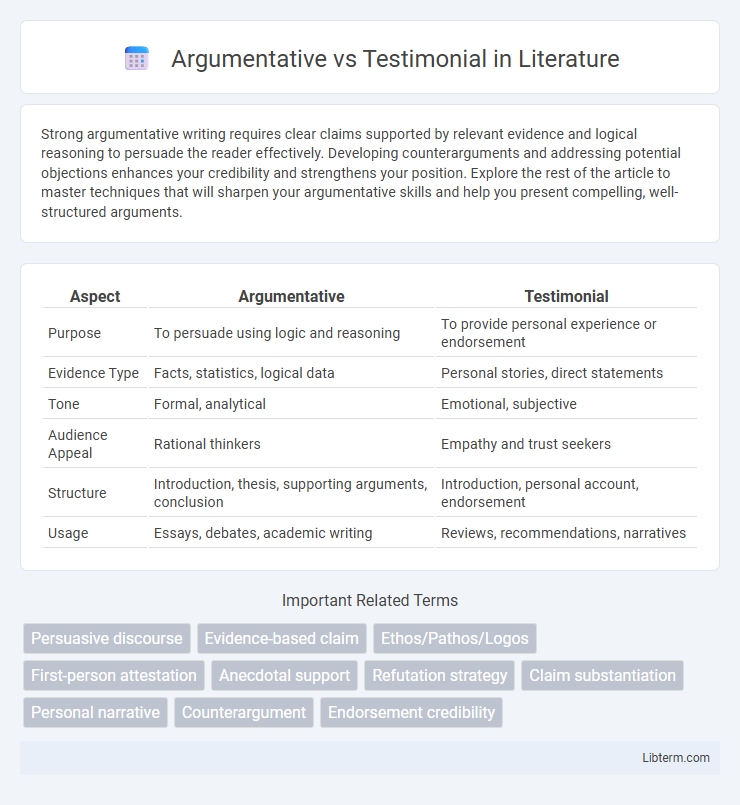
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Argumentative | Testimonial |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To persuade using logic and reasoning | To provide personal experience or endorsement |
| Evidence Type | Facts, statistics, logical data | Personal stories, direct statements |
| Tone | Formal, analytical | Emotional, subjective |
| Audience Appeal | Rational thinkers | Empathy and trust seekers |
| Structure | Introduction, thesis, supporting arguments, conclusion | Introduction, personal account, endorsement |
| Usage | Essays, debates, academic writing | Reviews, recommendations, narratives |
Understanding Argumentative and Testimonial Styles
Argumentative style emphasizes presenting clear claims supported by evidence, logical reasoning, and persuasive techniques to convince the audience of a specific viewpoint. Testimonial style relies on personal experiences, endorsements, or eyewitness accounts to build credibility and emotional connection with the audience. Understanding these styles involves recognizing that argumentative writing seeks to persuade through logic, while testimonial writing aims to influence through trust and relatability.
Core Differences: Argument vs Testimony
An argumentative text centers on presenting a clear claim supported by evidence and reasoning to persuade the audience, emphasizing logic and critical analysis. Testimonial writing relies on personal experiences or eyewitness accounts, aiming to build credibility and emotional connection through authentic narratives. The core difference lies in argumentation's focus on objective justification versus testimony's emphasis on subjective validation.
Structure of an Argumentative Approach
An argumentative approach features a clear claim supported by evidence and logical reasoning, typically structured into an introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs presenting supporting arguments and counterarguments, and a conclusion reinforcing the position. This structure ensures that each point is substantiated with data, examples, and expert quotes to persuade the audience effectively. The emphasis lies on critical analysis and coherent progression of ideas to maintain credibility and reader engagement throughout the argument.
Elements of a Testimonial Approach
The testimonial approach centers on personal experiences, emphasizing credibility, authenticity, and emotional appeal to persuade the audience effectively. Key elements include the witness's identity, detailed narrative of the experience, and specific examples that illustrate the benefits or outcomes. These components enhance trustworthiness and foster a strong connection between the subject and the audience.
Persuasive Techniques in Argumentative Writing
Argumentative writing employs logical reasoning, evidence, and structured claims to persuade readers through facts and sound arguments. Persuasive techniques such as ethos, pathos, and logos are strategically used to establish credibility, appeal to emotions, and present rational evidence, enhancing the writer's position. In contrast, testimonial writing leans heavily on personal experience and endorsements rather than structured argumentation and critical analysis.
Emotional Appeal in Testimonial Narratives
Testimonial narratives leverage emotional appeal by sharing personal experiences that evoke empathy and trust, creating a strong connection with the audience. Unlike argumentative texts that prioritize logic and evidence, testimonials emphasize feelings and authenticity to persuade effectively. This emotional resonance often enhances credibility and motivates action based on shared human experiences.
Effectiveness: When to Use Argumentative or Testimonial
Argumentative content excels in effectiveness when aiming to persuade through logic, facts, and evidence, making it ideal for debates, academic writing, or policy discussions. Testimonial content proves most effective when seeking to build trust and emotional connection by sharing personal experiences or endorsements, often used in marketing or customer reviews. Choosing between argumentative and testimonial approaches depends on the audience's need for rational justification versus emotional reassurance.
Credibility and Evidence in Both Styles
Argumentative writing establishes credibility through logical reasoning, supported by well-researched evidence, statistics, and expert opinions to persuade readers effectively. Testimonial writing relies on personal experiences or endorsements to build trust, using firsthand accounts or celebrity support as evidence of authenticity. Both styles use evidence to enhance credibility, but argumentative texts emphasize rational proof while testimonials prioritize emotional connection.
Common Pitfalls in Argumentative and Testimonial Writing
Common pitfalls in argumentative writing include weak thesis statements, reliance on logical fallacies, and insufficient evidence to support claims, which undermine the overall persuasiveness. Testimonial writing often suffers from lack of credibility, overgeneralization, and emotional bias that can diminish the trustworthiness of the narrative. Effective writing requires clear, well-supported arguments or genuine, balanced testimonials to engage and convince the audience.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Audience
Argumentative content is effective for audiences that value logical reasoning and evidence-based conclusions, leveraging facts, statistics, and expert opinions to persuade. Testimonial content resonates more with audiences seeking personal experiences and emotional connections, using authentic stories or endorsements to build trust. Selecting the right approach depends on understanding the audience's preferences, whether they are more influenced by rational arguments or relatable personal narratives.
Argumentative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com