Dramatic moments captivate audiences by evoking intense emotions and creating memorable experiences. They heighten tension and highlight pivotal points in storytelling, making your engagement deeper and more impactful. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how dramatic elements enhance narratives and emotional connection.
Table of Comparison
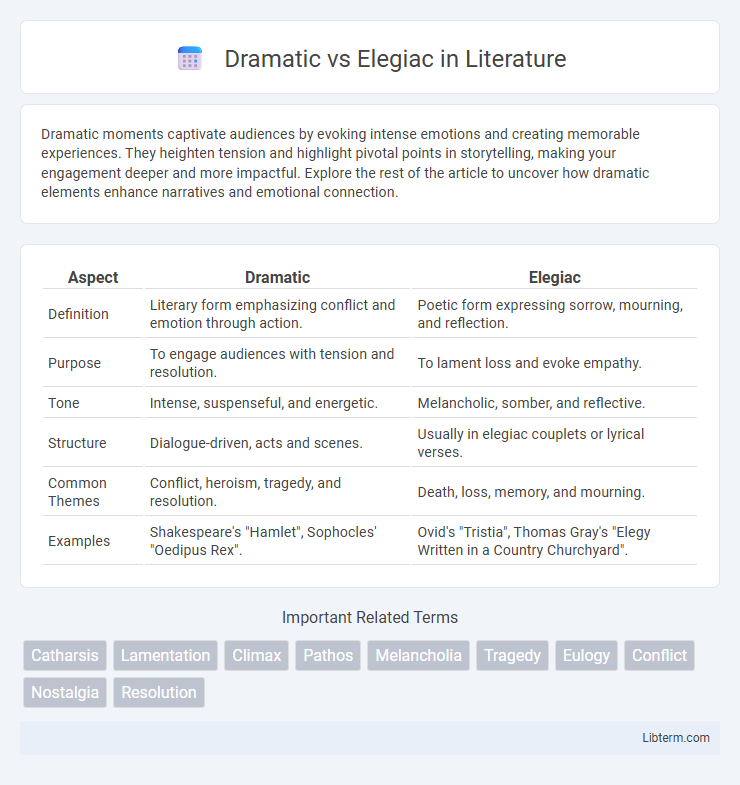
| Aspect | Dramatic | Elegiac |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary form emphasizing conflict and emotion through action. | Poetic form expressing sorrow, mourning, and reflection. |
| Purpose | To engage audiences with tension and resolution. | To lament loss and evoke empathy. |
| Tone | Intense, suspenseful, and energetic. | Melancholic, somber, and reflective. |
| Structure | Dialogue-driven, acts and scenes. | Usually in elegiac couplets or lyrical verses. |
| Common Themes | Conflict, heroism, tragedy, and resolution. | Death, loss, memory, and mourning. |
| Examples | Shakespeare's "Hamlet", Sophocles' "Oedipus Rex". | Ovid's "Tristia", Thomas Gray's "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard". |
Understanding Dramatic and Elegiac Modes
Dramatic mode centers on vivid, intense emotions and conflict, often portrayed through dialogue or action to evoke immediate engagement and tension. Elegiac mode emphasizes reflection, mourning, and lamentation, expressing sorrow or loss in a contemplative and melodic manner. Understanding these modes enhances literary analysis by distinguishing between active emotional expression and introspective grief in texts.
Defining the Dramatic Tone
The dramatic tone is characterized by intense emotion, conflict, and dynamic action, often revealing tension between characters or within a narrative. This tone emphasizes vivid expressions and situations, creating suspense and engaging the audience through heightened stakes and passion. Unlike the elegiac tone, which reflects mournful and reflective emotions, the dramatic tone drives the plot forward with urgency and active confrontation.
Elegiac: Essence and Characteristics
Elegiac poetry captures a melancholic reflection on loss and longing, often articulated through a mournful tone and rhythmic couplets rooted in classical traditions. Its essence lies in expressing grief or lamentation with an introspective and somber mood, contrasting the intense conflict and resolution found in dramatic works. Key characteristics include a focus on personal emotion, themes of mortality, and a melodic, contemplative form that evokes a timeless sense of sorrow and beauty.
Historical Roots of Dramatic and Elegiac Forms
The dramatic form traces its historical roots to ancient Greek theater, where plays by playwrights like Sophocles and Euripides emphasized conflict and dialogue within structured acts, shaping the foundation of Western drama. Elegiac poetry originates from the classical elegy of ancient Greece and Rome, particularly associated with poets such as Propertius and Ovid, characterized by its mournful tone and themes of loss or reflection, often written in elegiac couplets. Both forms evolved through centuries, with drama expanding into diverse genres and elegiac verse influencing lyric poetry across cultures.
Structural Differences: Drama vs Elegy
Dramatic works are structured around acts and scenes, emphasizing dialogue and stage directions to convey conflict and character development, while elegies follow a lyrical format, typically composed in quatrains or tercets with a consistent meter and rhyme scheme to express mourning or lamentation. Drama often progresses through rising action, climax, and resolution, enabling dynamic interaction between characters, whereas elegies maintain a reflective tone, evolving through thematic stanzas that move from grief to consolation. These structural distinctions influence how emotions are portrayed: drama manifests through performative tension and plot, whereas elegy relies on rhythmic language and repetition to evoke a somber mood.
Emotional Impact: Contrast in Effect
Dramatic works evoke intense, immediate emotional responses through conflict, tension, and dynamic action, often leaving audiences energized or unsettled. Elegiac compositions create a reflective, mournful atmosphere by emphasizing loss, nostalgia, and resignation, leading to a more subdued, contemplative emotional impact. The contrast lies in drama's provocation of active engagement versus elegy's invitation to sorrowful introspection.
Themes Explored: Conflict vs. Reflection
Dramatic themes often center on intense conflict, highlighting clashes between characters, ideas, or emotions that drive the narrative's tension and urgency. Elegiac themes focus on reflection, exploring loss, mourning, and the passage of time through contemplative and melancholic tones. The contrast between dramatic conflict and elegiac introspection shapes how stories evoke emotional responses and convey deeper meanings.
Language and Imagery Distinctions
Dramatic language relies on vivid, intense expressions and dynamic imagery to evoke strong emotions and tension, often employing metaphors, similes, and action-driven scenes. Elegiac language features more subdued, reflective tones with melancholic and mournful imagery, highlighting themes of loss and remembrance through soft, lyrical phrasing and natural or somber symbols like autumn leaves or fading light. The contrast in imagery emphasizes the immediacy and conflict in drama versus the introspection and sorrow in elegy.
Famous Works: Dramatic and Elegiac Examples
William Shakespeare's *Macbeth* stands as a quintessential dramatic work, showcasing intense conflict and complex character development through its vivid portrayal of ambition and tragedy. In contrast, elegiac poems like Alfred Lord Tennyson's *In Memoriam A.H.H.* express profound mourning and lamentation over loss, embodying the reflective and somber tone characteristic of elegies. Other famous dramatic examples include Sophocles' *Oedipus Rex*, while elegiac works often feature compositions such as John Milton's *Lycidas*.
Choosing the Right Mode for Your Narrative
Selecting between dramatic and elegiac modes depends on your narrative's emotional intent and thematic focus. Dramatic mode emphasizes tension, conflict, and active character decisions to engage readers through intense, fast-paced scenes. Elegiac mode, by contrast, embraces reflection, mourning, and a contemplative tone to evoke deep emotions related to loss and memory, making it ideal for stories centered on grief or nostalgic remembrance.
Dramatic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com