An elegy is a reflective poem that mourns the loss of someone or something significant, often expressing deep sorrow and contemplation. It captures the emotions of grief and remembrance through poignant language and solemn tone. Explore the rest of the article to understand the structure, themes, and famous examples of elegies.
Table of Comparison
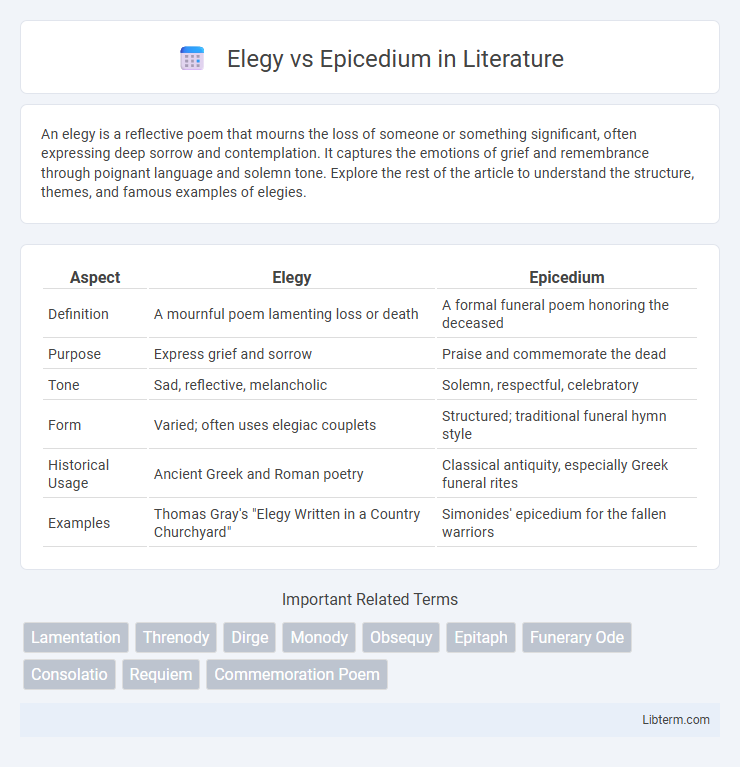
| Aspect | Elegy | Epicedium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mournful poem lamenting loss or death | A formal funeral poem honoring the deceased |
| Purpose | Express grief and sorrow | Praise and commemorate the dead |
| Tone | Sad, reflective, melancholic | Solemn, respectful, celebratory |
| Form | Varied; often uses elegiac couplets | Structured; traditional funeral hymn style |
| Historical Usage | Ancient Greek and Roman poetry | Classical antiquity, especially Greek funeral rites |
| Examples | Thomas Gray's "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard" | Simonides' epicedium for the fallen warriors |
Introduction to Elegy and Epicedium
Elegy and epicedium both serve as poetic forms that express mourning and reflection on loss, but they differ in scope and usage. Elegy typically encompasses a broader meditation on sorrow or lamentation, often evolving through various stages of grief, whereas epicedium is a specific funeral song or poem composed to honor the deceased immediately after death. Understanding the distinctions between elegy's reflective nature and epicedium's ceremonial function helps clarify their roles in literary and historical contexts of mourning.
Defining Elegy: Origins and Evolution
Elegy originates from ancient Greek poetry, initially composed as mournful songs or laments for the deceased, evolving over time into a broader poetic form expressing sorrow or reflection. Classical elegies, often written in elegiac couplets, contrasted with epicedium, which specifically served as funeral hymns honoring the dead. The evolution of elegy expanded its thematic scope beyond mourning, encompassing personal grief, philosophical meditation, and loss, distinguishing it from the more narrowly focused epicedium.
Understanding Epicedium: Historical Role
Epicedium, a poetic form rooted in ancient Greek and Roman traditions, served as a solemn funeral song or poem honoring the deceased, often performed at funerals or commemorative events. Unlike the elegy, which broadly encompasses lamentation and reflective themes in various contexts, the epicedium is specifically designed to mourn and celebrate the life of a person who has passed away. Historically, epicedium played a crucial role in ritual practices, reinforcing social memory by preserving the virtues and achievements of the departed within the community's collective consciousness.
Key Differences Between Elegy and Epicedium
Elegy and epicedium are both poetic forms expressing mourning, but elegance typically reflects personal grief or loss, often exploring themes of sorrow and reflection in a versatile structure, whereas an epicedium specifically serves as a formal funeral song or lamentation dedicated to a deceased individual, often performed at funerals or commemorative events. Elegies employ varied metrical patterns and emotional depth, while epicediums are characterized by a solemn tone and ritualistic function within classical traditions. The key difference lies in the elegy's broader thematic scope versus the epicedium's exclusive focus on honoring the dead with ceremonial reverence.
Similarities in Tone and Theme
Elegy and epicedium both convey somber and reflective tones, frequently addressing themes of loss, mourning, and tribute to the deceased. They share a focus on expressing grief and honoring the memory of those who have passed away through poetic lamentation. The emotional depth and respectful tone present in both forms create a poignant atmosphere centered on remembrance.
Notable Examples of Elegy in Literature
Elegies are poetic compositions expressing sorrow or mourning, often commemorating the dead, with notable examples including John Milton's "Lycidas" and W.H. Auden's "In Memory of W.B. Yeats." Epicedium, closely related, specifically serves as a funeral song or lament, traditionally performed at funerals or placed on tombs. Elegies in literature frequently explore themes of loss and remembrance, marked by a reflective, somber tone distinct from the ceremonial nature of epicedium.
Famous Epicedium Compositions
Famous epicedium compositions include John Milton's "Lycidas," a pastoral elegy commemorating poet Edward King, and W. H. Auden's "In Memory of W. B. Yeats," which honors the Irish poet's legacy. Unlike general elegies that express sorrow broadly, epicedium specifically serve as funeral oration poems, often highlighting the virtues of the deceased. These compositions are pivotal in literary tradition for their formal structure and cultural role in memorializing prominent figures.
Function and Purpose in Rituals and Literature
Elegies serve as reflective poems expressing personal sorrow and mourning for the deceased, often used in literature to explore grief and loss on an intimate level. Epicediums function primarily as formal, public funeral hymns or poems designed to honor and celebrate a person's life and achievements within ritualistic ceremonies. Both forms play crucial roles in rituals and literature by facilitating communal remembrance and individual emotional processing through structured poetic expression.
Cultural Impact and Modern Usage
Elegy traditionally expresses personal grief and mourning, often reflecting on loss with emotional depth, influencing Western literature and mourning rituals. Epicedium, a specific form of funeral song or poem, serves as a public tribute to notable figures, shaping cultural memory and commemorative practices in antiquity and beyond. Modern usage of elegy extends to various art forms, including music and film, while epicedium rarely appears outside historical or academic contexts, highlighting elegy's broader cultural resonance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Elegy and Epicedium
Elegy and epicedium both serve to honor the deceased, but elegy offers a more personal and reflective tone, often expressing sorrow and consolation, while epicedium is traditionally a formal funeral song emphasizing praise and commemoration. Selecting between elegy and epicedium depends on the desired emotional impact and cultural context, with elegy fitting intimate and contemplative memorials, and epicedium suited for ceremonial and public tributes. Understanding the nuances of elegy and epicedium ensures the most appropriate and meaningful expression of mourning and remembrance.
Elegy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com