An epilogue provides closure by revealing the final outcomes of the story's characters and events, enhancing your understanding of the narrative's lasting impact. It often offers a glimpse into the future or reflects on the story's themes and lessons. Discover how an epilogue can deepen your appreciation by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
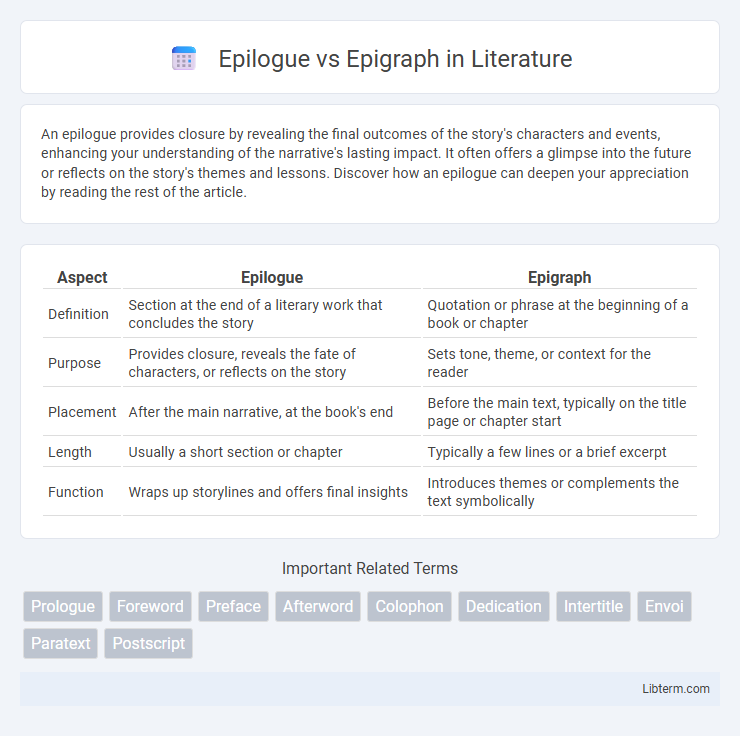
| Aspect | Epilogue | Epigraph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Section at the end of a literary work that concludes the story | Quotation or phrase at the beginning of a book or chapter |
| Purpose | Provides closure, reveals the fate of characters, or reflects on the story | Sets tone, theme, or context for the reader |
| Placement | After the main narrative, at the book's end | Before the main text, typically on the title page or chapter start |
| Length | Usually a short section or chapter | Typically a few lines or a brief excerpt |
| Function | Wraps up storylines and offers final insights | Introduces themes or complements the text symbolically |
Understanding Epilogues and Epigraphs
Epilogues serve as concluding sections in literary works, providing closure, insight into characters' futures, or thematic reflections beyond the main narrative. Epigraphs are brief quotations or phrases placed at the beginning of a chapter or book, setting the tone, hinting at themes, or offering context for the story. Understanding the distinct functions of epilogues and epigraphs enhances literary analysis by clarifying how authors frame and conclude their narratives.
Defining the Epilogue
The epilogue serves as a concluding section of a literary work, providing closure and often revealing the fate of characters after the main narrative ends. It differs from an epigraph, which is a brief quotation or phrase placed at the beginning of a text to set the tone or theme. Epilogues are essential for delivering a final reflection or tying up loose ends in novels, plays, or films.
What is an Epigraph?
An epigraph is a brief quotation or saying placed at the beginning of a literary work, chapter, or essay to suggest its theme or set the tone. This literary device often draws from famous authors, historical figures, or relevant texts, enriching the reader's understanding before diving into the main content. Unlike an epilogue, which concludes a story, an epigraph serves as a thematic introduction, providing context or insight upfront in novels, poems, or academic writings.
Purpose of an Epilogue in Literature
An epilogue in literature serves to provide closure by revealing the aftermath of the story's main events, often offering insight into characters' futures or resolving lingering plot threads. Unlike an epigraph, which is a brief quotation or phrase placed at the beginning of a work to set the thematic tone, the epilogue functions as a conclusive commentary. This narrative device enhances reader satisfaction and deepens understanding of the story's ultimate message.
Role of Epigraphs in Storytelling
Epigraphs serve as thematic signposts, offering readers a lens through which to interpret the narrative that follows. By presenting a relevant quote, phrase, or excerpt at the beginning of a story, epigraphs enrich the storytelling by setting tone, context, or foreshadowing key themes. Their strategic placement guides reader expectations and deepens the connection to the unfolding plot, differentiating them from epilogues which summarize or conclude the story after its events.
Key Differences: Epilogue vs Epigraph
An epilogue serves as a concluding section at the end of a literary work, providing closure or future insight about the story or characters, whereas an epigraph is a brief quotation or phrase placed at the beginning, setting a thematic tone. Epilogues typically function to resolve loose ends or offer reflections post-narrative, while epigraphs are used to contextualize or foreshadow the text's content. The key difference lies in their placement and purpose: epilogues follow the main text, epigraphs precede it.
When to Use an Epilogue
An epilogue is used at the end of a literary work to provide closure, reveal the fate of characters, or offer insight into events following the main story. Writers choose an epilogue when they want to extend the narrative beyond the climax or resolution, adding depth and context to the plot. Epilogues are especially common in novels and plays to address unanswered questions or set up sequels.
How to Choose an Effective Epigraph
Selecting an effective epigraph involves choosing a quote or phrase that resonates thematically with the main text and sets the tone for the reader's experience. It should be concise, impactful, and relevant to the story's core message, enhancing the reader's understanding before the narrative begins. Avoid epigraphs that are overly obscure or unrelated, ensuring they complement the book's themes rather than distract from them.
Famous Examples of Epilogues and Epigraphs
Famous examples of epilogues include Shakespeare's *The Tempest*, where Prospero directly addresses the audience to provide closure, and Jane Austen's *Pride and Prejudice*, which offers insights into the characters' futures post-narrative. Well-known epigraphs feature Franz Kafka's *The Trial*, beginning with a quote from Max Brod that sets a thematic tone, and T.S. Eliot's *The Waste Land*, which incorporates multiple literary references to deepen the poem's context. These literary devices enrich narratives by framing the story's themes and leaving lasting impressions through strategic placement at the beginning or end of works.
Enhancing Your Writing with Epilogues and Epigraphs
Epilogues and epigraphs serve distinct purposes in writing, with epilogues providing a concluding insight that enhances the reader's understanding of the narrative's aftermath, while epigraphs set the tone or theme through a relevant quote or excerpt at the beginning. Incorporating an epilogue can deepen the emotional resonance and closure for your audience, whereas an epigraph enriches context and encourages reflection before the story unfolds. Mastering the use of both tools strategically boosts the depth and impact of literary works, making your writing more engaging and thematically layered.
Epilogue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com