The plot of a story serves as the structured sequence of events that drive the narrative forward, creating tension and engagement for the reader. Effective plotting involves a clear beginning, middle, and end, with well-timed conflicts and resolutions that enhance character development. Explore the rest of the article to uncover techniques for crafting compelling plots that captivate your audience.
Table of Comparison
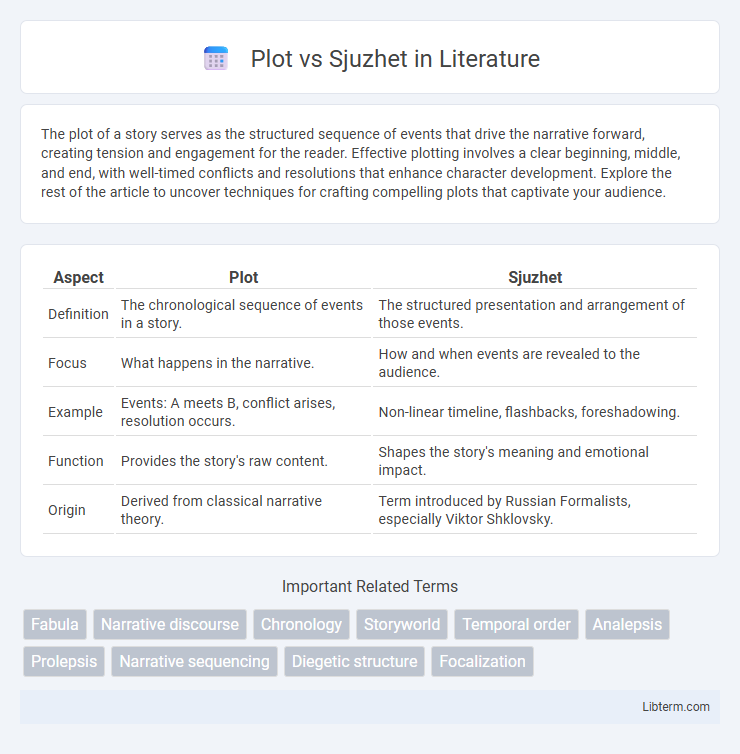
| Aspect | Plot | Sjuzhet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The chronological sequence of events in a story. | The structured presentation and arrangement of those events. |
| Focus | What happens in the narrative. | How and when events are revealed to the audience. |
| Example | Events: A meets B, conflict arises, resolution occurs. | Non-linear timeline, flashbacks, foreshadowing. |
| Function | Provides the story's raw content. | Shapes the story's meaning and emotional impact. |
| Origin | Derived from classical narrative theory. | Term introduced by Russian Formalists, especially Viktor Shklovsky. |
Understanding Plot: The Backbone of Storytelling
Plot serves as the backbone of storytelling by organizing events in a logical, cause-and-effect sequence that drives the narrative forward. Understanding plot involves recognizing its structure--the exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution--that shapes the story's progression and maintains audience engagement. Unlike sjuzet, which refers to the chronological arrangement of events, plot emphasizes the purposeful arrangement to highlight conflict and character development.
Defining Sjuzhet: Story Structure and Sequence
Sjuzhet refers to the specific arrangement and presentation of story events as they unfold in a narrative, emphasizing how the sequence shapes audience perception and thematic development. Unlike plot, which outlines all story events in their chronological order, sjuzhet deliberately manipulates time, perspective, and narrative flow to create suspense, reveal character motivations, or highlight motifs. Understanding sjuzhet is crucial for analyzing storytelling techniques that influence pacing, emotional impact, and cognitive engagement within literature and film.
Plot vs Sjuzhet: Key Differences Explained
Plot and sjuzhet differ fundamentally in narrative structure; plot refers to the chronological sequence of events in a story, while sjuzhet represents how these events are presented or arranged by the storyteller. The plot encompasses the story's raw timeline, whereas the sjuzhet involves manipulations like flashbacks, foreshadowing, or non-linear order to shape readers' perception. Understanding this distinction clarifies narrative techniques used to create suspense, thematic depth, and emotional impact in literature and film.
Historical Perspectives on Plot and Sjuzhet
Plot refers to the chronological sequence of events in a narrative, whereas sjuzhet denotes the specific way these events are presented or structured. Historical perspectives trace sjuzhet back to Russian Formalism, where scholars like Viktor Shklovsky emphasized the distinction between raw story content (fabula) and its artistic arrangement (sjuzhet). Over time, this conceptual framework has influenced literary theory by highlighting how narrative manipulation shapes audience perception and meaning.
Narrative Order: Chronology in Plot and Sjuzhet
Narrative order distinguishes plot and sjuzhet by structuring events chronologically or non-linearly. Plot follows a chronological sequence, presenting events in the order they occur in time. Sjuzhet manipulates this order, often employing flashbacks, foreshadowing, or parallel timelines to enrich the storytelling experience and deepen meaning.
The Role of Time Manipulation in Sjuzhet
In narrative theory, sjuzhet refers to the structured presentation of events, often employing time manipulation techniques such as flashbacks, flash-forwards, and temporal loops to create complexity and engage the audience. Unlike the linear progression of plot, sjuzhet rearranges chronological events, emphasizing thematic elements and character development through non-linear storytelling. Time manipulation in sjuzhet enhances narrative depth by revealing hidden motivations and altering perception, making the story more immersive and intellectually stimulating.
How Plot and Sjuzhet Shape Reader Experience
Plot structures events chronologically, providing clear cause-and-effect sequences that guide readers through a coherent narrative, enhancing understanding and emotional engagement. Sjuzhet manipulates the presentation of these events--through flashbacks, foreshadowing, or non-linear timelines--creating suspense and deeper thematic resonance. The interplay between plot and sjuzhet shapes reader experience by balancing clarity with artistic complexity, influencing pacing, interpretation, and emotional impact.
Examples of Plot and Sjuzhet in Classic Literature
Plot in classic literature refers to the chronological sequence of events, such as the straightforward timeline of events in "Romeo and Juliet," where the story progresses from the meeting to the tragic conclusion. Sjuzhet, on the other hand, represents the narrative structure and order in which these events are presented, like in "Wuthering Heights," where non-linear storytelling and flashbacks reveal the layered intricacies of the characters' lives. The difference between plot and sjuzhet is notably illustrated in "Heart of Darkness," where the plot unfolds in a linear fashion but the sjuzhet employs a framed narrative and multiple perspectives to deepen thematic exploration.
Practical Tips for Writers: Balancing Plot and Sjuzhet
Writers can enhance narrative depth by carefully distinguishing between plot--the chronological sequence of events--and sjuzhet--the structured presentation of those events. Practical tips include outlining the plot first to establish the story's skeleton, then experimenting with narrative techniques such as flashbacks or nonlinear storytelling to craft the sjuzhet. Balancing these elements allows authors to maintain clarity while engaging readers through creative temporal manipulation.
Why Plot vs Sjuzhet Matters in Modern Narratives
Plot and sjuzhet represent the chronological sequence of events and the narrative's presentation order, respectively, shaping audience perception and engagement. Understanding the distinction allows storytellers to manipulate time, create suspense, and deepen thematic resonance, critical in modern narratives where non-linear storytelling dominates. This approach enhances emotional impact and cognitive involvement, making plot versus sjuzhet a vital tool for innovative narrative structures in film, literature, and digital media.
Plot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com