Mimesis refers to the artistic representation or imitation of reality in literature, art, and philosophy, emphasizing how creators mirror the external world or human behavior. This concept explores the relationship between reality and its depiction, influencing narrative techniques and artistic expression throughout history. Discover how mimesis shapes your understanding of creativity and perception by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
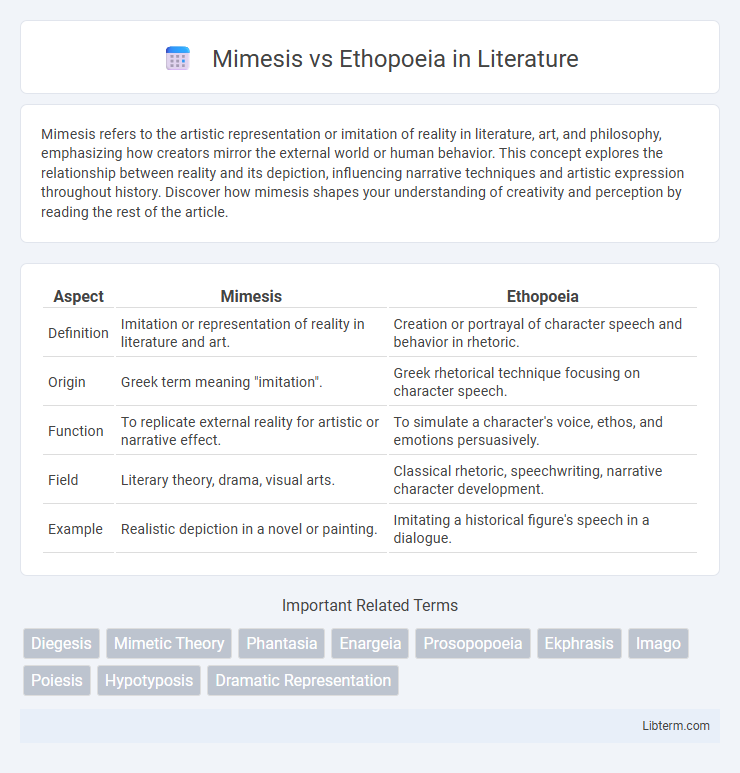
| Aspect | Mimesis | Ethopoeia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Imitation or representation of reality in literature and art. | Creation or portrayal of character speech and behavior in rhetoric. |
| Origin | Greek term meaning "imitation". | Greek rhetorical technique focusing on character speech. |
| Function | To replicate external reality for artistic or narrative effect. | To simulate a character's voice, ethos, and emotions persuasively. |
| Field | Literary theory, drama, visual arts. | Classical rhetoric, speechwriting, narrative character development. |
| Example | Realistic depiction in a novel or painting. | Imitating a historical figure's speech in a dialogue. |
Understanding Mimesis: Definition and Origins
Mimesis, originating from ancient Greek philosophy, refers to the imitation or representation of reality through art, literature, and performance, aiming to capture the essence of human experience. It serves as a foundational concept in dramatic theory, notably explored by Aristotle in "Poetics," where mimesis is seen as a natural human tendency to learn and express through imitation. Understanding mimesis involves recognizing its role in reflecting reality and emotions, shaping narrative structures, and influencing audience perception across diverse artistic forms.
Ethopoeia Explained: Meaning and Historical Context
Ethopoeia is the rhetorical practice of impersonating or representing the character, emotions, and speech of another person, often used in ancient Greek and Roman literature to evoke vivid character portrayal. Unlike mimesis, which aims to imitate actions or events, ethopoeia emphasizes the internal emotions and moral qualities through speech or behavior imitation. Historically, ethopoeia was central to forensic and deliberative rhetoric, enabling speakers to persuasively adopt personas to influence audiences in legal or political contexts.
Key Differences Between Mimesis and Ethopoeia
Mimesis involves the direct imitation of reality, aiming to represent characters and actions as they appear in real life, often emphasizing external behavior and physical actions. Ethopoeia focuses on the internal characterization by crafting or adopting a persona's thoughts, emotions, and speech to convey psychological depth and moral qualities. The key difference lies in mimesis's emphasis on external representation and ethopoeia's focus on internal voice and ethical perspective.
The Role of Imitation in Mimesis
Mimesis centers on the imitation of real-life actions and behaviors to create a lifelike representation that evokes emotional and cognitive responses. This form of imitation aims to reproduce reality with fidelity, highlighting external appearances and observable phenomena. In contrast, ethopoeia focuses more on imitating the character's mindset and personal traits, shaping deeper psychological engagement rather than external mimicry.
Ethopoeia and the Art of Character Representation
Ethopoeia is the rhetorical art of character representation through speech, enabling a speaker to impersonate and convey the personality, emotions, and moral qualities of another individual. Unlike mimesis, which broadly involves imitation of actions or events, ethopoeia specifically involves crafting persuasive and authentic character portrayals in discourse. Mastery of ethopoeia enhances narrative depth and emotional engagement by vividly embodying characters' voices and intentions.
Mimesis in Classical Literature and Philosophy
Mimesis in classical literature and philosophy refers to the imitation or representation of reality, particularly emphasized in Aristotle's Poetics as the fundamental process through which art mirrors human actions and experiences. This concept underlines the role of artistic creation in reflecting societal values, emotions, and moral lessons, shaping audiences' understanding of the world. Mimesis contrasts with ethopoeia, which involves the artistic construction or presentation of character and personality, highlighting a focus on authentic depiction over creative invention.
Ethopoeia in Ancient Rhetoric and Oratory
Ethopoeia in ancient rhetoric and oratory involves the strategic imitation of character or persona to persuade audiences through vivid moral portrayal. It emphasizes embodying the ethos of a speaker or character to evoke trust and emotional resonance, contrasting with mimesis, which broadly refers to general imitation in art. Ethopoeia's effectiveness hinges on nuanced adaptation of speech style, tone, and mannerisms to align with the perceived identity and values of the persona represented.
Comparative Analysis: Functions in Storytelling
Mimesis and Ethopoeia serve distinct yet complementary functions in storytelling by shaping character representation and audience engagement. Mimesis emphasizes the literal imitation of reality through direct depiction of actions and dialogues, fostering authenticity and immersion in the narrative. Ethopoeia, by contrast, involves the rhetorical crafting of a character's voice and persona, allowing storytellers to convey emotions, intentions, and moral qualities, thereby enhancing psychological depth and persuasive effect.
Modern Applications of Mimesis and Ethopoeia
Mimesis, the imitation of real-world behaviors and events, finds modern application in virtual reality, immersive theater, and AI-driven simulations that replicate human experiences for training and entertainment. Ethopoeia, the art of character embodiment through speech and gesture, is prominently utilized in digital marketing, character animation, and interactive storytelling to create relatable and persuasive personas. These classical rhetorical strategies enhance user engagement by combining authentic representation with personalized narrative voices in contemporary media and technology.
Conclusion: Relevance in Contemporary Discourse
Mimesis and Ethopoeia remain crucial in contemporary discourse for understanding representation and character construction across media. Mimesis emphasizes the faithful imitation of reality, influencing realist narratives and visual arts, while Ethopoeia highlights the creative embodiment of persona and rhetoric, essential for persuasive communication and identity formation. Their interplay enriches critical analysis, enabling nuanced interpretations of cultural texts and social interactions.
Mimesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com