Anxiety is a natural response to stress characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, or fear that can affect daily life and decision-making. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective coping strategies can help manage your anxiety and improve overall well-being. Discover practical tips and professional advice in the rest of this article to take control of your mental health.
Table of Comparison
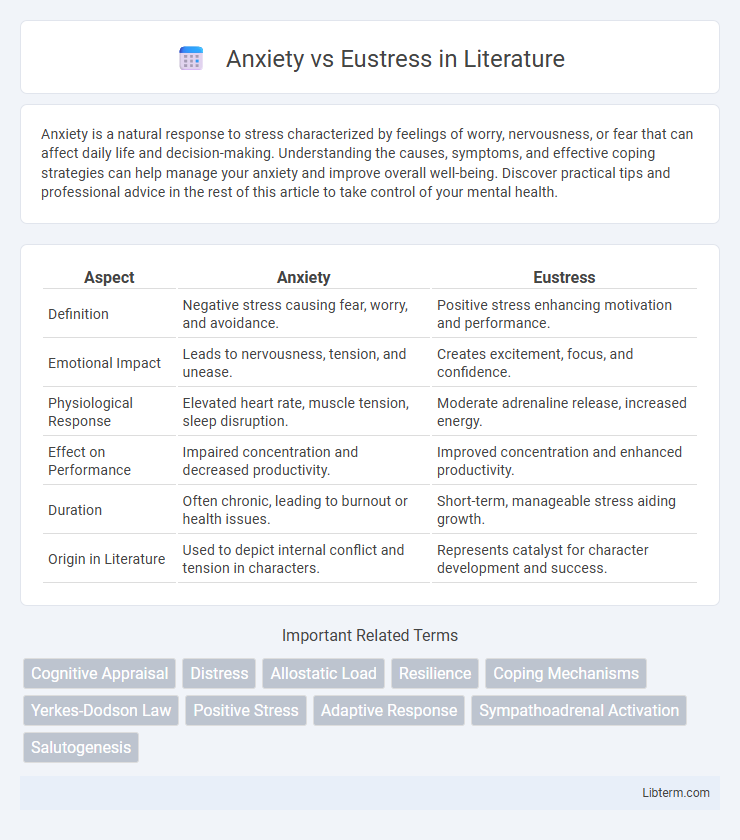
| Aspect | Anxiety | Eustress |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Negative stress causing fear, worry, and avoidance. | Positive stress enhancing motivation and performance. |
| Emotional Impact | Leads to nervousness, tension, and unease. | Creates excitement, focus, and confidence. |
| Physiological Response | Elevated heart rate, muscle tension, sleep disruption. | Moderate adrenaline release, increased energy. |
| Effect on Performance | Impaired concentration and decreased productivity. | Improved concentration and enhanced productivity. |
| Duration | Often chronic, leading to burnout or health issues. | Short-term, manageable stress aiding growth. |
| Origin in Literature | Used to depict internal conflict and tension in characters. | Represents catalyst for character development and success. |
Understanding Anxiety and Eustress
Anxiety and eustress represent two distinct psychological responses to stressors, with anxiety characterized by overwhelming negative feelings and eustress associated with positive, motivating energy. Anxiety triggers a fight-or-flight reaction linked to cortisol release, impairing cognitive function and increasing heart rate, whereas eustress activates the sympathetic nervous system to enhance focus and resilience. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for managing stress effectively, allowing individuals to leverage eustress for performance improvement while mitigating anxiety's detrimental effects on mental health.
Defining Anxiety: Causes and Symptoms
Anxiety is a psychological state characterized by excessive worry, fear, and nervousness, often triggered by stressors such as trauma, genetics, or environmental factors. Common symptoms include rapid heartbeat, sweating, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances, which can impair daily functioning. Understanding the physiological and cognitive aspects of anxiety helps differentiate it from eustress, a positive form of stress that enhances motivation and performance.
What is Eustress? Positive Stress Explained
Eustress is a form of positive stress that enhances motivation, focus, and performance, distinguishing it from anxiety, which typically impairs functioning. This beneficial stress response activates the body's fight-or-flight mechanism in a manageable way, promoting resilience and growth. Eustress is often experienced during challenging yet achievable tasks, such as public speaking or athletic competition, providing a sense of accomplishment and well-being.
Key Differences: Anxiety vs Eustress
Anxiety is a negative emotional state characterized by excessive worry, nervousness, and fear, often impairing daily functioning, whereas eustress is a positive form of stress that motivates and enhances performance, leading to personal growth and improved resilience. Anxiety triggers the body's fight-or-flight response excessively, causing physiological symptoms like increased heart rate and muscle tension, while eustress activates a manageable level of stress beneficial for focus and energy. The key difference lies in their impact on mental health: anxiety can contribute to disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder, whereas eustress supports adaptive coping mechanisms and goal achievement.
Physiological Effects: Stress on the Body
Anxiety triggers a heightened state of arousal characterized by increased heart rate, elevated cortisol levels, and muscle tension, often leading to chronic stress-related health issues such as hypertension and weakened immune function. In contrast, eustress, or positive stress, promotes adaptive physiological responses, including moderate adrenaline release and enhanced cognitive focus, which improve performance and resilience. Understanding these distinct stress responses clarifies how eustress supports bodily homeostasis while anxiety disrupts it, emphasizing the importance of managing negative stress for overall health.
Psychological Impact: Anxiety Versus Eustress
Anxiety triggers chronic stress responses that can impair cognitive function, reduce emotional regulation, and increase susceptibility to mental health disorders such as depression. In contrast, eustress activates adaptive psychological mechanisms that enhance motivation, resilience, and problem-solving abilities, promoting overall well-being. The differential impact on neurochemical pathways highlights anxiety's association with heightened cortisol levels, whereas eustress supports balanced adrenal function and positive affect.
Triggers: What Leads to Anxiety or Eustress?
Triggers for anxiety often include overwhelming situations, perceived threats, and prolonged stressors that activate the body's fight-or-flight response, leading to feelings of fear or worry. In contrast, eustress arises from challenges that are perceived as manageable and motivating, such as achievable deadlines or exciting new opportunities, which enhance focus and performance. Understanding the nature and context of these triggers helps differentiate harmful anxiety from beneficial eustress.
Coping Strategies: Managing Anxiety and Embracing Eustress
Effective coping strategies for managing anxiety include mindfulness meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and regular physical exercise, which help reduce stress hormones and improve emotional regulation. Embracing eustress involves setting achievable goals, maintaining a positive mindset, and engaging in challenges that foster personal growth and motivation. Balancing these approaches enhances resilience, improves mental health, and boosts overall productivity.
Benefits of Eustress in Daily Life
Eustress enhances motivation, focus, and productivity by triggering a positive stress response that helps individuals tackle challenges effectively. It improves resilience, encourages personal growth, and fosters problem-solving skills, contributing to overall mental well-being. Regular experience of eustress supports better performance at work or school and promotes a balanced, healthy lifestyle.
Transforming Anxiety into Eustress: Practical Tips
Transforming anxiety into eustress involves cognitive reframing techniques that shift negative perceptions into empowering challenges, enhancing motivation and performance. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, and goal-setting help regulate physiological responses and focus energy positively. Incorporating regular physical activity and maintaining a balanced routine further support emotional resilience and improve the ability to channel anxiety into productive eustress.
Anxiety Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com