Effective critique requires clear identification of strengths and weaknesses, supported by specific examples to ensure constructive feedback. Objectivity is essential to evaluate the subject fairly while maintaining a respectful tone. Explore the article further to learn how to master the art of delivering impactful critiques.
Table of Comparison
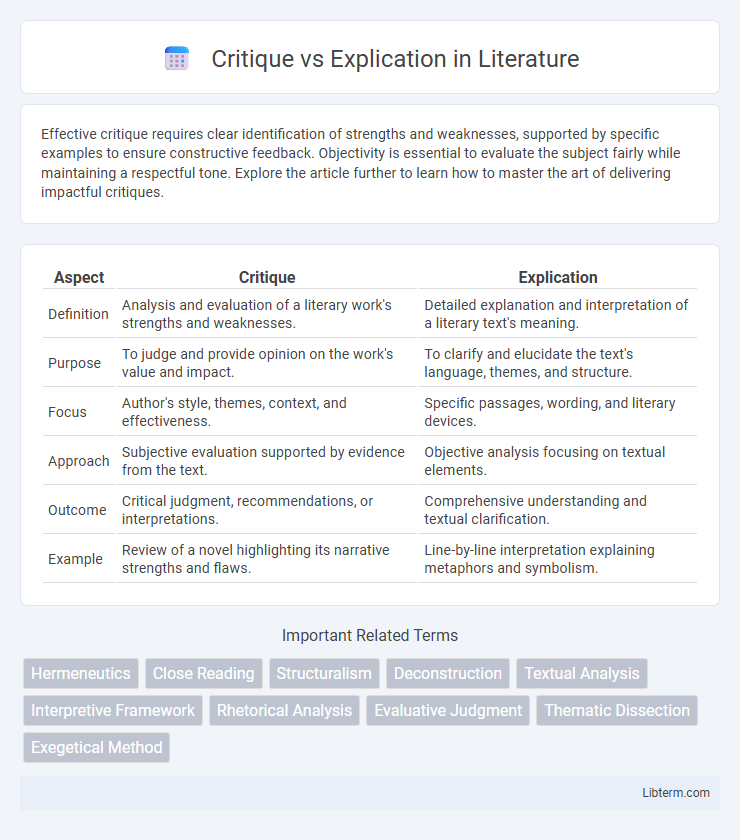
| Aspect | Critique | Explication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analysis and evaluation of a literary work's strengths and weaknesses. | Detailed explanation and interpretation of a literary text's meaning. |
| Purpose | To judge and provide opinion on the work's value and impact. | To clarify and elucidate the text's language, themes, and structure. |
| Focus | Author's style, themes, context, and effectiveness. | Specific passages, wording, and literary devices. |
| Approach | Subjective evaluation supported by evidence from the text. | Objective analysis focusing on textual elements. |
| Outcome | Critical judgment, recommendations, or interpretations. | Comprehensive understanding and textual clarification. |
| Example | Review of a novel highlighting its narrative strengths and flaws. | Line-by-line interpretation explaining metaphors and symbolism. |
Understanding Critique: Definition and Purpose
Critique involves systematically evaluating a work's strengths and weaknesses to enhance understanding and foster improvement. It aims to provide a balanced analysis that highlights both value and areas for development, supporting informed judgment and deeper insight. The purpose of critique is to engage with the subject critically, encouraging reflection and constructive feedback rather than mere summary.
The Essence of Explication: A Semantic Approach
Explication emphasizes a detailed, line-by-line analysis to uncover the intrinsic meaning and structure of a text, prioritizing semantic clarity over subjective interpretation. This method systematically decodes the linguistic and conceptual elements, ensuring a precise understanding of the author's intended message. In contrast to critique, explication avoids evaluative judgments, aiming instead to elucidate the text's essence through semantic precision.
Key Differences Between Critique and Explication
Critique involves evaluating and analyzing a text or work to assess its strengths, weaknesses, and underlying meanings, often incorporating subjective judgments. Explication focuses on a detailed, objective explanation or interpretation of specific passages or elements within the work, clarifying its meaning and structure without overt evaluation. Key differences include critique's emphasis on assessment and opinion versus explication's commitment to thorough, neutral analysis and elucidation.
The Role of Subjectivity in Critique
Critique inherently involves subjectivity as it reflects the critic's personal interpretations, emotions, and biases, influencing how a work is evaluated and understood. This subjective lens allows for diverse perspectives, making critique a dynamic dialogue rather than a fixed analysis. In contrast, explication strives for objectivity by systematically unpacking the text's structure, themes, and language without imposing personal judgment.
Objectivity and Detailed Analysis in Explication
Explication emphasizes detailed analysis by systematically breaking down a text's components to reveal underlying meanings and structures with objectivity, avoiding personal opinions or emotional responses. Unlike critique, which often reflects subjective judgment and evaluation, explication prioritizes evidence-based interpretation grounded in the text itself. This method enhances clarity and precision, making it essential for academic literary studies and rigorous textual examinations.
Methods and Techniques Used in Critique
Critique employs analytical methods such as evaluation, interpretation, and argumentation to assess the strengths and weaknesses of a subject, often incorporating theoretical frameworks and comparative analysis. Techniques used include evidence-based reasoning, contextualization, and subjective reflection to provide a balanced judgment. This approach contrasts with explication, which focuses on detailed explanation and clarification of meaning without evaluative judgment.
Strategies for Effective Explication
Effective explication involves careful analysis of the text's structure, language, and meaning to clarify complex ideas for the reader. Employing close reading techniques allows the explainer to highlight key themes and rhetorical devices, fostering deeper comprehension. Integrating contextual information and relevant examples enhances the clarity and relevance of the explication, distinguishing it from subjective critique.
Applications in Literary and Academic Contexts
Critique involves evaluating and interpreting texts to assess meaning, effectiveness, and impact, serving as a tool for generating original insights and fostering critical thinking in both literary and academic contexts. Explication focuses on detailed, line-by-line analysis to clarify language, structure, and themes, supporting precise understanding and textual evidence in scholarly discussions. Together, these methods enhance literary analysis by combining evaluative judgment with meticulous textual examination.
Common Pitfalls in Critique and Explication
Critique often suffers from bias and superficial judgment, leading to unfair evaluations rather than constructive feedback, while explication can falter by being overly literal or failing to engage with underlying themes and contexts. Common pitfalls in critique include ignoring the author's intent and relying on personal preference instead of objective analysis. Explication frequently falls short by focusing too narrowly on textual details without synthesizing broader meanings, resulting in fragmented rather than insightful interpretations.
Enhancing Interpretation: Choosing the Right Approach
Critique deepens understanding by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of a work, emphasizing analytical judgment and contextual relevance. Explication enhances interpretation through detailed, line-by-line analysis that uncovers underlying meanings and literary techniques. Selecting the appropriate method depends on whether the goal is to assess overall impact or to elucidate specific textual elements for richer comprehension.
Critique Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com