Appositive phrases provide essential clarification by renaming a nearby noun, enriching your sentence's meaning. Predicate nominatives follow linking verbs to identify or rename the subject, while direct address explicitly calls out a person or group for emphasis. Explore the rest of the article to master these grammatical elements and enhance your writing clarity.
Table of Comparison
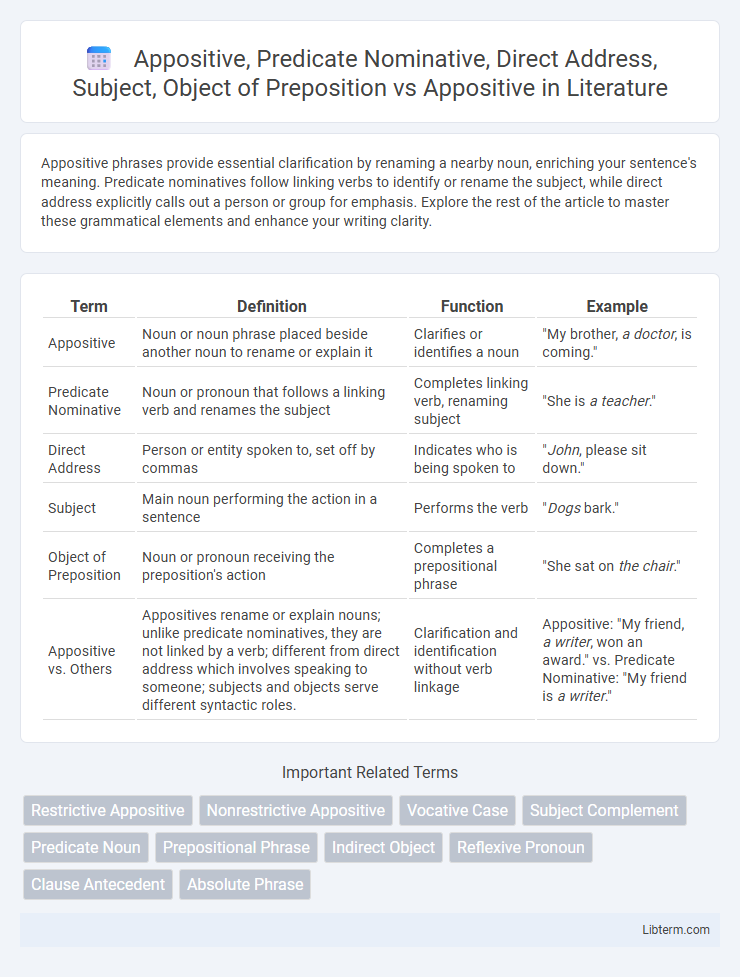
| Term | Definition | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appositive | Noun or noun phrase placed beside another noun to rename or explain it | Clarifies or identifies a noun | "My brother, a doctor, is coming." |
| Predicate Nominative | Noun or pronoun that follows a linking verb and renames the subject | Completes linking verb, renaming subject | "She is a teacher." |
| Direct Address | Person or entity spoken to, set off by commas | Indicates who is being spoken to | "John, please sit down." |
| Subject | Main noun performing the action in a sentence | Performs the verb | "Dogs bark." |
| Object of Preposition | Noun or pronoun receiving the preposition's action | Completes a prepositional phrase | "She sat on the chair." |
| Appositive vs. Others | Appositives rename or explain nouns; unlike predicate nominatives, they are not linked by a verb; different from direct address which involves speaking to someone; subjects and objects serve different syntactic roles. | Clarification and identification without verb linkage | Appositive: "My friend, a writer, won an award." vs. Predicate Nominative: "My friend is a writer." |
Understanding Appositives: Definition and Examples
Appositives are nouns or noun phrases placed next to another noun to rename or explain it, enhancing clarity in sentences. Unlike a predicate nominative, which follows linking verbs and renames the subject, appositives directly modify another noun without a verb link. Understanding the difference between objects of prepositions, which follow prepositions to complete phrases, and appositives helps in parsing sentence structure and improving grammatical precision.
The Role of the Predicate Nominative in Sentences
The predicate nominative serves as a noun or pronoun that follows a linking verb and renames or identifies the subject, creating a clear equivalence between the two. Unlike appositives, which provide additional information about a nearby noun, predicate nominatives are essential to completing the meaning of the linking verb and defining the subject's identity. This role is distinct from direct address and objects of prepositions, as predicate nominatives function grammatically as subjects' complements within the sentence structure.
Direct Address: Identifying and Using It Correctly
Direct address involves speaking directly to a person or entity, typically set off by commas, and is crucial for clarity and tone in writing. Unlike appositives, which rename a noun, or predicate nominatives that follow linking verbs and identify the subject, direct address explicitly calls attention to the listener or reader. Correctly identifying direct address requires recognizing the noun or pronoun being spoken to, often marked by punctuation, distinguishing it from objects of prepositions or appositive phrases.
What is a Subject? Grasping the Core of a Sentence
A subject is the person, place, thing, or idea that performs the action or is described in a sentence, forming its core. Unlike an appositive, which renames or clarifies a noun, the subject serves as the grammatical foundation that drives the sentence's meaning. Understanding the subject clarifies sentence structure, distinguishing it from predicate nominatives, direct addresses, or objects of prepositions, which serve different syntactic roles.
Differentiating Objects of Prepositions
Objects of prepositions serve as the nouns or pronouns following a preposition, completing its meaning. An appositive renames or clarifies another noun and is not part of the prepositional phrase, whereas an object of preposition is integral to it. Differentiating these involves recognizing that objects of prepositions always follow prepositions, while appositives provide additional information about a nearby noun without being governed by a preposition.
Appositive vs. Predicate Nominative: Key Differences
An appositive is a noun or noun phrase placed next to another noun to rename or explain it, such as "My friend, a doctor, will arrive soon." A predicate nominative follows a linking verb and renames the subject, for example, "She is a teacher." Unlike a predicate nominative, which completes the verb and links directly to the subject, an appositive simply provides additional information without being part of the sentence's verb structure.
Appositive vs. Direct Address: Spotting the Distinction
An appositive renames or clarifies a noun and is usually set off by commas, as in "My friend, a skilled musician, plays guitar." Direct address involves speaking directly to someone, using their name or title, such as "Emily, can you help me?" Appositives provide additional information about a subject or object, whereas direct address identifies the person being spoken to, affecting sentence punctuation and meaning.
Appositive vs. Subject: Clarifying Their Functions
Appositives rename or provide additional information about a noun directly beside them, such as in "My friend, a skilled artist, painted this." Subjects perform the action or are described in the sentence, exemplified by "The artist painted a mural." Unlike subjects, appositives do not act or possess but clarify or specify, distinguishing their grammatical function from objects of prepositions, which follow prepositions to form phrases like "in the garden.
Appositive vs. Object of Preposition: How to Tell Them Apart
An appositive is a noun or noun phrase that renames or explains another noun right beside it, providing additional information, such as "My brother, a skilled guitarist, plays tonight." The object of a preposition, however, completes the meaning of a prepositional phrase and follows a preposition, like "I sat beside my brother." To distinguish them, note that an appositive directly renames a noun without a preposition, while the object of a preposition always follows a preposition and functions within that phrase.
Mastering Sentence Analysis: Practice with Appositives and Related Elements
Mastering sentence analysis involves understanding appositives, which rename or clarify a noun, and predicate nominatives that follow linking verbs to restate the subject. Direct address uses nouns or phrases to speak directly to someone within a sentence, while distinguishing between the object of a preposition and an appositive clarifies their grammatical roles--objects receive the preposition's action, whereas appositives provide additional information. Practice identifying these elements enhances syntactic accuracy and deepens comprehension of complex sentence structures.
Appositive, Predicate Nominative, Direct Address, Subject, Object of Preposition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com