Narrative shapes the way stories are told, influencing how information is perceived and understood by audiences. It weaves together events, characters, and emotions to create compelling and memorable experiences. Discover how mastering narrative can transform your communication by reading the rest of the article.
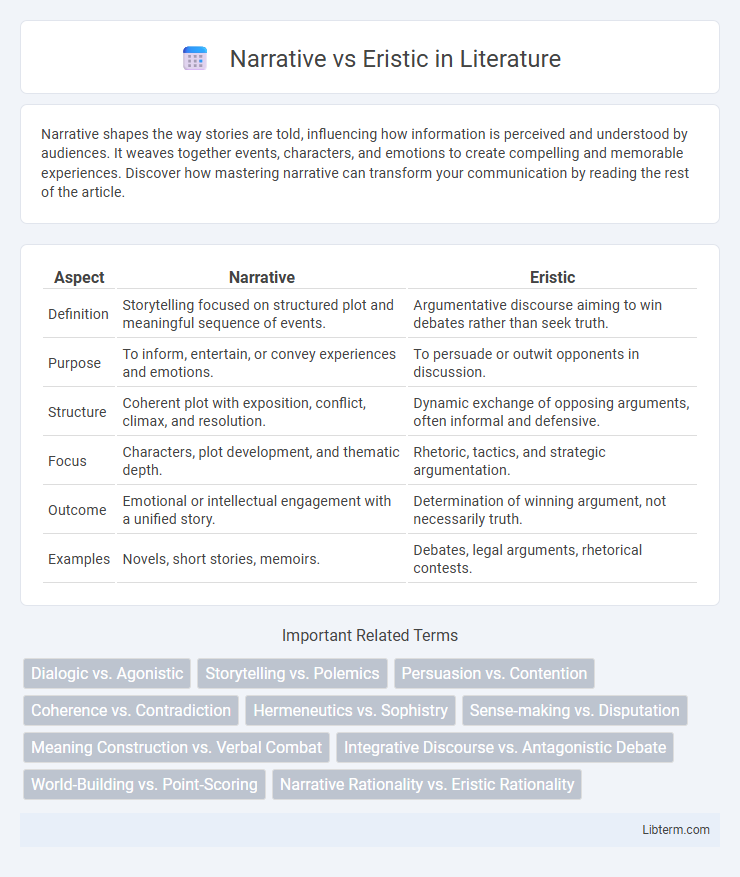
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Narrative | Eristic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storytelling focused on structured plot and meaningful sequence of events. | Argumentative discourse aiming to win debates rather than seek truth. |
| Purpose | To inform, entertain, or convey experiences and emotions. | To persuade or outwit opponents in discussion. |
| Structure | Coherent plot with exposition, conflict, climax, and resolution. | Dynamic exchange of opposing arguments, often informal and defensive. |
| Focus | Characters, plot development, and thematic depth. | Rhetoric, tactics, and strategic argumentation. |
| Outcome | Emotional or intellectual engagement with a unified story. | Determination of winning argument, not necessarily truth. |
| Examples | Novels, short stories, memoirs. | Debates, legal arguments, rhetorical contests. |
Understanding Narrative: Definition and Scope
Narrative refers to the structured account of events or experiences, often conveyed through storytelling to create meaning and engage an audience. It encompasses various forms, including written, oral, and visual mediums, that organize information temporally or thematically to provide coherence and insight. Understanding narrative involves recognizing its role in shaping perspectives, conveying cultural values, and facilitating communication by connecting facts with emotional and contextual significance.
Defining Eristic: An Overview
Eristic refers to a form of argumentation aimed at winning debates through disputation rather than seeking truth, often prioritizing rhetorical skill over factual accuracy. It contrasts with narrative approaches that focus on coherent storytelling and meaning-making, highlighting the adversarial nature of eristic dialogue. Rooted in ancient philosophical traditions, eristic emphasizes defeating opponents, sometimes at the expense of constructive discourse and shared understanding.
Key Differences Between Narrative and Eristic
Narrative centers on storytelling aimed at conveying meaning, experiences, or values, using structured plots, characters, and coherent sequences. Eristic revolves around argumentation focused on winning debates or disputing opponents, often employing rhetorical strategies and confrontational dialogue. Key differences include the purpose--narrative seeks understanding and engagement, while eristic aims for victory in argument--and the approach, where narrative is constructive and eristic is competitive.
Purposes and Goals: Narrative vs Eristic
Narrative aims to convey meaning, share experiences, and build understanding through coherent storytelling that connects events and ideas. Eristic focuses on winning arguments and asserting dominance in discourse, often prioritizing persuasion over truth or clarity. The purpose of narrative is fostering empathy and insight, while eristic seeks to challenge and undermine opposing viewpoints for rhetorical advantage.
Role in Communication: Storytelling vs Argumentation
Narrative plays a crucial role in communication by using storytelling to convey experiences, emotions, and values, fostering connection and understanding. Eristic centers on argumentation, emphasizing winning debates and asserting viewpoints through logic and rhetoric. While narrative builds empathy and shared meaning, eristic drives critical thinking and conflict resolution in discourse.
Cognitive Impact: How Narrative and Eristic Shape Thought
Narrative structures engage cognitive processes by organizing information into coherent, causally connected events, enhancing memory retention and empathy through story immersion. Eristic discourse, centered on argumentative debate and contradiction, activates critical thinking and analytical reasoning by challenging assumptions and fostering dialectical skills. Together, narrative and eristic paradigms shape thought by balancing emotional engagement with rational scrutiny, influencing how individuals process, evaluate, and internalize information.
Applications in Literature and Debate
Narrative techniques emphasize storytelling elements such as plot, character development, and thematic coherence, commonly applied in literature to engage readers and convey deeper meanings. Eristic approaches prioritize argumentation, conflict, and the art of debate, often used in rhetorical settings to challenge opposing views and persuade audiences. In literary criticism and formal debate, understanding the balance between narrative and eristic methods enhances the effectiveness of communication and interpretation strategies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Narrative Approaches
Narrative approaches enhance engagement by structuring information in a coherent, relatable storyline, aiding memory retention and emotional connection. They may, however, introduce bias or oversimplification, potentially distorting complex issues and limiting critical analysis. While narratives foster empathy and understanding, they can restrict objective evaluation by prioritizing subjective viewpoints over factual accuracy.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Eristic Techniques
Eristic techniques excel in persuasive argumentation by exploiting rhetorical strategies and logical fallacies to challenge opponents effectively, often dominating debates through aggressive defense and refutation. However, their strength is also a weakness, as reliance on manipulation and contentious tactics can undermine constructive dialogue, reduce mutual understanding, and polarize discussions. The inherent adversarial nature of eristic methods limits their capacity for collaborative problem-solving, contrasting with the more coherent and truth-seeking approach of narrative techniques.
Choosing the Right Approach: Narrative or Eristic?
Choosing the right approach between narrative and eristic depends on your communication goals and audience engagement. Narrative prioritizes storytelling and shared understanding, ideal for building consensus and conveying complex ideas through relatable experiences. Eristic, focused on argumentation and winning debates, suits situations demanding critical analysis or when challenging opposing views assertively is necessary.
Narrative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com