An antonym is a word that has the opposite meaning of another word, such as "hot" versus "cold" or "happy" versus "sad." Understanding antonyms enhances your vocabulary and helps you express ideas more precisely and clearly. Explore the rest of the article to discover how antonyms can improve your language skills and communication.
Table of Comparison
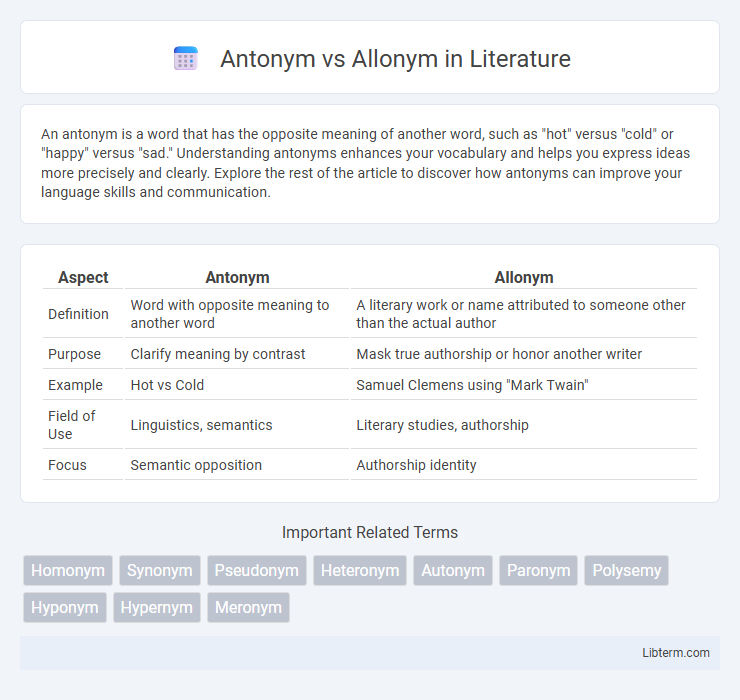
| Aspect | Antonym | Allonym |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Word with opposite meaning to another word | A literary work or name attributed to someone other than the actual author |
| Purpose | Clarify meaning by contrast | Mask true authorship or honor another writer |
| Example | Hot vs Cold | Samuel Clemens using "Mark Twain" |
| Field of Use | Linguistics, semantics | Literary studies, authorship |
| Focus | Semantic opposition | Authorship identity |
Introduction to Antonym and Allonym
Antonyms are words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," playing a crucial role in language by enhancing clarity and contrast. Allonyms refer to names or words attributed to someone other than the actual author, often used in literary or scholarly contexts to indicate pseudonyms or borrowed authority. Understanding the distinction between antonyms and allonyms highlights their unique functions in semantics and authorship attribution.
Defining Antonym: Meaning and Examples
An antonym is a word that has the opposite meaning of another word, such as "hot" versus "cold" or "happy" versus "sad." These words help create contrast in language, enhancing clarity and expression. Understanding antonyms is essential for vocabulary development and effective communication.
Understanding Allonym: Definition and Usage
An allonym is a name used by an author that belongs to another person, often employed to attribute a work to a well-known figure, enhancing credibility or anonymity. Unlike an antonym, which denotes the opposite meaning of a word, an allonym serves as a pseudonym linked to an actual individual rather than a fictitious name. Writers and scholars frequently use allonyms to explore different perspectives or avoid direct association with controversial content.
Key Differences Between Antonym and Allonym
Antonyms are words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," while allonyms refer to names or words used by an author that belong to another individual, often as a pseudonym or pen name. The key difference lies in their linguistic roles: antonyms represent semantic opposites, whereas allonyms are associated with authorship and attribution. Understanding antonyms aids in language comprehension and vocabulary expansion, whereas recognizing allonyms is important in literary studies and authorship analysis.
Common Misconceptions About Antonym vs Allonym
Antonym and allonym are often confused due to their similar prefixes, but antonyms are words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," while allonyms refer to a name used by someone other than the original author, often in literary or pseudonymous contexts. A common misconception is that allonym relates to word opposites, when in fact it concerns authorship and naming rather than semantics. Understanding the distinct linguistic roles of antonyms in vocabulary and allonyms in attribution clarifies their unique functions.
Importance of Antonyms in Language
Antonyms play a crucial role in language by enhancing clarity and precision through the expression of opposite meanings, which aids in effective communication and comprehension. Unlike allonyms, which involve the use of another person's name as a pseudonym, antonyms directly contribute to vocabulary development and conceptual understanding by allowing speakers to contrast ideas and emotions. Mastery of antonyms supports language learners in expanding their linguistic range and facilitates nuanced expression in both written and spoken contexts.
Uses and Significance of Allonyms in Literature
Allonyms are pseudonymous names used by authors to attribute their works to other persons, enhancing authenticity or paying homage in literature, unlike antonyms which are words with opposite meanings. The use of allonyms allows writers to explore different styles or perspectives while retaining creative freedom and can create layers of meaning that engage readers in intertextual analysis. Allonyms hold significance in literary traditions by fostering anonymity, enabling social or political commentary, and challenging authorship conventions.
Practical Examples: Antonym vs Allonym
Antonyms are words with opposite meanings, such as "hot" and "cold," demonstrating clear contrast in language use. Allonyms refer to names used by one person but actually belonging to another, like a writer publishing a book under a famous author's name, for example, using Mark Twain as an allonym instead of a pseudonym. Understanding these distinctions clarifies communication and attribution in both linguistic and literary contexts.
Antonym and Allonym in Academic Writing
Antonyms are words with opposite meanings, crucial in academic writing for clarifying contrasts and enhancing argument precision. Allonyms refer to works published under another person's name, often explored in academic discussions on authorship ethics and attribution. Understanding the distinct roles of antonyms and allonyms supports clearer expression and integrity in scholarly texts.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Term
Selecting the correct term hinges on understanding that an antonym represents a word with the opposite meaning, whereas an allonym is a name used by someone other than the original author. Precision in language use is crucial for clear communication, especially in literature, linguistics, and legal contexts. Properly distinguishing between antonym and allonym ensures accurate interpretation and application in both written and verbal exchanges.
Antonym Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com