Archetypes represent universal symbols and themes deeply rooted in the human psyche, influencing storytelling, psychology, and branding. Understanding these patterns can enhance your ability to connect with audiences or explore personal identity on a profound level. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover how archetypes shape narratives and impact your world.
Table of Comparison
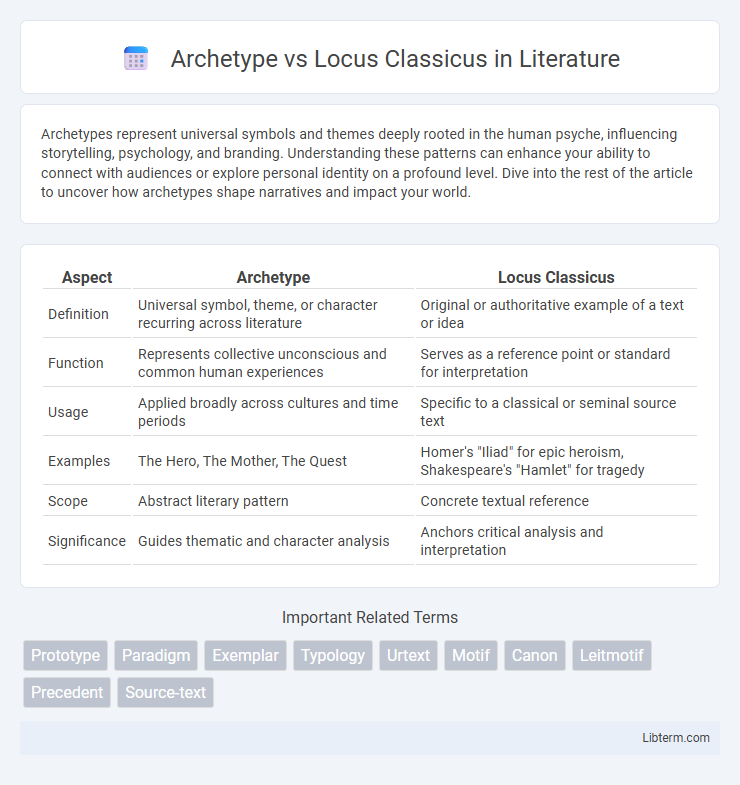
| Aspect | Archetype | Locus Classicus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Universal symbol, theme, or character recurring across literature | Original or authoritative example of a text or idea |
| Function | Represents collective unconscious and common human experiences | Serves as a reference point or standard for interpretation |
| Usage | Applied broadly across cultures and time periods | Specific to a classical or seminal source text |
| Examples | The Hero, The Mother, The Quest | Homer's "Iliad" for epic heroism, Shakespeare's "Hamlet" for tragedy |
| Scope | Abstract literary pattern | Concrete textual reference |
| Significance | Guides thematic and character analysis | Anchors critical analysis and interpretation |
Introduction to Archetype and Locus Classicus
An archetype represents a universal symbol or pattern recurring in literature, mythology, and psychology, deeply rooted in collective unconsciousness. Locus classicus refers to the original or most authoritative example or passage in classical literature that defines or illustrates a particular concept. Understanding the distinction between this foundational source and the generalized archetype enhances interpretation in literary and cultural studies.
Defining Archetype: Core Concepts
An archetype represents a universal, primal symbol or theme deeply embedded in the collective unconscious, serving as a foundational template for human experiences and narratives. It embodies core concepts such as recurring patterns, innate ideas, and symbolic imagery that transcend cultures and epochs. The archetype functions as an original model from which variations and manifestations arise, distinguishing it from locus classicus, which refers to the earliest or most authoritative textual example of a concept.
Understanding Locus Classicus: Meaning and Usage
Locus classicus is a Latin term meaning "classic place," referring to the most authoritative or original source of a specific concept or text, often cited to establish precedence or authenticity. It is widely used in academic, legal, and literary contexts to pinpoint the definitive example or primary reference that clarifies the meaning or application of an idea. Understanding locus classicus helps scholars and researchers trace the origin and validate interpretations by identifying the foundational text or passage that sets the standard.
Historical Origins of Archetype
The historical origins of the archetype concept trace back to Carl Jung's analytical psychology, where archetypes are described as universal, primordial images residing in the collective unconscious. These archetypes represent fundamental human motifs and symbolic patterns appearing across various cultures and mythologies throughout history. In contrast, locus classicus refers to the original or most authoritative source of a concept or text, highlighting a specific classic reference rather than the broader, innate psychological structures embodied by archetypes.
Historical Origins of Locus Classicus
The historical origins of Locus Classicus trace back to classical Latin literature, where the term referred to a definitive passage or authoritative source exemplifying a concept or argument. Used by ancient scholars and rhetoricians, Locus Classicus served as a foundational reference point grounding interpretations in established texts, thereby preserving cultural and intellectual traditions. This contrasts with Archetype, which broadly denotes an original model or prototype underlying various manifestations across different contexts.
Key Differences Between Archetype and Locus Classicus
Archetype represents the original model or ideal example from which copies or variations are derived, often used in literature and psychology to describe universal symbols or themes. Locus Classicus refers to the definitive or most authoritative source text or passage that exemplifies a concept or practice, commonly cited for reference or scholarly study. The key difference lies in archetype being a conceptual pattern existing abstractly across works, while locus classicus is a specific tangible instance anchoring the idea historically or textually.
Archetype in Literature and Mythology
In literature and mythology, the archetype represents universal symbols, themes, or characters that resonate across cultures and time periods, serving as foundational templates in storytelling. These recurring motifs, such as the Hero, the Mentor, or the Trickster, embody fundamental human experiences and emotions, enabling readers to connect with narratives on a profound psychological level. Unlike a locus classicus, which refers to a definitive, often cited source or passage exemplifying a concept, archetypes function as broad, dynamic patterns that influence character development and plot structure throughout diverse literary works.
Locus Classicus in Scholarly Discourse
Locus classicus refers to a canonical text or passage widely cited as an authoritative example or origin in scholarly discourse, serving as a foundational reference point for academic arguments or interpretations. It functions as a critical benchmark in disciplines such as literature, philosophy, and law, anchoring debates and analyses by providing an established, often original source. Scholars rely on locus classicus to trace historical contexts, validate theories, or establish standard meanings within specialized fields.
Modern Applications of Archetype and Locus Classicus
Modern applications of archetypes leverage Jungian psychology to analyze consumer behavior, narrative structures, and brand identity development in marketing and media. Locus classicus references serve as authoritative sources in legal, literary, and academic fields to validate interpretations, establish precedents, or clarify historical contexts. Integrating archetypes with locus classicus enhances interdisciplinary research, enabling deeper cultural and psychological insights across contemporary studies.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Archetype and Locus Classicus
Selecting between archetype and locus classicus depends on the contextual application and purpose of reference. An archetype embodies a universal, original model influencing numerous adaptations, while a locus classicus serves as a definitive, authoritative text or passage frequently cited within scholarship. Clarity in intent--whether highlighting foundational patterns or pinpointing authoritative evidence--guides the optimal choice in literary or academic settings.
Archetype Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com