A dirge is a somber song or lament expressing grief, often performed at funerals to honor the deceased. Rooted in ancient traditions, dirges evoke deep emotional responses and serve as a powerful medium for mourning and reflection. Discover how understanding dirges can enrich Your appreciation of cultural rituals and their profound meanings in the full article.
Table of Comparison
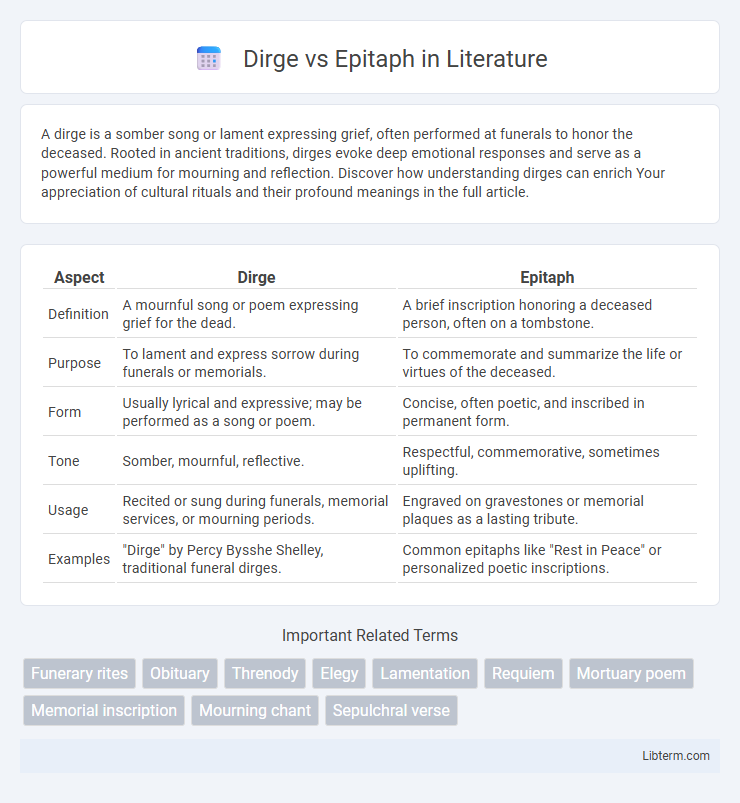
| Aspect | Dirge | Epitaph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mournful song or poem expressing grief for the dead. | A brief inscription honoring a deceased person, often on a tombstone. |
| Purpose | To lament and express sorrow during funerals or memorials. | To commemorate and summarize the life or virtues of the deceased. |
| Form | Usually lyrical and expressive; may be performed as a song or poem. | Concise, often poetic, and inscribed in permanent form. |
| Tone | Somber, mournful, reflective. | Respectful, commemorative, sometimes uplifting. |
| Usage | Recited or sung during funerals, memorial services, or mourning periods. | Engraved on gravestones or memorial plaques as a lasting tribute. |
| Examples | "Dirge" by Percy Bysshe Shelley, traditional funeral dirges. | Common epitaphs like "Rest in Peace" or personalized poetic inscriptions. |
Understanding Dirge and Epitaph: A Brief Overview
A dirge is a mournful song or poem expressing grief, typically performed during funerals or wakes to honor the deceased's memory. An epitaph is a brief inscription on a tombstone or monument, summarizing the life or virtues of the departed in a concise, often poetic form. Both dirges and epitaphs serve as cultural expressions of mourning and remembrance, with dirges focusing on auditory lamentation and epitaphs on lasting written tribute.
Origins and Historical Context
Dirges originated in ancient funeral rites as mournful songs meant to accompany the deceased's journey, rooted in oral traditions across diverse cultures such as Greek and Roman ceremonies. Epitaphs emerged from epitaph inscriptions on tombstones, dating back to ancient civilizations like Egypt and Mesopotamia, serving as concise tributes capturing the deceased's life or virtues. Both forms reflect historical attitudes toward death, with dirges emphasizing communal lamentation and epitaphs offering personal or commemorative memorials.
Literary Definitions: Dirge vs Epitaph
A dirge is a mournful, somber song or poem expressing grief and lamentation, typically performed at funerals or memorials to honor the deceased. An epitaph is a brief inscription or poem engraved on a tombstone, summarizing the life, virtues, or legacy of the deceased in a concise and often poignant manner. While dirges evoke emotional mourning through lyrical expression, epitaphs serve as enduring literary tributes etched in stone.
Structural Differences Between Dirge and Epitaph
A dirge is a mournful, lyrical poem often performed with music or chanting, structured to express grief and lamentation in a longer, more emotional format. An epitaph is a brief, inscribed text found on tombstones, summarizing the deceased's life or virtues in concise, poetic form for memorial purposes. While dirges emphasize emotional expression through verse and rhythm, epitaphs prioritize brevity and clarity in commemorating the dead.
Purpose and Function in Literature
A dirge serves as a mournful song or poem expressing grief and sorrow, often performed during funerals or memorials to honor the deceased. An epitaph, by contrast, is a brief inscription on a tombstone or monument that summarizes the life or character of the departed in a concise and commemorative manner. While dirges evoke emotional mourning, epitaphs function as enduring tributes, capturing legacy and remembrance in literature.
Emotional Tone and Expression
A dirge carries a raw, sorrowful emotional tone, often expressing intense grief and mourning through mournful melodies and slow, somber rhythms. An epitaph conveys a more reflective and respectful expression, encapsulating remembrance and honoring the deceased with concise and dignified language. Both serve to memorialize loss, but the dirge channels active sorrow while the epitaph offers enduring tribute.
Cultural and Religious Significance
A dirge is a somber, mournful song or hymn performed during funerals or memorials, prominently featured in Western Christian traditions to express grief and honor the deceased. An epitaph, often inscribed on gravestones, serves as a brief literary tribute summarizing the life, virtues, or legacy of the departed, carrying deep cultural and religious symbolism across various societies. Both dirges and epitaphs reflect the human need to commemorate death, embodying spiritual beliefs and cultural practices surrounding mourning and remembrance.
Notable Examples in Poetry and Prose
Dirges often appear in poetry and prose to convey mourning through expressive, lamenting verses, with notable examples including Thomas Gray's "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard" which mourns death with somber reflection. Epitaphs typically offer brief commemorations inscribed on tombstones, exemplified by William Shakespeare's succinct epitaph emphasizing legacy and mortality. Literary works like Walt Whitman's "When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd" blend dirge-like lament with epitaph elements, illustrating the thematic interplay within elegiac literature.
Modern Usage and Adaptations
Dirges primarily serve as mournful songs or poems expressing grief at funerals, often performed with minimalistic, haunting melodies reflecting personal loss. Epitaphs appear as engraved inscriptions on tombstones or memorial plaques, succinctly commemorating the deceased with impactful phrases or quotes that encapsulate their life or legacy. Modern adaptations of dirges include contemporary music genres incorporating somber tones, while epitaphs increasingly adopt personalized digital memorials on online platforms.
Choosing Between Dirge and Epitaph
Choosing between a dirge and an epitaph depends on the context of remembrance and tone desired. A dirge is a mournful song or poem expressing sorrow during funerals or memorial services, emphasizing emotional grief. An epitaph, inscribed on a tombstone, offers a succinct tribute that highlights the deceased's life or legacy, making it suitable for lasting memorialization.
Dirge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com