Fairy tales enchant readers with timeless stories of magic, adventure, and moral lessons that span generations. These narratives often feature mythical creatures, heroic quests, and enchanted settings that ignite your imagination and convey deeper truths about life. Explore the rest of this article to discover how fairy tales continue to influence culture and inspire creativity.
Table of Comparison
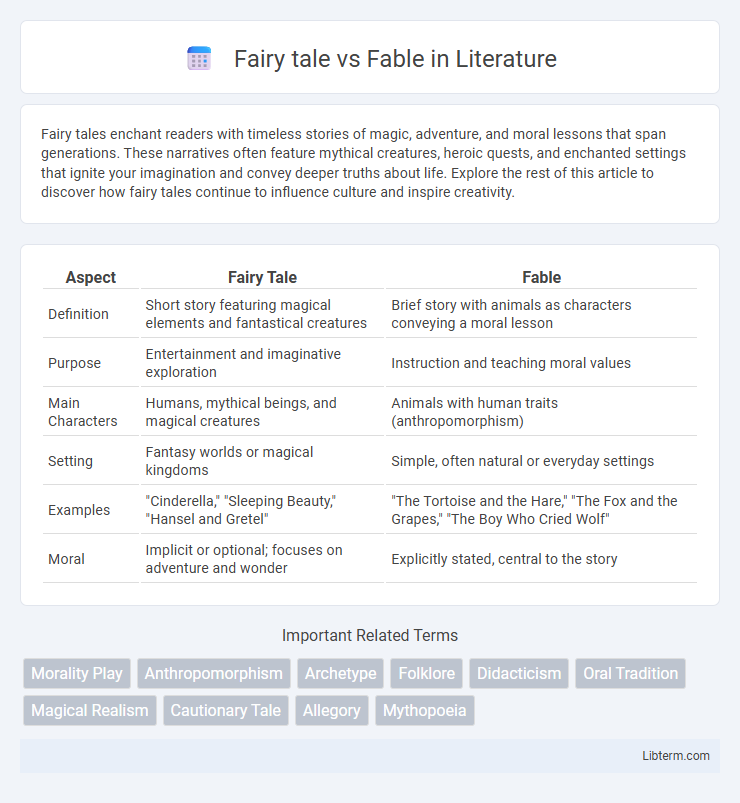
| Aspect | Fairy Tale | Fable |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short story featuring magical elements and fantastical creatures | Brief story with animals as characters conveying a moral lesson |
| Purpose | Entertainment and imaginative exploration | Instruction and teaching moral values |
| Main Characters | Humans, mythical beings, and magical creatures | Animals with human traits (anthropomorphism) |
| Setting | Fantasy worlds or magical kingdoms | Simple, often natural or everyday settings |
| Examples | "Cinderella," "Sleeping Beauty," "Hansel and Gretel" | "The Tortoise and the Hare," "The Fox and the Grapes," "The Boy Who Cried Wolf" |
| Moral | Implicit or optional; focuses on adventure and wonder | Explicitly stated, central to the story |
Understanding Fairy Tales and Fables
Fairy tales feature magical characters and enchanted settings often designed to entertain and convey cultural values, while fables use animals and inanimate objects as characters to illustrate moral lessons. Understanding fairy tales involves recognizing their emphasis on wonder and folklore traditions, whereas fables focus on concise storytelling with clear ethical takeaways. Both genres utilize narrative tools to transmit wisdom but differ significantly in purpose and style.
Origins and Historical Background
Fairy tales originate primarily from European folklore, with early collections like the Brothers Grimm and Charles Perrault's works cementing their place in literary history, often featuring magical creatures and moral lessons embedded in fantastical narratives. Fables trace back to ancient civilizations such as Aesop's Greece and the Indian Panchatantra, emphasizing concise stories with anthropomorphized animals to convey ethical teachings. The historical background of fairy tales involves oral traditions evolving into written forms during the 17th and 18th centuries, while fables have consistently served as didactic tools across cultures since antiquity.
Key Characteristics of Fairy Tales
Fairy tales typically feature magical elements, enchanted creatures, and a clear distinction between good and evil, often set in a fantastical world. They include narrative motifs such as quests, transformations, and moral lessons aimed at entertaining and teaching children. Unlike fables, which use animals as allegorical figures to convey explicit morals, fairy tales emphasize wonder and imaginative storytelling with human or supernatural characters.
Defining Traits of Fables
Fables are short stories featuring anthropomorphic animals that convey moral lessons, often concluding with explicit morals or proverbs. Unlike fairy tales, which involve magical elements and mythical creatures, fables emphasize practical wisdom and ethical teachings through simple, clear narratives. Classic examples include Aesop's fables, such as "The Tortoise and the Hare," which highlight universal truths and human behaviors.
Main Themes and Moral Lessons
Fairy tales often explore themes of magic, heroism, and the triumph of good over evil, with main characters undergoing fantastical adventures that emphasize hope and transformation. Fables focus primarily on imparting clear moral lessons through animal protagonists or personified objects, highlighting practical virtues such as honesty, kindness, and wisdom. While fairy tales inspire imagination and cultural values, fables deliver concise ethical guidance rooted in everyday human behavior.
Common Characters and Archetypes
Fairy tales commonly feature archetypal characters such as princesses, witches, fairies, and heroic princes who embody themes of magic and transformation. Fables often include anthropomorphic animals like foxes, wolves, and turtles serving as moral exemplars or tricksters to convey ethical lessons. Both genres utilize these recurring characters to simplify complex human traits and societal values, reinforcing cultural norms through symbolic storytelling.
Narrative Structure and Style
Fairy tales typically feature complex narratives with magical settings, archetypal characters, and a clear moral lesson woven through an imaginative story structure. Fables employ a concise narrative style, often featuring anthropomorphic animals as protagonists, delivering straightforward, explicit morals at the conclusion. While fairy tales emphasize immersive world-building and plot development, fables prioritize brevity and direct ethical instruction.
Influence on Culture and Society
Fairy tales shape cultural identity by embedding moral lessons and fantastical elements that reflect societal values and collective imagination, often influencing art, literature, and traditions. Fables deliver concise ethical teachings through anthropomorphized animals, reinforcing social norms and behavioral expectations across generations. Both genres contribute to cultural continuity and education, yet fairy tales typically inspire imagination and creativity, while fables emphasize practical wisdom and moral clarity.
Modern Adaptations and Relevance
Modern adaptations of fairy tales often emphasize imaginative worlds and moral lessons while incorporating contemporary themes such as gender equality and diversity to remain culturally relevant. Fables continue to use concise storytelling paired with clear ethical teachings, frequently updated to address current social issues and promote critical thinking in modern audiences. Both genres evolve through various media including film, literature, and digital platforms, ensuring their enduring significance in education and entertainment.
How to Differentiate Fairy Tales from Fables
Fairy tales feature magical beings and fantastical events aimed at entertainment, often emphasizing moral lessons through imaginative storytelling. Fables are short narratives that use animals or inanimate objects as characters to directly convey clear ethical teachings or practical morals. Differentiating them involves noting that fairy tales prioritize wonder and fantasy, while fables focus on concise moral instruction with symbolic representation.
Fairy tale Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com