Romance ignites deep emotional connections that enrich your life through passion, trust, and mutual understanding. Exploring romantic relationships fosters personal growth and strengthens bonds that provide lasting happiness. Discover the secrets to nurturing meaningful romance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
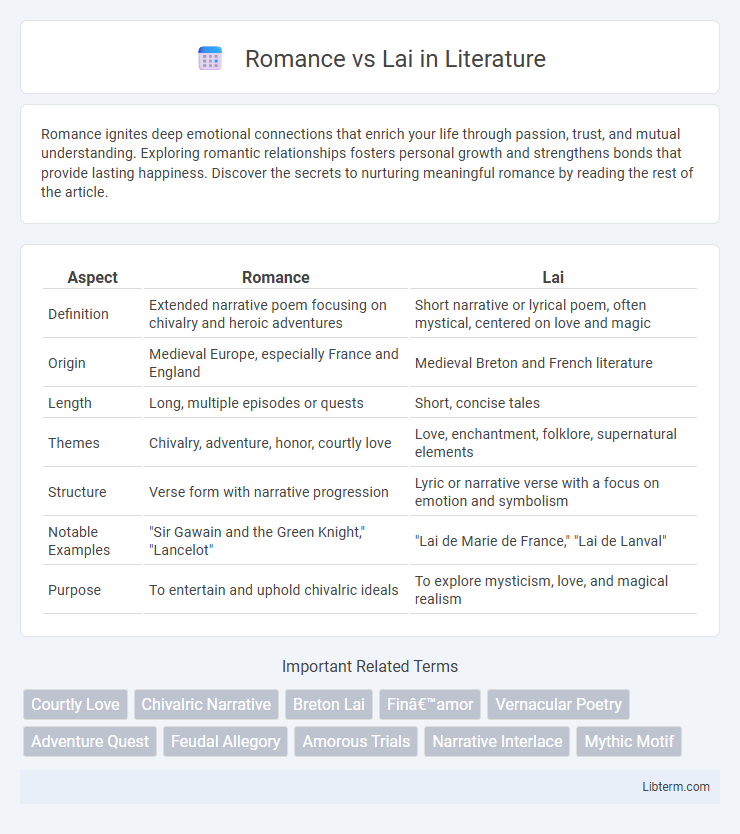
| Aspect | Romance | Lai |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extended narrative poem focusing on chivalry and heroic adventures | Short narrative or lyrical poem, often mystical, centered on love and magic |
| Origin | Medieval Europe, especially France and England | Medieval Breton and French literature |
| Length | Long, multiple episodes or quests | Short, concise tales |
| Themes | Chivalry, adventure, honor, courtly love | Love, enchantment, folklore, supernatural elements |
| Structure | Verse form with narrative progression | Lyric or narrative verse with a focus on emotion and symbolism |
| Notable Examples | "Sir Gawain and the Green Knight," "Lancelot" | "Lai de Marie de France," "Lai de Lanval" |
| Purpose | To entertain and uphold chivalric ideals | To explore mysticism, love, and magical realism |
Introduction to Romance and Lai
Romance and Lai are medieval narrative forms that highlight different storytelling traditions: Romance typically features chivalric adventures, love, and heroic quests, often set in a courtly context. In contrast, Lai is a shorter, lyrical narrative poem originating from Old French and Breton literature, characterized by themes of love, magic, and supernatural elements. Both genres influence medieval literature but serve distinct narrative and poetic functions.
Defining the Romance Genre
The Romance genre is defined by its focus on the emotional and romantic relationships between characters, often culminating in a hopeful or happy ending. Lais, a medieval narrative form, blend romantic themes with elements of adventure and the supernatural, distinguished by their concise, lyrical storytelling. While Romance emphasizes character development and emotional depth, Lais prioritize brevity and incorporation of folkloric motifs.
Understanding the Lai Narrative Form
The Lai narrative form, with its origins in medieval French and Breton tradition, emphasizes concise, lyrical storytelling that blends romantic adventure with elements of magic and chivalry, distinguishing it from the broader Romance genre known for epic scope and complex plots. Understanding the Lai involves recognizing its structure--typically a brief, self-contained poem with a focus on themes like love, honor, and supernatural intervention. This form's unique blend of narrative and lyrical facets offers insight into medieval culture's values and artistic expressions, highlighting the nuanced interplay between personal emotion and heroic ideals in Romance literature.
Origins and Historical Background
Romance literature originated in medieval Europe, characterized by narratives centered on chivalry, adventure, and courtly love, evolving from Old French and Latin influences. The Lai, a specific form of medieval French lyrical poetry and narrative, emerged primarily in the 12th century, attributed to poets like Marie de France, emphasizing short, lyrical tales with themes of love and supernatural elements. Both genres share roots in medieval oral and manuscript traditions, reflecting the sociocultural values and literary aesthetics of the High Middle Ages.
Structure and Style: Romance vs. Lai
Romance narratives typically feature extended, episodic structures that emphasize chivalric adventures and heroic quests, characterized by elaborate descriptions and formal, elevated language. In contrast, the lai is a shorter, lyrical form with a tighter, more unified plot, often employing poetic and musical elements that create an intimate, emotional tone. The stylistic distinction lies in romance's grandeur and complexity versus the lai's concise, melodic storytelling.
Common Themes and Motifs
Romance and lai share common themes such as love, chivalry, and adventure, often exploring the complexities of human emotions and heroic quests. Both genres frequently incorporate motifs like magical elements, supernatural beings, and tests of loyalty or bravery that drive the narrative forward. These recurring themes and motifs highlight the cultural values of medieval society and emphasize ideals of honor, courtly love, and moral virtue.
Characterization in Romances and Lais
Romances often feature idealized, larger-than-life characters embodying chivalric virtues like honor, bravery, and courtly love, emphasizing heroic quests and moral dilemmas. Lais portray more intimate, nuanced characterizations, focusing on personal emotions, complex relationships, and realistic human flaws within shorter, episodic narratives. The characterization in romances promotes societal ideals, whereas lais explore individual experiences and emotional intricacies.
Role of Gender and Love
Romance narratives often emphasize traditional gender roles, portraying men as protectors and women as objects of affection, which reinforces stereotypical dynamics in love relationships. In contrast, Lai literature, particularly medieval Breton lais, tends to subvert these norms by highlighting female agency and complex emotional experiences, presenting love as a transformative and empowering force for both genders. This contrast reveals differing cultural attitudes toward gender and love, where Romance solidifies social hierarchy and Lai explores personal identity and mutual respect.
Influence on Medieval and Modern Literature
Romance and lai genres significantly shaped medieval and modern literature by emphasizing themes of chivalry, courtly love, and supernatural elements, which influenced narrative structures and character archetypes. Romances like "Sir Gawain and the Green Knight" introduced complex heroism and moral dilemmas, while lais such as Marie de France's works contributed lyrical storytelling and Celtic motifs. These genres collectively enriched literary traditions, inspiring countless adaptations and reinterpretations across European literature.
Lasting Legacy and Contemporary Relevance
Romance literature's lasting legacy lies in its foundational influence on Western storytelling, inspiring genres such as fantasy and historical fiction with timeless themes of heroism and love. Lai, a medieval French poetic form, preserves cultural heritage through its lyrical narratives and melodic structure, maintaining contemporary relevance in the study of medieval literature and folklore. Both forms continue to shape modern literary analysis, demonstrating enduring significance in cultural and artistic contexts.
Romance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com