Syuzhet is a powerful R package designed for sentiment analysis and narrative structure detection in texts. It leverages lexicons and algorithms to identify emotional arcs, helping you understand the underlying sentiments and progression in stories or documents. Explore this article to discover how Syuzhet can transform your text analysis projects.
Table of Comparison
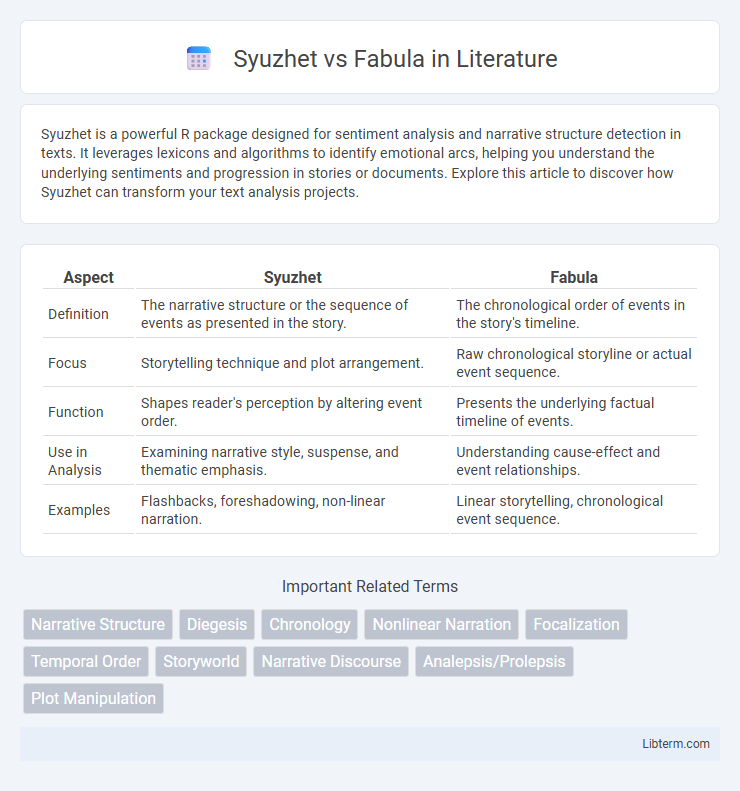
| Aspect | Syuzhet | Fabula |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The narrative structure or the sequence of events as presented in the story. | The chronological order of events in the story's timeline. |
| Focus | Storytelling technique and plot arrangement. | Raw chronological storyline or actual event sequence. |
| Function | Shapes reader's perception by altering event order. | Presents the underlying factual timeline of events. |
| Use in Analysis | Examining narrative style, suspense, and thematic emphasis. | Understanding cause-effect and event relationships. |
| Examples | Flashbacks, foreshadowing, non-linear narration. | Linear storytelling, chronological event sequence. |
Introduction to Syuzhet and Fabula
Syuzhet and Fabula are fundamental concepts in narratology that distinguish between the narrative structure and the raw story content. Syuzhet refers to the way a story is organized and presented to the audience, encompassing the sequence of events, plot devices, and narrative techniques. Fabula represents the chronological sequence of events as they occur within the story world, independent of presentation or narrative style, allowing analysis of story time versus narrative time.
Defining Syuzhet: Narrative Structure
Syuzhet refers to the narrative structure organizing the sequence and presentation of events within a story, distinguishing it from Fabula, which represents the raw chronological order of events. Syuzhet emphasizes how events are arranged to create suspense, thematic emphasis, or emotional impact, shaping the audience's experience beyond mere plot chronology. In literary analysis, understanding Syuzhet is crucial for interpreting the storyteller's artistic choices influencing narrative perception.
Understanding Fabula: Chronological Events
Fabula refers to the chronological sequence of events in a story, emphasizing the raw timeline without narrative manipulation. Understanding fabula involves identifying each event as it occurs in real time, providing a foundation for analyzing the plot's structure and temporal flow. This contrasts with syuzhet, which reorganizes events to create suspense, thematic emphasis, or emotional impact.
Theoretical Origins of Syuzhet and Fabula
Syuzhet originates from Russian Formalism, emphasizing the narrative structure as the sequence of events presented in the story, while Fabula refers to the chronological order of the raw events themselves. Foundational theorists like Viktor Shklovsky and Boris Tomashevsky developed the concept of Syuzhet to highlight the artful arrangement of narrative elements, contrasting with the Fabula's straightforward timeline. The distinction between Syuzhet and Fabula remains pivotal in narratology, highlighting the manipulation of time in storytelling to shape audience perception and engagement.
Differences Between Syuzhet and Fabula
Syuzhet refers to the structured sequence and presentation of events in a narrative, while Fabula represents the chronological order of events as they occur within the story world. The primary difference lies in syuzhet's manipulation of time and perspective to create narrative tension, contrasting with fabula's linear progression that reflects the story's causal relationships. Understanding the distinction between syuzhet and fabula is essential for analyzing narrative techniques and the impact of storytelling methods on audience perception.
How Syuzhet Shapes Reader Experience
Syuzhet structures the narrative by carefully manipulating the chronological order of events, creating suspense and deepening engagement through unexpected plot twists and non-linear storytelling. This technique enhances emotional impact by aligning the reader's perspective with thematic developments and character arcs, making the experience more immersive. By distinguishing between the story's raw content (fabula) and its presentation (syuzhet), authors using syuzhet effectively control pacing, tension, and revelation to shape reader interpretation and connection.
Fabula’s Role in Story Comprehension
Fabula plays a critical role in story comprehension by representing the chronological sequence of events as they actually occur in the narrative world, independent of their presentation order. Unlike Syuzhet, which structures the narrative through the organization of events as presented to the audience, Fabula provides the foundational timeline essential for understanding cause-and-effect relationships and character motivations. Analyzing Fabula enables deeper insight into plot development and narrative coherence, facilitating a clearer interpretation of story elements across different storytelling techniques.
Syuzhet and Fabula in Classic Literature
Syuzhet and Fabula are fundamental narrative structures in classic literature, with Syuzhet representing the chronological arrangement of events as presented in the story, while Fabula refers to the raw sequence of events in their natural order. Classic novels often employ Syuzhet to create suspense, manipulate time, and enhance thematic depth, deviating from the linear Fabula to engage readers more profoundly. Understanding the interplay between Syuzhet and Fabula is essential for literary analysis, revealing how authors craft complex narratives beyond straightforward chronology.
Modern Applications in Film and Media
Syuzhet and Fabula, foundational concepts in narratology, have found extensive application in modern film and media analysis to differentiate between story structure and narrative presentation. Syuzhet refers to the chronological arrangement of events as presented to the audience, while Fabula represents the actual sequence of events in the story's timeline, enabling creators to manipulate time for dramatic effect. Contemporary filmmakers and media analysts leverage these concepts to craft nonlinear narratives, enhance viewer engagement, and deepen storytelling complexity through techniques such as flashbacks, foreshadowing, and parallel plotlines.
Conclusion: Syuzhet vs Fabula in Narrative Theory
Syuzhet and Fabula represent two fundamental components in narrative theory, where Syuzhet refers to the specific arrangement of events in a story, and Fabula denotes the chronological sequence of those events. Analyzing narratives through the lens of Syuzhet emphasizes the author's role in structuring and presenting the story, while Fabula focuses on the underlying raw events independent of their presentation. Understanding the distinction between Syuzhet and Fabula enhances narrative analysis by clarifying how storytelling techniques influence audience perception and thematic interpretation.
Syuzhet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com