Allegory is a powerful literary device that conveys complex ideas through symbolic figures, actions, or events, allowing deeper layers of meaning to emerge beyond the surface narrative. It enriches storytelling by linking abstract concepts with concrete imagery, helping you grasp moral, political, or philosophical messages more vividly. Explore the rest of the article to discover how allegory shapes some of the most memorable works in literature.
Table of Comparison
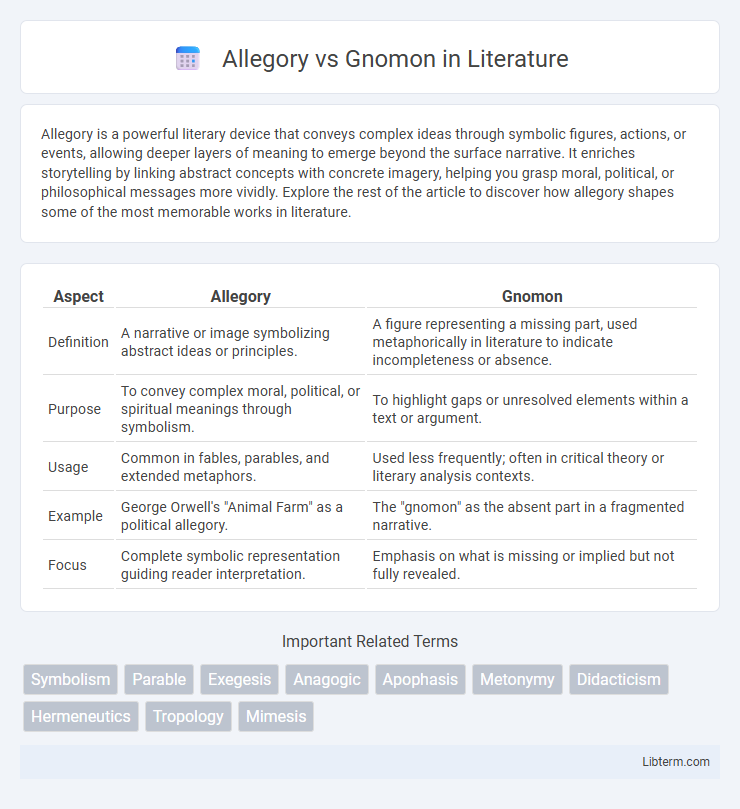
| Aspect | Allegory | Gnomon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A narrative or image symbolizing abstract ideas or principles. | A figure representing a missing part, used metaphorically in literature to indicate incompleteness or absence. |
| Purpose | To convey complex moral, political, or spiritual meanings through symbolism. | To highlight gaps or unresolved elements within a text or argument. |
| Usage | Common in fables, parables, and extended metaphors. | Used less frequently; often in critical theory or literary analysis contexts. |
| Example | George Orwell's "Animal Farm" as a political allegory. | The "gnomon" as the absent part in a fragmented narrative. |
| Focus | Complete symbolic representation guiding reader interpretation. | Emphasis on what is missing or implied but not fully revealed. |
Introduction to Allegory and Gnomon
Allegory serves as a narrative device where characters, events, or settings symbolize broader concepts, often conveying moral, political, or spiritual meanings beneath the surface story. A gnomon, derived from ancient Greek geometry, refers to a shape that, when added to another, forms a new figure maintaining proportional harmony, commonly used in mathematical and architectural contexts. Understanding the distinction between allegory and gnomon highlights how the former operates in symbolic storytelling while the latter functions as a geometric tool for spatial and proportional relationships.
Defining Allegory: Meaning and Usage
Allegory is a literary and artistic device where abstract ideas or principles are expressed through characters, events, or symbols, creating a layered narrative that conveys deeper moral, spiritual, or political meanings. It functions by representing complex concepts in a symbolic form, enabling audiences to interpret and derive significance beyond the literal storyline. This technique is widely utilized in literature, visual arts, and film to communicate themes such as justice, human nature, or societal critique.
Understanding Gnomon: Origins and Applications
Gnomon, originating from ancient Greek mathematics, refers to a geometric figure added to a shape to form a larger one, often used in number theory and geometry. Its applications span from constructing polygonal shapes in art and architecture to representing growth patterns in nature through mathematical modeling. Understanding gnomon's principles aids in deciphering complex numerical relationships and enhances the interpretation of spatial structures.
Historical Contexts of Allegory and Gnomon
Allegory traces its historical roots to ancient literature and art, prominently used in Greco-Roman culture to convey complex moral and philosophical ideas through symbolic figures and narratives. Gnomon originates from ancient Greek mathematics and astronomy, specifically as a tool or concept used by early mathematicians like Euclid to understand geometric progressions and by astronomers to measure shadows and time with sundials. Both concepts evolved within distinct intellectual traditions--allegory shaping literary and artistic interpretation, while gnomon influenced scientific inquiry and practical measurement methods.
Structural Differences Between Allegory and Gnomon
Allegory employs a comprehensive narrative structure where characters, events, and settings collectively symbolize broader abstract concepts or moral lessons. In contrast, gnomon functions as a structural element that signifies a missing or added part, typically altering a geometric figure without conveying a complex narrative. The primary distinction lies in allegory's layered storytelling framework versus gnomon's role as a singular, spatial modification used in mathematical or symbolic contexts.
Allegory vs Gnomon in Literature
Allegory in literature uses symbolic figures and actions to convey deeper moral, spiritual, or political meanings beyond the narrative's surface, often allowing multiple layers of interpretation. The gnomon, while less common as a literary device, represents something that completes or reveals the whole, serving as a metaphorical tool to indicate absence or an incomplete element within a text's structure or meaning. Understanding the distinction between allegory and gnomon enriches literary analysis by highlighting how authors embed complex ideas: allegories construct an extended metaphorical framework, whereas gnomons emphasize what is missing or implied to shape the reader's understanding.
Symbolism and Interpretation in Allegory and Gnomon
Allegory employs extended symbolism to convey complex moral, spiritual, or political meanings through characters, events, and narratives, requiring interpretive analysis to decode hidden messages. Gnomon functions as a symbolic pointer or indicator, often representing knowledge or insight, and its interpretation depends on the contextual relationship to the whole, highlighting specific aspects of a concept or system. Both forms rely on symbolic representation, but allegory presents a comprehensive, layered narrative, while gnomon offers a focused, directional symbol demanding contextual understanding for accurate interpretation.
Cultural Significance and Influences
Allegory and gnomon hold distinct cultural significance, with allegory serving as a symbolic narrative tool deeply embedded in literature, art, and religious texts to convey moral, philosophical, or political messages. Gnomon, primarily a geometric concept used in ancient sundials, influences cultural developments in timekeeping, architecture, and mathematics, symbolizing measurement and cosmic order in various civilizations. The interplay between allegory and gnomon highlights the fusion of abstract ideas and practical knowledge, reflecting humanity's quest to interpret and structure reality.
Modern Perspectives: Allegory and Gnomon Today
Modern perspectives on allegory emphasize its role in interpreting symbolic meanings beyond literal narratives, often used in literature, art, and cultural studies to reveal deeper philosophical or political insights. The concept of the gnomon, rooted in ancient geometry and timekeeping, has evolved into a metaphor for discovering unknown elements within a known framework, influencing contemporary fields such as mathematics, design, and critical theory. Today's interdisciplinary approaches highlight allegory and gnomon as complementary tools for exploring hidden structures and generating new knowledge in various intellectual domains.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Allegory and Gnomon
Choosing between allegory and gnomon depends on the desired narrative complexity and interpretive engagement; allegory offers layered symbolism fostering thematic depth, while gnomon emphasizes structural significance and spatial relationships. For literary or artistic works seeking rich metaphorical meaning, allegory provides powerful tools to convey abstract ideas through concrete figures. In contrast, gnomon suits contexts where form and geometric insight drive understanding, highlighting the interplay between parts and the whole.
Allegory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com