Discover a fascinating miscellany of topics that span from everyday curiosities to profound insights, offering a diverse blend of knowledge to enrich your understanding. This curated collection invites exploration of intriguing facts, practical tips, and surprising discoveries, all designed to engage your curiosity and expand your perspective. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover a world of captivating information tailored just for you.
Table of Comparison
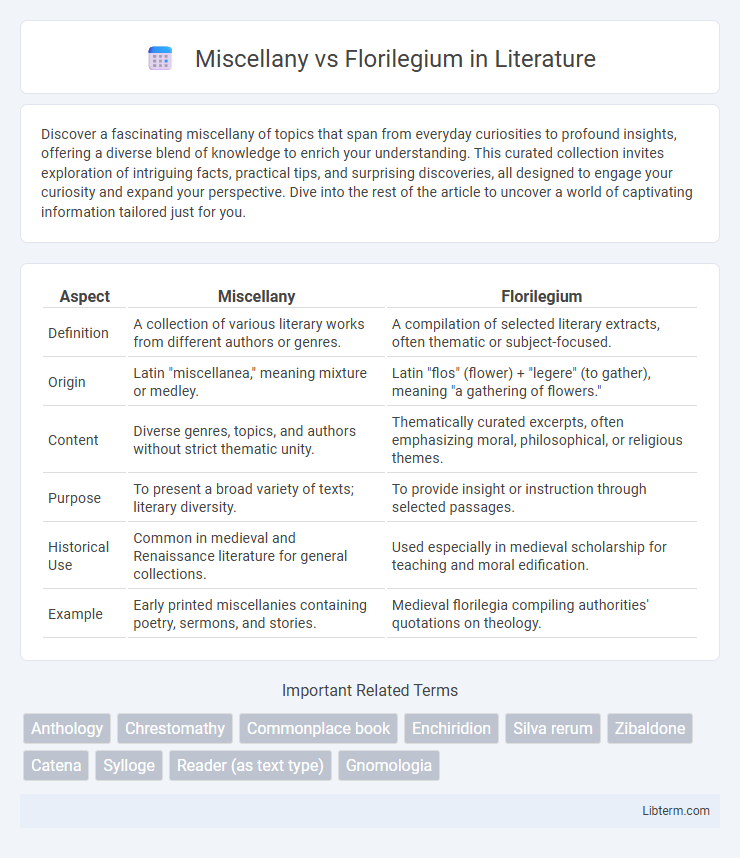
| Aspect | Miscellany | Florilegium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A collection of various literary works from different authors or genres. | A compilation of selected literary extracts, often thematic or subject-focused. |
| Origin | Latin "miscellanea," meaning mixture or medley. | Latin "flos" (flower) + "legere" (to gather), meaning "a gathering of flowers." |
| Content | Diverse genres, topics, and authors without strict thematic unity. | Thematically curated excerpts, often emphasizing moral, philosophical, or religious themes. |
| Purpose | To present a broad variety of texts; literary diversity. | To provide insight or instruction through selected passages. |
| Historical Use | Common in medieval and Renaissance literature for general collections. | Used especially in medieval scholarship for teaching and moral edification. |
| Example | Early printed miscellanies containing poetry, sermons, and stories. | Medieval florilegia compiling authorities' quotations on theology. |
Understanding Miscellany: Definition and Origins
Miscellany refers to a collection of various texts, often diverse in subject matter and origin, compiled into a single manuscript or volume. Originating in the medieval period, miscellanies served as repositories for poetry, prose, and scholarly notes, reflecting the eclectic interests of their creators. These compilations contrast with florilegia, which are specifically anthologies of selected excerpts emphasizing thematic or moral teachings.
Florilegium Explained: Meaning and Historical Context
Florilegium, derived from Latin meaning "a gathering of flowers," refers to a medieval anthology compiling excerpts from classical, religious, and philosophical texts valued for their moral or intellectual significance. Historically, florilegia served as educational tools in monastic and scholarly settings during the Middle Ages, preserving and transmitting knowledge before the invention of the printing press. Unlike miscellanies, which are more general and diverse collections, florilegia specifically curate selected passages centered around thematic or scholarly purposes.
Key Differences: Miscellany vs Florilegium
Miscellany refers to a collection of various writings or texts compiled into a single volume without a specific unifying theme, often including diverse genres and subjects. Florilegium, in contrast, specifically denotes an anthology of selected excerpts or quotations from notable authors, usually focused on a particular topic or theme, serving as a curated compilation of wisdom or literary highlights. The key difference lies in miscellany's broad, eclectic nature versus florilegium's intentional, thematic selection of passages.
The Evolution of Anthologies in Literary History
Miscellanies originated as diverse collections of texts and genres, reflecting medieval and Renaissance readers' appetite for a broad intellectual experience, while florilegia specifically curated excerpts from authoritative texts, emphasizing thematic or moral instruction. Over time, the evolution from miscellanies to florilegia illustrates a shift toward more specialized anthologies aimed at educating and preserving key literary or philosophical ideas, culminating in the modern concept of thematic anthologies. This progression highlights how literary anthologies evolved from general compilations into focused collections that shaped literary history by influencing textual transmission and reader engagement.
Purpose and Function: Why Collections Matter
Miscellanies serve as diverse compilations of texts, gathering various genres and subjects to preserve cultural knowledge and provide broad insight into a particular era or theme. Florilegia, by contrast, focus on curated excerpts, often thematic or author-specific, aiming to highlight and disseminate key ideas or literary excellence for educational or devotional purposes. Both collections matter because they safeguard intellectual heritage, facilitate knowledge transmission, and reflect the values and priorities of their compilers and societies.
Compilation Methods: How Miscellanies and Florilegia Are Assembled
Miscellanies are assembled through the collection of diverse texts from multiple genres and authors, often compiled without strict thematic constraints, resulting in varied content within a single volume. Florilegia are curated by selecting excerpts specifically chosen for their thematic or intellectual coherence, typically focusing on a particular subject or moral lesson. The compilation method of miscellanies emphasizes breadth and diversity, while florilegia prioritize thematic unity and purposeful selection.
Notable Examples of Miscellanies
Notable examples of miscellanies include the "Harleian Miscellany," a comprehensive 18th-century collection of tracts and documents, and the "Archbishop Parker's Miscellany," an important anthology of medieval and early modern texts. Unlike florilegia, which primarily compile excerpts of notable authors or thematic selections, miscellanies encompass a broader range of subjects and genres, such as poetry, prose, legal writings, and historical records. These diverse compilations highlight the eclectic nature of miscellanies and their role in preserving varied literary and documentary materials.
Famous Florilegia in Literature and Beyond
Florilegia, curated anthologies of literary and philosophical excerpts, have historically preserved the wisdom of classical and medieval texts, featuring works like the 12th-century "Speculum Majus" by Vincent of Beauvais. Unlike miscellanies, which are varied collections without a specific thematic focus, florilegia emphasize instructional and moral extracts, influencing Renaissance humanism and educational curricula. In literature and beyond, florilegia have contributed to knowledge transmission, inspiring compilations like Erasmus's "Adagia" and serving as sources for early encyclopedias and textual studies.
Influence on Modern Anthologies and Collections
Miscellanies and florilegia both serve as foundational formats influencing modern anthologies and collections by preserving diverse texts or thematic excerpts respectively, enabling curated literary experiences. Miscellanies compile varied works across genres, shaping eclectic anthology structures that reflect cultural and intellectual diversity. Florilegia, emphasizing selective excerpts from authoritative sources, inform thematic or topical anthologies by providing concentrated thematic insights and canonical authority.
Choosing the Right Form: Miscellany or Florilegium?
Choosing between miscellany and florilegium depends on the intended purpose and content organization. A miscellany compiles diverse writings or texts from multiple sources without strict thematic coherence, ideal for broad literary collections or archival purposes. A florilegium, by contrast, thoughtfully selects and arranges excerpts or passages around a specific theme or author, making it optimal for focused study or thematic anthologies.
Miscellany Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com