Syncope refers to a sudden, temporary loss of consciousness usually caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. Understanding the underlying causes such as dehydration, heart problems, or blood pressure issues is essential to prevent future episodes. Discover more about syncope symptoms, triggers, and treatment options to safeguard your health in the full article.
Table of Comparison
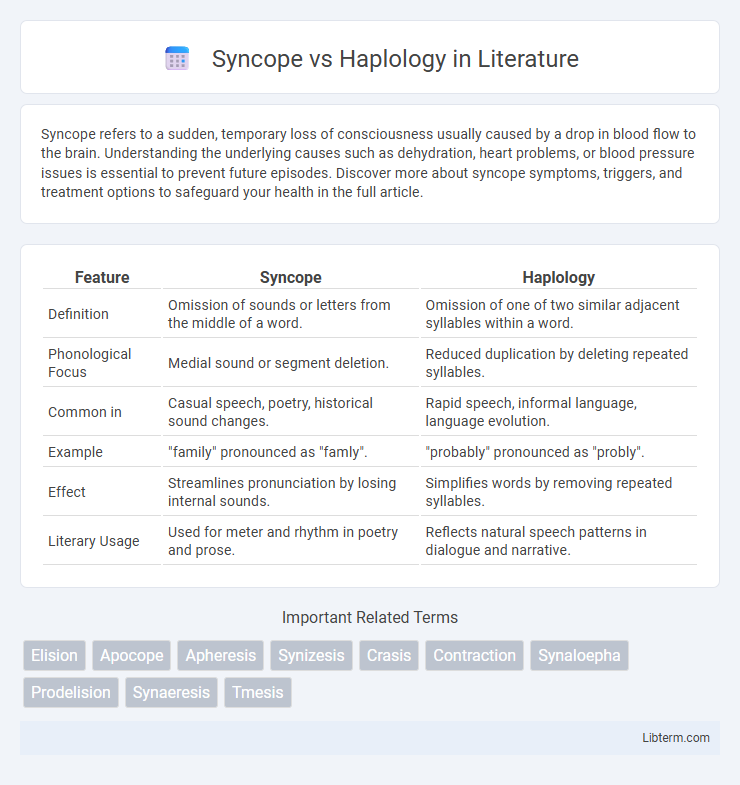
| Feature | Syncope | Haplology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of sounds or letters from the middle of a word. | Omission of one of two similar adjacent syllables within a word. |
| Phonological Focus | Medial sound or segment deletion. | Reduced duplication by deleting repeated syllables. |
| Common in | Casual speech, poetry, historical sound changes. | Rapid speech, informal language, language evolution. |
| Example | "family" pronounced as "famly". | "probably" pronounced as "probly". |
| Effect | Streamlines pronunciation by losing internal sounds. | Simplifies words by removing repeated syllables. |
| Literary Usage | Used for meter and rhythm in poetry and prose. | Reflects natural speech patterns in dialogue and narrative. |
Understanding Syncope: Definition and Linguistic Role
Syncope refers to the linguistic phenomenon where sounds, typically vowels, are omitted from the interior of a word, simplifying pronunciation and often influencing word evolution. This process plays a significant role in language development by affecting phonological patterns and contributing to morphological changes across dialects. Understanding syncope aids in analyzing sound shifts and their impacts on language structure and historical linguistics.
Haplology Explained: Meaning and Usage in Language
Haplology is a linguistic phenomenon where one syllable is omitted when two similar syllables occur consecutively, simplifying pronunciation and enhancing speech fluidity. Unlike syncope, which involves the loss of sounds within a word regardless of similarity, haplology specifically targets repetitive syllables for omission. This process is common in language evolution and informal speech, influencing word forms such as "probably" often pronounced as "probly.
Historical Background of Syncope and Haplology
Syncope and haplology are phonological processes observed in historical linguistics, where syncope involves the loss of a medial vowel within a word, while haplology is the omission of one syllable in a sequence of similar syllables. Syncope dates back to Proto-Indo-European languages and is well-documented in the evolution of Latin into its Romance descendants, significantly shaping modern vocabulary through vowel reduction. Haplology's historical relevance emerges in various language families, including Germanic and Slavic, influencing morphological simplifications and the development of more concise word forms over time.
Key Differences Between Syncope and Haplology
Syncope involves the loss of sounds from the middle of a word, such as the omission of a vowel in "chocolate" becoming "choc'late," while haplology refers to the omission of one syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively, like "probably" pronounced as "probly." Syncope typically affects speech fluency by shortening words internally, whereas haplology simplifies pronunciation by reducing repeated syllables. Both phenomena result in phonetic simplification but differ in the specific position and nature of the sound omission within words.
Linguistic Examples of Syncope in Action
Syncope involves the omission of sounds or syllables within a word, often seen in English contractions like "fam'ly" for "family" and "ne'er" for "never," while haplology refers to the deletion of one of two similar adjacent syllables, as in "probly" from "probably." Examples of syncope show how linguistic economy influences spoken language, affecting words such as "chocolate" pronounced as "choc'late" and "camera" as "cam'ra." This phonological process enhances speech fluency by reducing syllabic complexity without altering the words' fundamental meanings.
Illustrative Cases of Haplology in Languages
Haplology involves the omission of one syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively, as seen in English words like "probably" pronounced as "probly." In contrast, syncope refers to the loss of medial sounds or syllables within a word, such as the Old English "hlaford" becoming "lord." Illustrative cases of haplology are evident in languages like Latin, where "ille ille" contracts to "ille," and in Japanese, where "kirei-kirei" reduces to "kirei.
Phonological Processes: Syncope vs Haplology
Syncope and haplology are key phonological processes affecting word forms by altering syllable structure; syncope involves the deletion of medial unstressed vowels, streamlining pronunciation, while haplology results in the omission of one of two adjacent similar syllables to avoid repetition. Both processes optimize speech fluency and efficiency by reducing syllabic complexity but differ in their targets--syncope deletes internal vowels regardless of syllable similarity, whereas haplology specifically targets consecutive similar syllables. Understanding these distinctions aids in phonological analysis and linguistic studies of language evolution and morphophonemic adaptation.
Impact on Language Evolution and Word Formation
Syncope involves the loss of sounds within a word, often simplifying pronunciation and accelerating linguistic change, while haplology results in the omission of repeated or similar syllables, streamlining word forms and enhancing language efficiency. Both processes significantly influence language evolution by reshaping word structures, contributing to the natural development of shorter, more efficient forms through phonetic reduction. These phonological phenomena play crucial roles in word formation, affecting morphological patterns and the emergence of new lexical variants across languages.
Syncope and Haplology in English and Other Languages
Syncope involves the deletion of a vowel or syllable within a word, commonly seen in English contractions like "family" pronounced as "famly," while haplology refers to the omission of a whole syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively, as in the reduction of Latin "reliquitissimus" to "reliquisimus." In English, syncope frequently alters the flow of speech for ease, whereas haplology is more prevalent in the evolution of Romance languages such as Spanish and Italian, where it simplifies word forms. Both processes demonstrate linguistic economy and are crucial in phonological studies across languages, reflecting natural tendencies toward simplification in spoken language.
Conclusion: Syncope and Haplology in the Study of Linguistics
Syncope and haplology are critical phenomena in phonological analysis, illustrating distinct patterns of sound omission within words. Syncope involves the loss of one or more sounds from the interior of a word, while haplology refers to the omission of a syllable when two identical or similar syllables occur in sequence. Understanding these processes provides valuable insights into historical language change, morphological simplification, and phonetic economy in linguistic evolution.
Syncope Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com