Emotional identification is the ability to recognize and understand your own emotions as well as those of others, playing a critical role in effective communication and empathy. Mastering this skill enhances personal relationships and aids in managing stress and decision-making. Discover practical strategies to improve your emotional identification in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
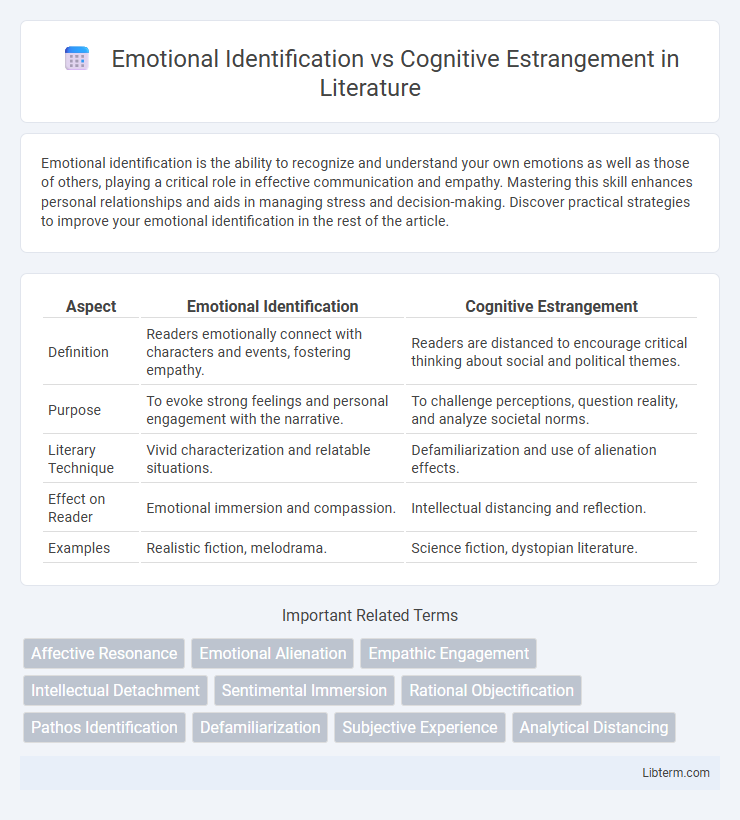
| Aspect | Emotional Identification | Cognitive Estrangement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Readers emotionally connect with characters and events, fostering empathy. | Readers are distanced to encourage critical thinking about social and political themes. |
| Purpose | To evoke strong feelings and personal engagement with the narrative. | To challenge perceptions, question reality, and analyze societal norms. |
| Literary Technique | Vivid characterization and relatable situations. | Defamiliarization and use of alienation effects. |
| Effect on Reader | Emotional immersion and compassion. | Intellectual distancing and reflection. |
| Examples | Realistic fiction, melodrama. | Science fiction, dystopian literature. |
Understanding Emotional Identification
Emotional identification involves the audience's ability to empathize deeply with characters by sharing their feelings and experiences, creating a personal connection that enhances narrative immersion. This process activates mirror neurons and emotional resonance, facilitating a compassionate response and fostering psychological engagement. Understanding emotional identification is crucial for creators aiming to evoke strong emotional impacts and build meaningful relationships between viewers and stories.
Defining Cognitive Estrangement
Cognitive estrangement refers to the process of perceiving familiar concepts, social norms, or realities in an unfamiliar or alien context, often used in literature and media to encourage critical reflection. This technique disrupts emotional identification by distancing the audience from immediate empathy, promoting analytical engagement instead. Defined by theorists like Darko Suvin, cognitive estrangement challenges conventional understanding by presenting alternative perspectives that provoke thoughtful reconsideration of the status quo.
Origins and Theoretical Backgrounds
Emotional identification originates from psychoanalytic theory, emphasizing empathy and the audience's emotional connection with characters to foster understanding and engagement. Cognitive estrangement, coined by literary theorist Darko Suvin, stems from science fiction studies and Marxist theory, highlighting the deliberate alienation of the audience to provoke critical reflection on societal norms. These contrasting theoretical backgrounds shape how narratives either immerse viewers emotionally or challenge them intellectually through defamiliarization techniques.
Key Differences Between Emotional Identification and Cognitive Estrangement
Emotional identification involves the audience's empathetic connection with characters, fostering shared feelings and personal involvement, whereas cognitive estrangement prompts critical detachment, encouraging viewers to analyze and question the narrative or social context. Emotional identification generates immersive experiences through affective resonance, while cognitive estrangement achieves intellectual engagement by disrupting emotional immersion to highlight underlying themes. These contrasting approaches serve distinct purposes in storytelling and audience response, with emotional identification emphasizing emotional alignment and cognitive estrangement fostering reflective distance.
Psychological Impacts of Emotional Engagement
Emotional identification fosters deep psychological connections by enabling individuals to share and understand feelings, which enhances empathy and emotional resilience. In contrast, cognitive estrangement promotes critical thinking and objective analysis by creating psychological distance, reducing emotional bias but potentially limiting emotional insight. Balancing emotional engagement with cognitive detachment optimizes mental health by supporting both empathy-driven relationships and rational decision-making processes.
The Role of Estrangement in Critical Thinking
Estrangement creates cognitive distance that challenges automatic emotional responses, enabling deeper critical analysis of social, cultural, or political issues depicted in texts or artworks. This technique disrupts familiar perceptions, encouraging audiences to question underlying assumptions and engage with alternative perspectives more objectively. By promoting reflective skepticism, estrangement enhances critical thinking skills crucial for evaluating complex narratives and ideologies.
Emotional Identification in Literature and Media
Emotional identification in literature and media allows audiences to deeply connect with characters by sharing their feelings, motivations, and experiences, fostering empathy and immersion in the narrative. This technique emphasizes relatable emotions and personal struggles, making stories resonate on a human level and enhancing the impact of themes and messages. Narrative devices such as first-person perspectives, internal monologues, and detailed character development are commonly used to facilitate emotional identification and create a powerful emotional engagement.
Cognitive Estrangement in Science Fiction and Art
Cognitive estrangement in science fiction and art creates a deliberate sense of alienation that encourages critical reflection on societal norms and realities by presenting familiar elements in unfamiliar ways. This technique disrupts emotional identification, allowing audiences to analyze human behavior, technology, and cultural constructs from an objective perspective. Classic examples include works like Aldous Huxley's "Brave New World" and films such as "Blade Runner," which use estrangement to question ethical, political, and philosophical paradigms.
Balancing Empathy and Distance: Practical Applications
Balancing empathy and distance in emotional identification versus cognitive estrangement involves fostering emotional connections with characters while maintaining critical perspective to enhance analytical thinking. This approach is crucial in education, where instructors encourage students to engage empathetically with narratives to deepen understanding yet remain distanced enough to critique underlying themes and societal issues effectively. Practical applications include therapeutic settings, where emotional identification aids in empathy development, while cognitive estrangement promotes objectivity, helping individuals manage emotional responses and foster resilience.
Choosing Between Identification and Estrangement in Storytelling
Choosing between emotional identification and cognitive estrangement in storytelling depends on the desired audience engagement and narrative impact. Emotional identification fosters deep empathy by allowing readers or viewers to connect intimately with characters' feelings, enhancing immersive experiences in genres like drama or romance. Cognitive estrangement, often used in science fiction or satire, encourages critical reflection by presenting unfamiliar or alien perspectives that challenge existing beliefs and stimulate intellectual inquiry.
Emotional Identification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com