Epic stories captivate audiences with grand narratives, larger-than-life characters, and timeless themes of heroism and adventure. These tales often explore profound human experiences and cultural values that resonate across generations. Discover how epic storytelling can inspire and enrich your own journey by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
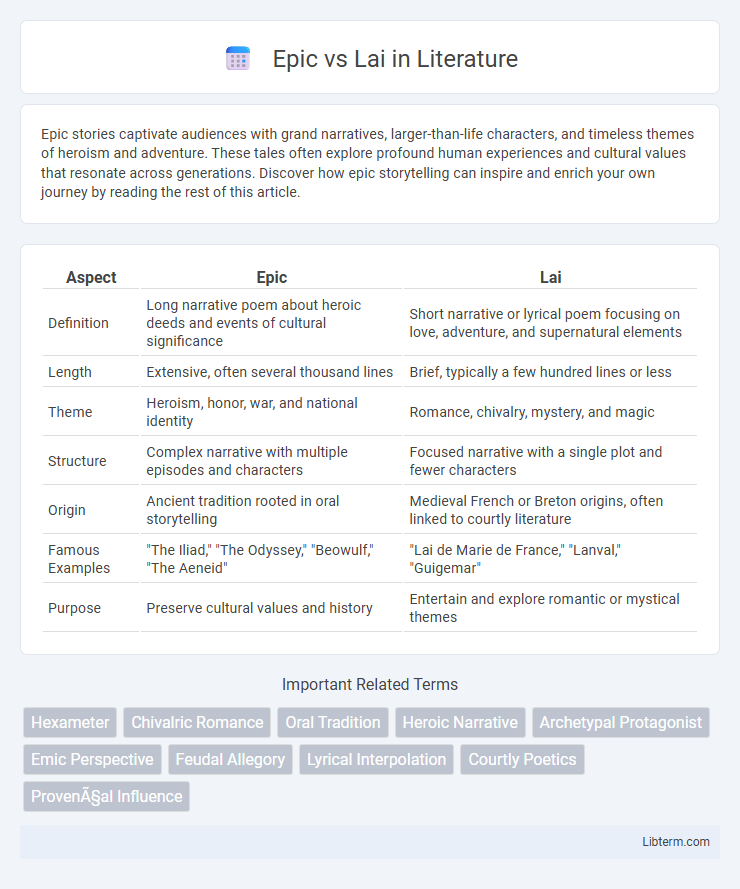
| Aspect | Epic | Lai |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long narrative poem about heroic deeds and events of cultural significance | Short narrative or lyrical poem focusing on love, adventure, and supernatural elements |
| Length | Extensive, often several thousand lines | Brief, typically a few hundred lines or less |
| Theme | Heroism, honor, war, and national identity | Romance, chivalry, mystery, and magic |
| Structure | Complex narrative with multiple episodes and characters | Focused narrative with a single plot and fewer characters |
| Origin | Ancient tradition rooted in oral storytelling | Medieval French or Breton origins, often linked to courtly literature |
| Famous Examples | "The Iliad," "The Odyssey," "Beowulf," "The Aeneid" | "Lai de Marie de France," "Lanval," "Guigemar" |
| Purpose | Preserve cultural values and history | Entertain and explore romantic or mystical themes |
Epic vs Lai: Overview and Key Differences
Epic and Lai are prominent players in the healthcare technology sector, each specializing in electronic health record (EHR) systems tailored for different clinical environments. Epic offers a comprehensive, integrated platform known for its extensive interoperability and robust patient management features, widely adopted by large hospital systems and academic medical centers. Lai, in contrast, focuses on modular, user-friendly solutions designed for smaller practices and outpatient clinics, emphasizing customization and ease of use to streamline workflow efficiency.
Historical Development of Epic and Lai
Epic poetry emerged in ancient Mesopotamia and Greece, exemplified by works like the "Epic of Gilgamesh" and Homer's "Iliad," serving as lengthy narratives that celebrate heroic deeds and cultural values. In contrast, the lai originated in medieval France during the 12th century, characterized by shorter, lyrical tales often involving chivalry and supernatural elements, with Marie de France being a prominent contributor. Both forms reflect evolving storytelling traditions, where epics laid foundational narrative structures while lais emphasized melodic and thematic conciseness.
Structure and Form: Epic vs Lai
Epics typically feature a long narrative structure with a formal, elevated style that chronicles heroic deeds and grand themes, often divided into cantos or books. Lais are shorter, lyrical poems usually composed in octosyllabic rhymed couplets, focusing on romantic or supernatural themes with a more intimate and personal tone. The structure of epics emphasizes complexity and breadth, while lais prioritize brevity and melodic form.
Themes and Motifs in Epic and Lai
Epic narratives emphasize grand themes such as heroism, fate, and the struggle between good and evil, often showcasing motifs like epic journeys, battles, and divine intervention. Lai stories concentrate on themes of love, magic, and transformation, frequently featuring motifs like enchanted objects, mysterious strangers, and moral lessons. The contrasting thematic focus highlights epics' societal and historical scope versus lais' intimate and personal nature.
Notable Examples of Epics and Lais
Epic poetry features monumental works like Homer's "Iliad" and "Odyssey," which depict heroic journeys and foundational myths with grand scale narratives and detailed character development. Lais, in contrast, are shorter narrative poems such as Marie de France's "Lanval" and "Yonec," emphasizing romantic and supernatural themes with lyrical, concise storytelling. Both forms showcase medieval literature's range, with epics focusing on heroic exploits and lais on personal, mystical experiences.
Narrative Techniques in Epic and Lai
Epic narratives employ expansive storytelling through extensive plots and numerous characters, often integrating heroic exploits and grand settings to convey cultural values. Lais utilize concise, lyrical structures with an emphasis on emotional depth and romantic or supernatural themes, typically presented in octosyllabic rhymes. Epic narratives rely on oral tradition and formulaic phrases, while lais prioritize personal expression and intricate symbolism within their brief format.
Cultural Significance of Epic and Lai
Epics embody foundational cultural narratives, preserving collective identity and historical memory through expansive storytelling of heroic deeds and ancestral values. Lais, brief narrative poems rooted in medieval Breton tradition, often explore themes of love, chivalry, and supernatural elements, reflecting societal norms and moral lessons in a more intimate format. Both forms significantly influence cultural heritage by transmitting values, beliefs, and social structures distinctive to their origins.
Influence on Modern Literature: Epic vs Lai
Epic poetry, characterized by lengthy narratives and heroic themes, significantly shaped modern literature by establishing foundational storytelling techniques and archetypes. Lai, a shorter medieval poetic form often centered on romantic and supernatural themes, influenced modern literature by inspiring lyrical brevity and thematic intimacy. The contrasting structures of Epic and Lai continue to enrich contemporary literary styles, blending grand narratives with personal emotions.
Epic and Lai: Reception Through the Ages
Epic and Lai represent distinct medieval narrative forms with unique reception histories; Epics, such as "The Song of Roland," were revered for their heroism and national identity, deeply influencing European literature from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance. Lais, short narrative poems often centered on love and chivalry, gained popularity through the works of Marie de France, shaping the tradition of courtly love and inspiring later romantic literature. Over centuries, Epic poetry remained a symbol of cultural valor, while Lais contributed significantly to the evolution of lyrical storytelling and medieval romance genres.
Choosing Between Epic and Lai for Storytelling
Selecting between Epic and Lai for storytelling depends on narrative scope and thematic focus; Epics are long, grand poems detailing heroic deeds and events significant to a culture or nation, ideal for expansive tales with complex plots. Lais are shorter, lyrical poems often centered around romantic or adventurous themes, suitable for intimate, character-driven stories with a focus on emotion and morality. Writers should consider the desired emotional impact and cultural resonance when choosing between the expansive, epic narrative style and the concise, lyrical form of a lai.
Epic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com