Asyndeton is a rhetorical device that involves omitting conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise and impactful expression. This technique accelerates the rhythm of sentences, enhancing their emotional intensity and persuasiveness. Explore the rest of the article to discover how you can effectively use asyndeton in your writing.
Table of Comparison
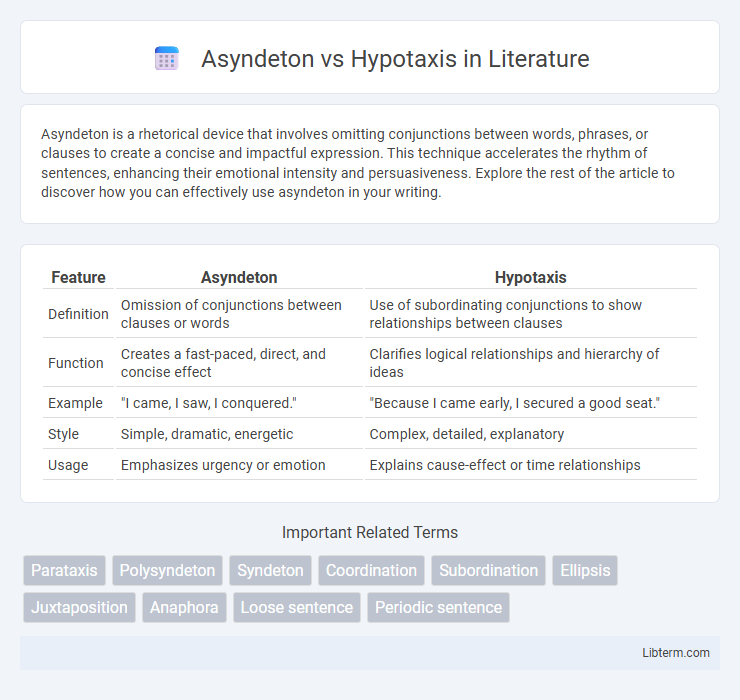
| Feature | Asyndeton | Hypotaxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of conjunctions between clauses or words | Use of subordinating conjunctions to show relationships between clauses |
| Function | Creates a fast-paced, direct, and concise effect | Clarifies logical relationships and hierarchy of ideas |
| Example | "I came, I saw, I conquered." | "Because I came early, I secured a good seat." |
| Style | Simple, dramatic, energetic | Complex, detailed, explanatory |
| Usage | Emphasizes urgency or emotion | Explains cause-effect or time relationships |
Introduction to Asyndeton and Hypotaxis
Asyndeton and hypotaxis are distinct syntactic techniques influencing sentence structure and rhythm. Asyndeton omits conjunctions between words or phrases to create a concise, impactful, and fast-paced effect, often enhancing emphasis and urgency. Hypotaxis, in contrast, organizes clauses using subordinating conjunctions, establishing a clear hierarchy and logical relationship that clarifies complex ideas and adds sophistication to writing.
Defining Asyndeton
Asyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the deliberate omission of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise and impactful effect. This technique accelerates the rhythm of the sentence, enhancing emphasis and intensity, often found in persuasive or poetic contexts. In contrast, hypotaxis involves the use of subordinating conjunctions to show clear relationships between ideas, emphasizing hierarchy and logical connection.
Defining Hypotaxis
Hypotaxis is a grammatical and rhetorical device characterized by the use of subordinate clauses to show the relationship between ideas, creating a hierarchy and clear structure within sentences. It contrasts with asyndeton, which employs the omission of conjunctions to produce concise and impactful expressions. Hypotactic structures enhance clarity and depth by explicitly linking concepts through conjunctions and relative pronouns, fostering logical connections and detailed explanations.
Key Differences Between Asyndeton and Hypotaxis
Asyndeton omits conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise, impactful effect, while hypotaxis employs multiple subordinate or coordinate conjunctions to establish clear relationships between ideas. The key difference lies in their sentence structure: asyndeton favors brevity and rhythm through omission, whereas hypotaxis emphasizes logical hierarchy and detailed connections. Asyndeton enhances dramatic intensity and speed, whereas hypotaxis provides clarity and complex, layered meaning.
Functions and Effects of Asyndeton
Asyndeton functions by eliminating conjunctions between phrases or clauses to create a rapid, concise, and impactful flow of ideas, enhancing the emotional intensity and urgency of the text. This rhetorical device accelerates the rhythm, emphasizing each element equally while creating a sense of immediacy and simplicity. By contrast, hypotaxis employs subordinating conjunctions to establish clear hierarchical relationships, enabling detailed and complex expression.
Functions and Effects of Hypotaxis
Hypotaxis structures sentences with subordinate clauses to clarify relationships and emphasize logical connections, enhancing coherence and depth in communication. It functions to show cause-and-effect, contrast, or time sequence clearly, guiding the reader through complex ideas systematically. The effect of hypotaxis is a more formal, precise, and analytical tone that aids in detailed explanation and nuanced argumentation.
Asyndeton and Hypotaxis in Literature
Asyndeton is a literary device characterized by the omission of conjunctions between phrases or clauses, creating a fast-paced and dramatic effect that enhances emphasis and intensity, often found in speeches and poetry. Hypotaxis involves the use of subordinating conjunctions to show the relationship between ideas, resulting in complex and nuanced sentences that clarify hierarchy and logical connections in literary texts. Writers employ asyndeton to evoke urgency and simplicity, while hypotaxis provides depth and detailed explanation, each shaping narrative rhythm and reader perception differently.
Examples of Asyndeton in Famous Works
Asyndeton, characterized by the omission of conjunctions, appears frequently in famous works such as Julius Caesar's "Veni, vidi, vici," highlighting speed and decisiveness. Ernest Hemingway employs asyndeton in "The Old Man and the Sea" with concise phrases like "He was an old man who fished alone," emphasizing simplicity and immediacy. Shakespeare's use of asyndeton in Macbeth's line "I have no spur to prick the sides of my intent, but only vaulting ambition," removes conjunctions to create intensity and urgency in the character's psyche.
Examples of Hypotaxis in Famous Works
Hypotaxis, a grammatical arrangement using subordinate clauses, is prominently illustrated in Shakespeare's "Hamlet," where complex sentences like "Though this be madness, yet there is method in't" showcase hierarchical relationships between ideas. In Jane Austen's "Pride and Prejudice," sentences such as "Because he is so rich, he can afford to be generous" demonstrate clear dependence between clauses, enhancing narrative clarity. The structured layering of ideas in Mary Shelley's "Frankenstein," exemplified by "If I cannot inspire love, I will cause fear," reveals the careful use of hypotaxis to express causality and consequence.
Choosing Between Asyndeton and Hypotaxis
Choosing between asyndeton and hypotaxis depends on the desired rhythm and clarity of a sentence. Asyndeton, characterized by the omission of conjunctions, creates a fast-paced, impactful effect that emphasizes urgency or intensity. Hypotaxis, with its use of subordinating conjunctions and complex sentence structures, enhances clarity and logical relationships, making it ideal for detailed explanations or nuanced arguments.
Asyndeton Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com