Ellipsis is a powerful punctuation tool that allows you to indicate omitted text or a trailing thought in your writing. It enhances readability by creating pauses or suspense, helping to convey tone and emotion effectively. Explore the rest of this article to discover how mastering ellipsis can improve your communication skills.
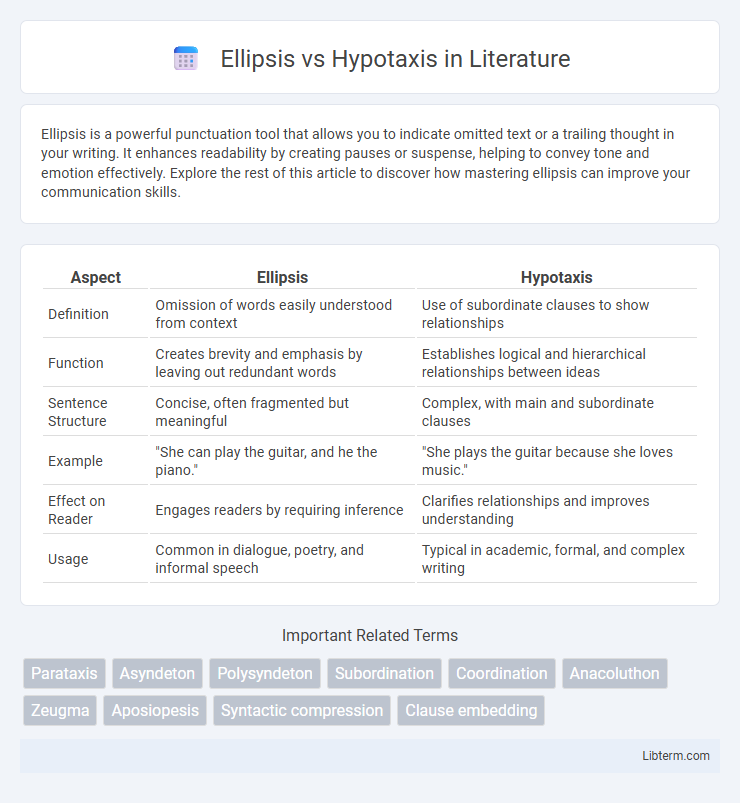
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ellipsis | Hypotaxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of words easily understood from context | Use of subordinate clauses to show relationships |
| Function | Creates brevity and emphasis by leaving out redundant words | Establishes logical and hierarchical relationships between ideas |
| Sentence Structure | Concise, often fragmented but meaningful | Complex, with main and subordinate clauses |
| Example | "She can play the guitar, and he the piano." | "She plays the guitar because she loves music." |
| Effect on Reader | Engages readers by requiring inference | Clarifies relationships and improves understanding |
| Usage | Common in dialogue, poetry, and informal speech | Typical in academic, formal, and complex writing |
Understanding Ellipsis: Definition and Usage
Ellipsis is a linguistic phenomenon where one or more words are omitted from a sentence because they are implied and understood from the context, enhancing brevity and avoiding redundancy. It frequently occurs in conversational English and literary texts, allowing speakers or writers to convey meaning efficiently without repeating information. Understanding ellipsis involves recognizing these omitted elements and interpreting the intended message based on prior discourse or shared knowledge between communicators.
Exploring Hypotaxis: Meaning and Characteristics
Hypotaxis refers to the grammatical arrangement of clauses where one is subordinated to another, creating a clear hierarchy of ideas and logical relationships. It is characterized by the use of subordinating conjunctions such as "because," "although," and "while," which link dependent clauses to main clauses, enhancing sentence complexity and clarity. This syntactic structure enables precise expression of cause, time, condition, or contrast, making hypotaxis essential for detailed and nuanced communication.
Grammatical Foundations: Ellipsis vs Hypotaxis
Ellipsis involves the omission of words that are grammatically understood, allowing sentences to remain complete without redundant elements, exemplified by phrases like "She can dance, and he can [dance] too." Hypotaxis employs subordinate clauses to show explicit dependence between ideas, using conjunctions such as "because," "although," or "if," as seen in "She dances because she loves music." These grammatical foundations reveal ellipsis's reliance on contextual inference, contrasting with hypotaxis's clear clause hierarchy and syntactic connectivity.
Examples of Ellipsis in Sentences
Ellipsis in sentences occurs when certain words are intentionally omitted because they are implied or understood from context, such as in "She can play the guitar, and he can [play the guitar] too." Another example is "I ordered the chicken, and John the steak," where the verb "ordered" is omitted in the second clause. Ellipsis enhances sentence conciseness and fluidity by avoiding unnecessary repetition while maintaining clarity.
Illustrative Hypotaxis Constructions
Illustrative hypotaxis constructions demonstrate the use of subordinate clauses to elaborate on or clarify the main clause, often employing phrases like "for example," "such as," or "namely" to introduce specific instances. This syntactic structure highlights logical relationships and enhances textual cohesion by explicitly linking details through dependent clauses. In contrast to ellipsis, which omits redundant information, hypotaxis uses full subordinate constructions to provide clear and detailed exemplifications within complex sentences.
The Purpose of Ellipsis in Writing
Ellipsis serves to enhance conciseness and create rhythm by deliberately omitting words that are implied, allowing readers to infer missing information for a more engaging and efficient narrative. It streamlines communication by removing redundancy while maintaining clarity, which contrasts with hypotaxis that relies on explicit conjunctions and subordinate clauses to clarify relationships between ideas. This technique deepens reader engagement by prompting active interpretation and emphasizing key concepts without overloading the text.
Why Writers Use Hypotaxis
Writers use hypotaxis to create complex sentences that clearly show the logical relationships between ideas, enhancing the clarity and depth of their arguments. This technique allows for detailed explanations and nuanced contrasts, which can guide readers through sophisticated reasoning processes. By structuring sentences with subordinating conjunctions, authors emphasize the hierarchy of information, making communication more precise and persuasive.
Ellipsis vs Hypotaxis: Key Differences
Ellipsis involves the omission of words that are understood from the context, enhancing brevity and cohesion in sentences. Hypotaxis relies on subordinating conjunctions to create complex sentence structures expressing clear hierarchical relationships between clauses. The key difference lies in ellipsis simplifying sentences by omission, while hypotaxis emphasizes syntactic complexity through explicit clause linkage.
Effects on Readability and Style
Ellipsis enhances readability by removing redundant elements, creating concise sentences that engage readers and foster a dynamic narrative style. Hypotaxis, with its use of subordinating conjunctions and complex sentence structures, can enrich textual depth and clarity but may slow reading pace and challenge comprehension. Balancing ellipsis and hypotaxis allows writers to control textual rhythm, tailoring style to the audience's cognitive load and purpose.
Choosing Between Ellipsis and Hypotaxis
Choosing between ellipsis and hypotaxis depends on the desired sentence clarity and rhythm; ellipsis omits redundant elements for brevity, while hypotaxis employs explicit subordinate clauses to convey complex relationships. Writers aiming for concise, impactful statements favor ellipsis, enhancing fluency without loss of meaning. Conversely, hypotaxis suits formal or detailed prose, ensuring precise logical connections through clear syntactic hierarchy.
Ellipsis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com