Abstraction simplifies complex systems by focusing on the essential features while hiding unnecessary details, making it easier to manage and understand information. In programming, it helps create reusable and maintainable code by defining clear interfaces and reducing dependencies. Explore the rest of the article to see how abstraction can enhance your development process and problem-solving skills.
Table of Comparison
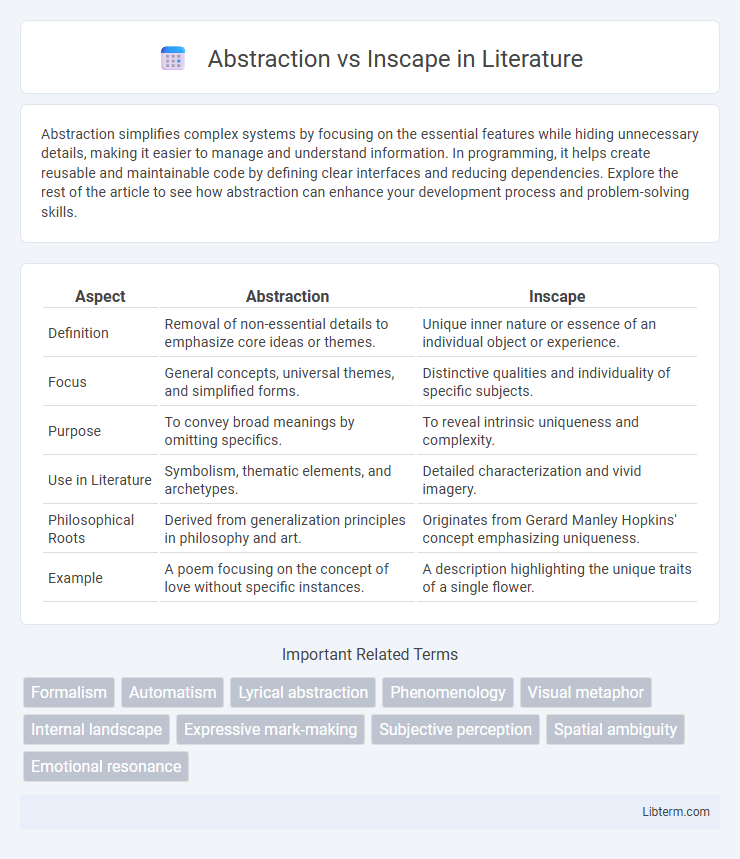
| Aspect | Abstraction | Inscape |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of non-essential details to emphasize core ideas or themes. | Unique inner nature or essence of an individual object or experience. |
| Focus | General concepts, universal themes, and simplified forms. | Distinctive qualities and individuality of specific subjects. |
| Purpose | To convey broad meanings by omitting specifics. | To reveal intrinsic uniqueness and complexity. |
| Use in Literature | Symbolism, thematic elements, and archetypes. | Detailed characterization and vivid imagery. |
| Philosophical Roots | Derived from generalization principles in philosophy and art. | Originates from Gerard Manley Hopkins' concept emphasizing uniqueness. |
| Example | A poem focusing on the concept of love without specific instances. | A description highlighting the unique traits of a single flower. |
Understanding Abstraction and Inscape
Understanding abstraction involves recognizing the process of simplifying complex realities by focusing on essential qualities while omitting irrelevant details. Inscape refers to the unique inner nature or distinctive design that defines the identity of an object or experience, emphasizing its inherent individuality. Together, abstraction and inscape aid in analyzing and interpreting both the general patterns and the unique characteristics within art, literature, and philosophy.
Historical Context of Abstraction and Inscape
The historical context of abstraction traces back to early 20th-century movements such as Cubism and Abstract Expressionism, where artists like Kandinsky and Mondrian sought to represent emotions and ideas beyond realistic depictions. Inscape, a concept rooted in the 20th-century literary and visual arts, was popularized by poet Gerard Manley Hopkins and later adapted by visual artists to emphasize an inward perception of reality, capturing the unique essence or inner nature of a subject. Both abstraction and inscape emerged as responses to shifting cultural paradigms, reflecting a move away from external representation toward subjective interpretation and inner experience.
Key Characteristics of Abstraction
Abstraction emphasizes simplifying complex subjects by reducing details to core shapes, colors, and forms, often distorting reality to highlight conceptual elements. Key characteristics include the use of non-representational imagery, emphasis on geometric shapes, and reliance on color and texture to evoke emotion rather than depict visual reality. Unlike inscape, which captures the unique inner essence of a subject, abstraction prioritizes universal forms and patterns over specific individual traits.
Defining Features of Inscape
Inscape, a concept introduced by poet Gerard Manley Hopkins, emphasizes the unique, intrinsic design and individuality of natural objects, capturing their distinct essence and form. Unlike abstraction, which simplifies or distills visual elements to essential shapes or colors, inscape preserves intricate detail and specificity, highlighting the exceptional and irregular characteristics that define an entity's true nature. This detailed portrayal of uniqueness fosters a deeper appreciation of complexity and identity within art or literature.
Abstraction vs Inscape: Core Differences
Abstraction simplifies reality by reducing complex forms into basic shapes and colors, emphasizing universal concepts rather than specific details. Inscape represents the unique inner nature or essence of a subject, capturing individuality and distinct characteristics through intricate and expressive portrayal. The core difference lies in abstraction's focus on generalized interpretation, while inscape emphasizes personal, detailed representation of an object's true identity.
Influences on Artistic Expression
Abstraction transforms artistic expression by emphasizing shapes, colors, and forms, freeing artists from realistic representation and enabling emotional or conceptual exploration. Inscape, rooted in personal perception and internal vision, directs creativity toward capturing the essence of an individual's inner landscape or psychological state. Both approaches influence contemporary art by expanding the boundaries of visual language and inviting subjective interpretation.
Notable Artists and Movements
Abstraction, championed by artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian, emphasizes non-representational forms and geometric shapes, central to movements such as Abstract Expressionism and De Stijl. Inscape, explored by artists like Gerard Manley Hopkins and later visualized by painter Georgia O'Keeffe, focuses on representing the inner essence or subjective experience of landscapes and objects, aligning with Symbolism and certain strains of Expressionism. Both approaches profoundly influenced 20th-century modern art, shaping diverse aesthetics and philosophical interpretations within visual culture.
Applications in Contemporary Art
Abstraction in contemporary art emphasizes non-representational forms, utilizing color, shape, and texture to evoke emotions and ideas without depicting recognizable objects. Inscape, a concept rooted in visualizing the internal essence or spiritual core of subjects, enhances artworks by expressing unique personal or psychological landscapes. Both approaches influence modern artistic practices by expanding creative possibilities, with abstraction dominating in mediums like painting and sculpture, while inscape informs experimental genres such as digital art and mixed media installations.
Impact on Viewer Perception
Abstraction distills forms to their essential shapes and colors, encouraging viewers to interpret emotions and ideas subjectively, thereby amplifying personal engagement and imaginative response. Inscape, emphasizing the depiction of an internal landscape or essence, guides viewers toward a deeper understanding of the artist's inner world, fostering empathy and introspective reflection. The divergence in abstraction and inscape significantly influences viewer perception by either broadening interpretative possibilities or channeling a more focused, immersive emotional experience.
Future Trends in Abstraction and Inscape
Future trends in abstraction emphasize integrating advanced AI algorithms and immersive virtual reality to create dynamic, evolving artworks that challenge traditional perceptions. Inscape is leaning towards personalized digital experiences using augmented reality and biometric data, enabling a deeper emotional connection between the viewer and the art. Both abstraction and inscape are converging through technology, driving innovative expressions in contemporary art landscapes.
Abstraction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com