Dialect reflects the unique linguistic features, including vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar, that distinguish regional or social groups. Understanding these variations enriches your communication skills and cultural awareness. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how dialect shapes identity and social interaction.
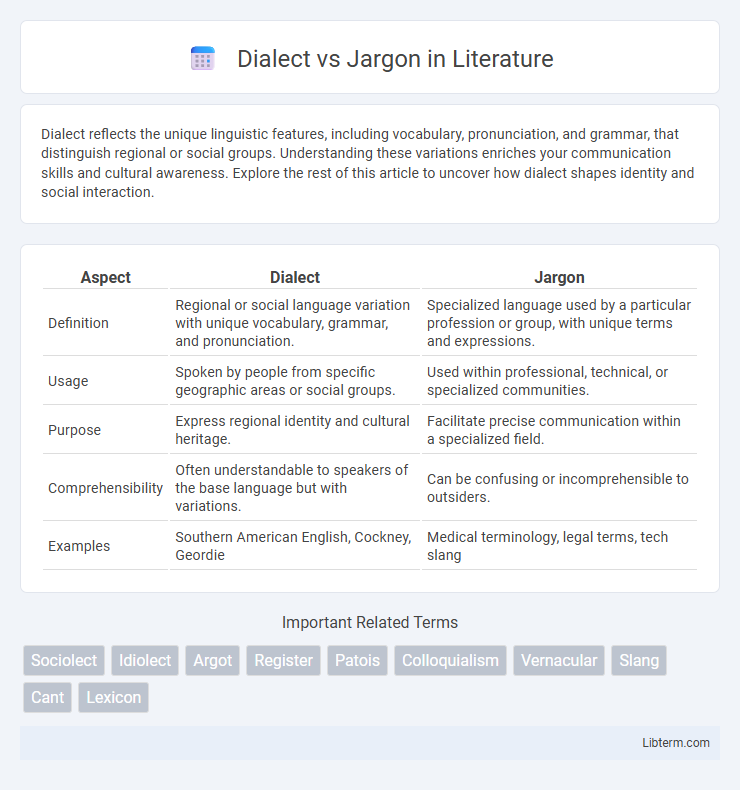
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dialect | Jargon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regional or social language variation with unique vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. | Specialized language used by a particular profession or group, with unique terms and expressions. |
| Usage | Spoken by people from specific geographic areas or social groups. | Used within professional, technical, or specialized communities. |
| Purpose | Express regional identity and cultural heritage. | Facilitate precise communication within a specialized field. |
| Comprehensibility | Often understandable to speakers of the base language but with variations. | Can be confusing or incomprehensible to outsiders. |
| Examples | Southern American English, Cockney, Geordie | Medical terminology, legal terms, tech slang |
Understanding Dialect: Definition and Features
Dialect refers to a regional or social variety of a language distinguished by unique pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. It reflects cultural identity and geographic origin, often evolving within specific communities over time. Key features include phonological differences, distinctive lexical items, and syntactic variations that distinguish it from the standard language and other dialects.
What is Jargon? Key Characteristics
Jargon refers to specialized terminology used by a particular profession, group, or activity, often unintelligible to outsiders. Key characteristics of jargon include technical language, precise definitions, and efficient communication within a specific field such as medicine, law, or technology. This specialized vocabulary enhances clarity and accuracy among experts but can create barriers to understanding for the general public.
Dialect vs Jargon: Core Differences
Dialect refers to regional or social variations in language encompassing distinct vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, while jargon consists of specialized terms used within particular professions or groups. Dialects reflect broader linguistic and cultural identity, whereas jargon serves as a technical shorthand that facilitates precise communication among insiders. Understanding core differences highlights how dialects shape everyday language and cultural expression, while jargon streamlines industry-specific dialogue.
Historical Origins of Dialects and Jargon
Dialects originate from historical linguistic evolution shaped by geographical, social, and cultural factors within specific communities, reflecting long-standing language variation over time. Jargon develops primarily within specialized professional or social groups as a form of coded language to facilitate precise and efficient communication. The historical origins of dialects are deeply rooted in regional language divergence, whereas jargon arises from the necessity of shared expertise and context in particular fields.
Social Functions of Dialect and Jargon
Dialect serves as a powerful social marker, reflecting regional identity, cultural heritage, and group belonging through distinct pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. Jargon functions primarily within specialized communities or professions, facilitating precise communication and reinforcing group cohesion by using technical terms understood only by insiders. Both dialect and jargon shape social interactions, enabling individuals to express solidarity or differentiate themselves within diverse societal contexts.
Geographic Distribution of Dialects
Dialects exhibit distinct geographic distribution patterns influenced by historical settlement, migration, and regional interactions, resulting in unique phonetic, lexical, and syntactic variations within a language. Unlike jargon, which is specialized language used by specific professional or social groups regardless of location, dialects are spatially rooted and reflect the cultural and environmental context of a particular area. Geographic boundaries such as mountains, rivers, and political borders often reinforce dialectal differences by limiting communication between communities.
Professional Spheres and Jargon Usage
Dialect refers to regional or social language variations characterized by distinct vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, while jargon consists of specialized terms used within professional spheres to facilitate precise communication. Jargon usage streamlines complex concepts and procedures unique to fields such as medicine, law, and technology, enhancing efficiency and clarity among experts. However, excessive jargon may create barriers for outsiders, highlighting the importance of context-sensitive language adaptation in professional environments.
Impact on Communication and Misunderstandings
Dialect variations often lead to regional communication barriers due to differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and syntax, which can cause misunderstandings among speakers from diverse areas. Jargon, specialized language used within particular professions or groups, may hinder effective communication when outsiders encounter unfamiliar terms, leading to confusion or misinterpretation. Both dialect and jargon impact clarity by creating linguistic gaps that challenge mutual understanding in interpersonal and cross-group exchanges.
Dialect and Jargon in Modern Media
Dialect in modern media reflects regional speech patterns, enriching storytelling with cultural authenticity and diversity, while jargon consists of specialized terminology used within specific professional or social groups to convey precise meaning efficiently. Media platforms leverage dialects to build relatable characters and settings, enhancing audience engagement through linguistic realism. Jargon serves as a tool in media to establish credibility and immerse viewers in particular fields such as medicine, technology, or gaming, highlighting expertise and community identity.
Preserving Dialects and Managing Jargon
Preserving dialects involves documenting unique linguistic features and promoting native speaker use to maintain cultural identity and heritage. Managing jargon requires clear communication strategies, such as defining specialized terms in professional contexts to ensure inclusivity and avoid misunderstandings. Both preserving dialects and managing jargon contribute to effective language usage within diverse communities and industries.
Dialect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com