Fables are short stories that convey important life lessons through animals and characters with human traits. These timeless tales use simple narratives to teach morals, making complex ideas easy to understand for readers of all ages. Explore the rest of the article to discover how fables can enrich your perspective and storytelling skills.
Table of Comparison
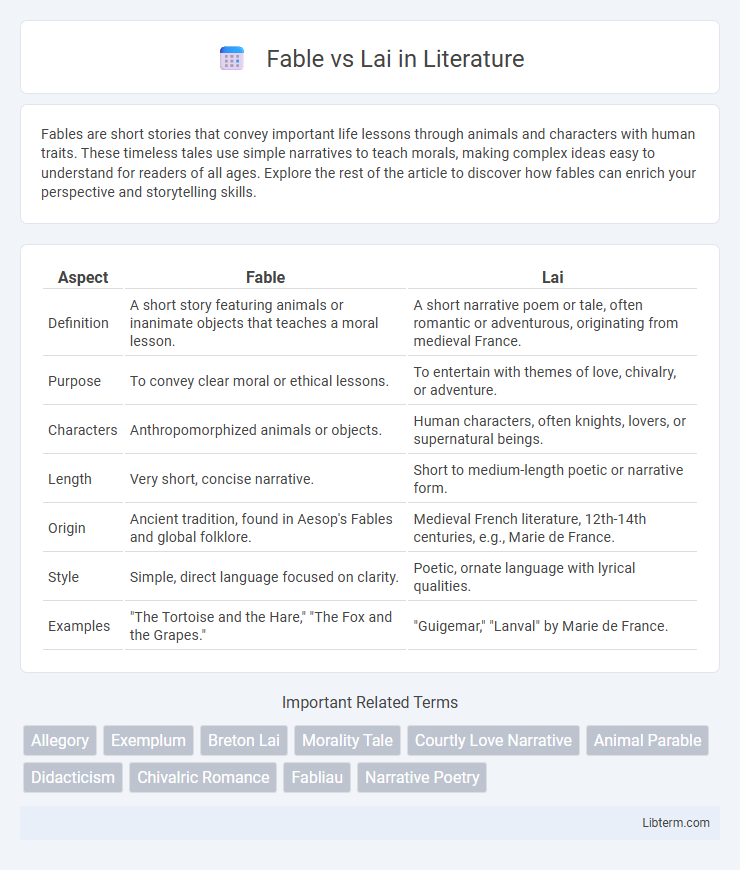
| Aspect | Fable | Lai |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A short story featuring animals or inanimate objects that teaches a moral lesson. | A short narrative poem or tale, often romantic or adventurous, originating from medieval France. |
| Purpose | To convey clear moral or ethical lessons. | To entertain with themes of love, chivalry, or adventure. |
| Characters | Anthropomorphized animals or objects. | Human characters, often knights, lovers, or supernatural beings. |
| Length | Very short, concise narrative. | Short to medium-length poetic or narrative form. |
| Origin | Ancient tradition, found in Aesop's Fables and global folklore. | Medieval French literature, 12th-14th centuries, e.g., Marie de France. |
| Style | Simple, direct language focused on clarity. | Poetic, ornate language with lyrical qualities. |
| Examples | "The Tortoise and the Hare," "The Fox and the Grapes." | "Guigemar," "Lanval" by Marie de France. |
Introduction to Fables and Lais
Fables are short stories featuring anthropomorphic animals that convey moral lessons, dating back to Aesop's ancient collections and widely used to teach ethical principles. Lais are narrative poems from medieval French literature, typically involving chivalric themes, romance, and supernatural elements, often inspired by Celtic folklore. Both forms serve distinct storytelling purposes: fables emphasize concise moral instruction, while lais explore complex narratives of love and adventure.
Defining Characteristics of Fables
Fables are short, allegorical stories that use animals or inanimate objects as characters to convey moral lessons or universal truths. These narratives emphasize clear, instructive messages often related to human behavior, making them distinct from other storytelling forms. The defining characteristics include personification, simplicity in plot, and explicit morals, which separate fables from tales like the Lai that focus more on romance and chivalric adventures.
Unique Features of Lais
Lais are narrative poems characterized by their short length, lyrical style, and focus on themes of love and chivalry, distinguishing them from fables which primarily teach moral lessons through animal characters or allegories. Originating in medieval French literature, lais often incorporate supernatural elements and personal emotions, offering intimate storytelling that blends romance with fantasy. Unlike fables, lais emphasize human experiences and courtly life, making them unique in medieval narrative traditions.
Historical Origins: Fables vs Lai
Fables trace their historical origins to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Greece, notably exemplified by Aesop's fables, which use animals as allegorical figures to convey moral lessons. In contrast, Lais originated in medieval Brittany and were popularized by poets like Marie de France, characterized by their narrative poetry blending romance and adventure with supernatural elements. The distinct evolution of fables emphasizes moral instruction, while lais focus on storytelling rich in emotional and fantastical motifs.
Common Themes Explored
Fable and Lai commonly explore themes of love, transformation, and the supernatural, often intertwining human emotions with magical or mythical elements. Both genres emphasize moral lessons and the consequences of desire, betrayal, and fate, reflecting medieval societal values and beliefs. Their narratives frequently highlight the tension between human vulnerability and mystical forces, illustrating the complexities of human experience within fantastical contexts.
Narrative Structure and Style
Fable employs a linear narrative structure with clear moral lessons, utilizing concise and straightforward language to emphasize its allegorical purpose. In contrast, Lai features a more intricate, episodic structure that interweaves romance and adventure, characterized by poetic and lyrical stylistic elements. The differing narrative frameworks and stylistic approaches reflect the distinct cultural and thematic intentions underlying each genre.
Use of Animals and Human Characters
Fable traditionally employs anthropomorphized animals as central characters to convey moral lessons, with animals embodying specific human traits such as cunning or honesty, making the narrative straightforward and universally accessible. Lai, rooted in medieval literature, integrates human characters often entwined with supernatural elements, emphasizing personal experiences and emotional depth rather than direct moral instruction. The use of animals in fables contrasts sharply with the human-centric storytelling of lais, highlighting differing narrative purposes and cultural contexts within these genres.
Moral Lessons: Implicit vs Explicit
Fables typically convey moral lessons explicitly, often ending with a clear and direct statement that summarizes the ethical teaching, making the intended message unmistakable. In contrast, lais embed their morals implicitly within rich narratives and symbolic elements, encouraging readers to interpret and reflect on underlying themes rather than presenting a straightforward moral. This difference highlights how fables aim for immediate clarity in ethical instruction while lais foster deeper contemplation and personal insight.
Influence on Literature and Culture
Fable and lai significantly shaped literature and culture through their unique narrative forms; fables use animal characters to convey moral lessons, profoundly influencing folklore, children's literature, and ethical storytelling traditions. Lais, medieval narrative poems often centered on themes of love and chivalry, enriched courtly literature and inspired the development of romantic and lyrical poetry across Europe. Both genres contributed to cultural values and literary structures by embedding moral and social ideals within engaging stories.
Modern Adaptations and Relevance
Modern adaptations of Fable vs Lai emphasize their distinct narrative structures and thematic relevance in contemporary storytelling. Fable's allegorical nature allows for flexible reinterpretations across various media, reinforcing moral lessons in a modern context. Lai's focus on courtly love and chivalry resonates with current explorations of romance and human emotion, maintaining its cultural significance today.
Fable Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com