Intrusive narration breaks the fourth wall by directly addressing the reader, offering commentary or insights that go beyond the story's immediate events. This narrative technique can create a unique connection between the author and the audience, enriching the reading experience with humor or critical observation. Discover how intrusive narration shapes storytelling and enhances your engagement in the following article.
Table of Comparison
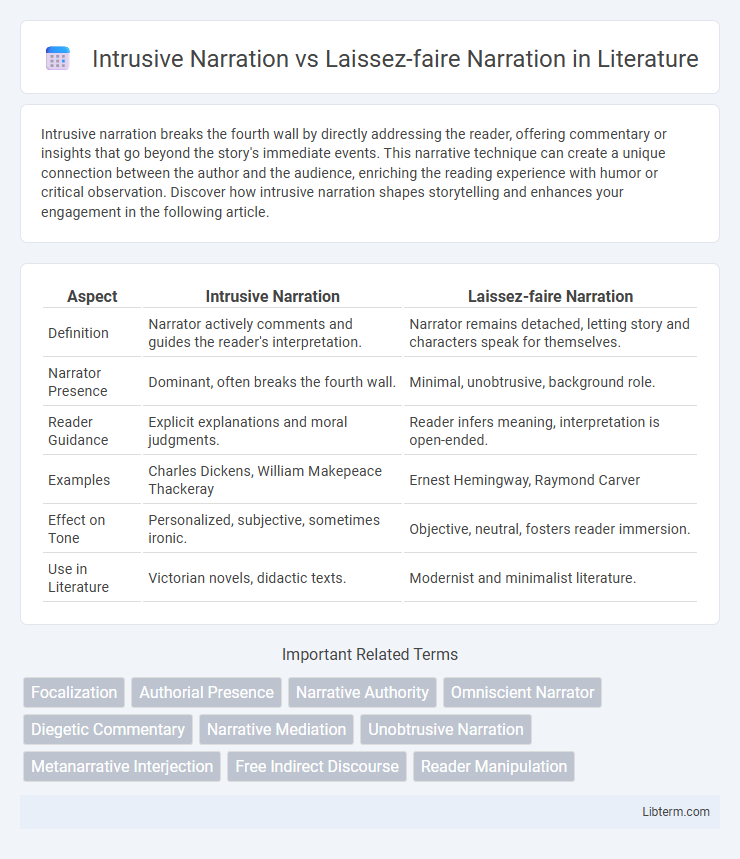
| Aspect | Intrusive Narration | Laissez-faire Narration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Narrator actively comments and guides the reader's interpretation. | Narrator remains detached, letting story and characters speak for themselves. |
| Narrator Presence | Dominant, often breaks the fourth wall. | Minimal, unobtrusive, background role. |
| Reader Guidance | Explicit explanations and moral judgments. | Reader infers meaning, interpretation is open-ended. |
| Examples | Charles Dickens, William Makepeace Thackeray | Ernest Hemingway, Raymond Carver |
| Effect on Tone | Personalized, subjective, sometimes ironic. | Objective, neutral, fosters reader immersion. |
| Use in Literature | Victorian novels, didactic texts. | Modernist and minimalist literature. |
Understanding Intrusive Narration
Intrusive narration actively involves the narrator who directly addresses the audience, offering personal insights, opinions, or commentary that shapes the reader's interpretation of the story. This narrative style breaks the fourth wall, creating a conversational tone and guiding the audience through the text with intentional bias or emotional influence. Understanding intrusive narration highlights its role in framing the narrative perspective, enriching thematic depth, and controlling the storytelling pace through explicit narrative interventions.
Defining Laissez-faire Narration
Laissez-faire narration is a storytelling approach characterized by minimal authorial intervention, allowing characters and events to unfold naturally without explicit moral judgments or direct commentary. This narrative style emphasizes an objective, neutral tone that empowers readers to interpret the story independently, fostering engagement through subtlety and openness. Contrasting with intrusive narration, laissez-faire narration maintains a hands-off perspective, prioritizing immersive experience over guiding audience interpretation.
Key Characteristics of Intrusive Narrators
Intrusive narrators actively intervene in the storytelling by offering direct commentary, opinions, or insights that shape the reader's understanding and response to the narrative. They often break the fourth wall, addressing the audience explicitly and providing context or moral judgments that ground the story within a particular viewpoint. This narrative style contrasts sharply with laissez-faire narration, where the narrator remains unobtrusive, allowing events and characters to unfold without overt guidance or interpretation.
Traits of Laissez-faire Narrators
Laissez-faire narrators exhibit minimal interference in the storytelling, allowing events and characters to unfold organically without overt authorial commentary or judgment. Their narrative style prioritizes objectivity, often refraining from guiding the reader's emotional response, which fosters a more immersive and interpretive experience. Characterized by subtlety and restraint, laissez-faire narration emphasizes showing rather than telling, enhancing reader engagement through authentic dialogue and detailed descriptions.
Effects on Storytelling and Reader Engagement
Intrusive narration directly addresses the reader, offering commentary or insights that shape interpretation and create intimacy, enhancing emotional engagement but potentially disrupting narrative immersion. Laissez-faire narration allows the story to unfold without overt authorial presence, promoting reader autonomy in interpretation and fostering a sense of realism and discovery. Balancing these narration styles influences pacing, tone, and depth of character development, thereby affecting how readers connect and invest in the narrative.
Common Literary Examples of Each Style
Intrusive narration is exemplified in Charles Dickens' "Bleak House," where the narrator frequently addresses the reader and offers personal commentary, creating a direct connection. Laissez-faire narration appears in Ernest Hemingway's "The Old Man and the Sea," characterized by minimal authorial intrusion, allowing events and character actions to unfold without explicit narrative judgment. These contrasting styles highlight the spectrum between overt narrative guidance and objective storytelling in literature.
Advantages of Intrusive Narration
Intrusive narration offers the advantage of direct engagement with the reader, providing clarity and enhancing understanding by explicitly guiding interpretation and emphasizing key themes. It allows the narrator to inject personal insights, background information, and commentary that enrich the narrative experience and deepen emotional resonance. This narrative style also facilitates a stronger authorial voice, ensuring that the story's moral or message is unmistakably conveyed.
Benefits of Laissez-faire Narration
Laissez-faire narration enhances reader engagement by allowing audiences to interpret the story without authorial interference, fostering a more immersive and personal experience. This narrative style encourages active participation, stimulating critical thinking and emotional investment as readers piece together plot and character motivations independently. Such autonomy can deepen connection to the text, promoting sustained interest and varied interpretations across diverse audiences.
Choosing the Right Narration Style for Your Story
Choosing the right narration style hinges on the story's tone and objective; intrusive narration, characterized by a narrator's direct commentary, enhances reader engagement through personality and guidance, ideal for humorous or reflective tales. Laissez-faire narration, offering an unobtrusive and objective viewpoint, allows readers to interpret the story independently, fitting mysteries or works aiming for ambiguity. Matching narration style to narrative purpose maximizes emotional impact and thematic clarity.
Recent Trends in Narrative Techniques
Recent trends in narrative techniques highlight a shift from intrusive narration, where authors directly guide readers with explicit commentary, towards laissez-faire narration that favors subtle storytelling and reader interpretation. Contemporary literature increasingly employs laissez-faire narration to create immersive experiences, allowing characters' actions and dialogues to reveal the plot without authorial intervention. Advances in digital storytelling and interactive media further support this trend by enabling audiences to engage with narratives in a non-linear, participatory manner.
Intrusive Narration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com