Caricatures exaggerate distinctive features to create humorous or satirical portraits that capture personality traits vividly. Artists use these drawings in politics, entertainment, and media to communicate complex ideas through visually striking imagery. Explore the rest of the article to discover how caricatures influence culture and art.
Table of Comparison
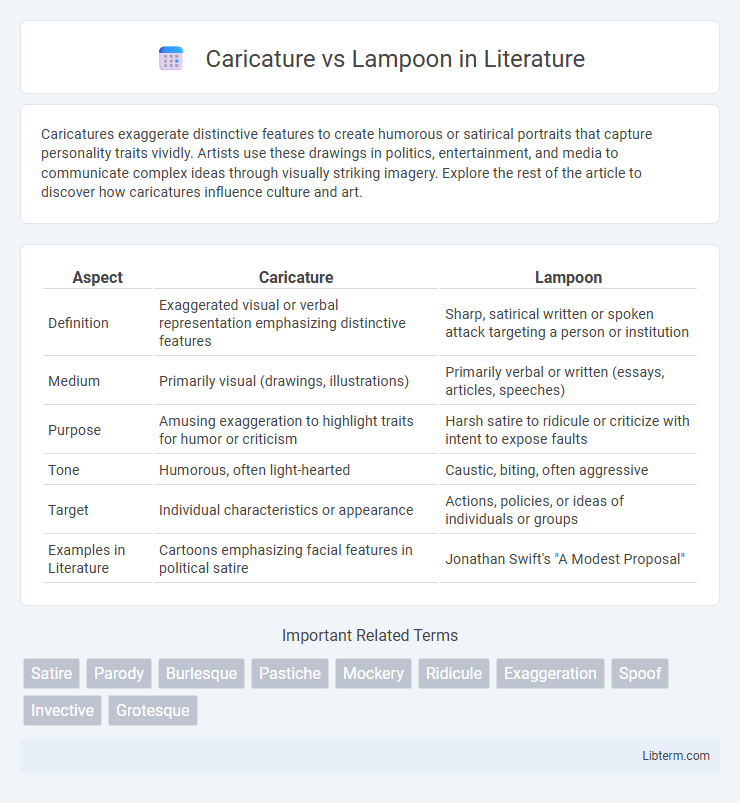
| Aspect | Caricature | Lampoon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exaggerated visual or verbal representation emphasizing distinctive features | Sharp, satirical written or spoken attack targeting a person or institution |
| Medium | Primarily visual (drawings, illustrations) | Primarily verbal or written (essays, articles, speeches) |
| Purpose | Amusing exaggeration to highlight traits for humor or criticism | Harsh satire to ridicule or criticize with intent to expose faults |
| Tone | Humorous, often light-hearted | Caustic, biting, often aggressive |
| Target | Individual characteristics or appearance | Actions, policies, or ideas of individuals or groups |
| Examples in Literature | Cartoons emphasizing facial features in political satire | Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal" |
Understanding Caricature: Definition and Purpose
Caricature is an artistic representation that exaggerates distinctive features or traits of a subject to create a recognizable and often humorous likeness. Its primary purpose is to emphasize particular qualities for entertainment, satire, or social commentary without necessarily conveying harsh criticism. Unlike lampoon, which aims for sharp ridicule or scorn, caricature balances exaggeration with artistic expression to engage viewers through visual distortion.
What is a Lampoon? Key Features Explained
A lampoon is a form of satirical writing or illustration that sharply criticizes or ridicules individuals, institutions, or social issues through humor and exaggeration. Key features of a lampoon include a biting tone, often harsh and direct mockery, aimed at exposing flaws or hypocrisy. Unlike caricatures that primarily distort physical features for humor, lampoons focus on biting commentary and social or political critique.
Historical Origins of Caricature and Lampoon
Caricature originated in the Renaissance era, particularly flourishing in 16th-century Italy with artists like Leonardo da Vinci using exaggerated features to highlight human flaws and social critique. Lampoon traces back to the 17th century, rooted in satirical poetry and prose in England, aiming to publicly ridicule individuals or institutions through humor and sharp criticism. Both forms evolved as powerful tools for social commentary, but caricature emphasizes visual exaggeration while lampoon relies primarily on textual satire.
Techniques Used in Caricature vs Lampoon
Caricature utilizes exaggeration of distinctive physical features and expressions to create a humorous or grotesque portrayal while maintaining recognizable likeness. Lampoon employs satire through witty, often biting commentary combined with exaggerated or symbolic imagery to criticize societal or political subjects. Both techniques rely on visual distortion, but caricature focuses on individual traits, whereas lampoon integrates broader narrative criticism.
Caricature in Art and Popular Culture
Caricature in art and popular culture is a visual representation that exaggerates distinctive features or traits to create a humorous or satirical effect, often emphasizing facial characteristics or body proportions. This technique is widely used by political cartoonists, illustrators, and animators to convey criticism or highlight personality quirks in an easily recognizable manner. Caricatures influence public perception by blending entertainment with social commentary, making complex issues accessible and engaging through exaggerated yet familiar imagery.
The Role of Lampoon in Satire and Critique
Lampoon plays a critical role in satire by sharply ridiculing public figures and institutions to expose flaws and provoke social or political change. Unlike caricature, which exaggerates physical features for humorous effect, lampoon targets behavior and ideology, using wit and irony to challenge authority and prompt reflection. This form of satire leverages humor as a powerful tool to criticize and dismantle entrenched power dynamics, amplifying voices of dissent.
Comparing Visual vs. Verbal Satire
Caricatures emphasize exaggerated visual features to highlight flaws or absurdities, making the satire immediately recognizable through imagery. Lampoons rely primarily on verbal wit and written critique, using irony, sarcasm, and humor to convey their message. Both forms serve as powerful tools for social commentary but differ in their reliance on visual distortion versus linguistic sharpness.
Caricature vs Lampoon: Impact on Society
Caricatures exaggerate physical features to create humorous or satirical portraits, often influencing public opinion by highlighting recognizable traits of political figures and celebrities. Lampoons use irony and mockery to severely criticize social institutions or individuals, provoking reflection and sometimes controversy. Both art forms shape societal discourse by challenging authority and encouraging critical thinking through distinct visual and rhetorical strategies.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Caricatures often enjoy broader legal protection under free speech as they are seen as artistic expressions or satire, while lampoons, which can be direct attacks or harsh criticisms, may face defamation claims if false statements harm an individual's reputation. Ethically, caricaturists must balance exaggeration with respect, avoiding offensive stereotypes or misinformation, whereas lampoon creators should ensure their work targets ideas or behaviors rather than personal attributes to maintain moral integrity. Both forms require careful navigation of copyright laws when using original images or content to prevent infringement while preserving freedom of expression.
Choosing Between Caricature and Lampoon
Choosing between caricature and lampoon depends on the intent and tone of the message. Caricature exaggerates physical features or traits for humorous or satirical effect, often highlighting recognizable personality aspects without harsh criticism. Lampoon employs sharp, often biting satire to criticize or ridicule its subject, usually addressing behaviors, politics, or social issues with a more pointed and confrontational approach.
Caricature Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com