Structuralism explores the underlying structures that shape culture, language, and human thought by analyzing relationships within systems. By identifying patterns and binary oppositions, it reveals how meaning is constructed beyond individual elements. Discover how structuralism influences various fields and impacts your understanding of society in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
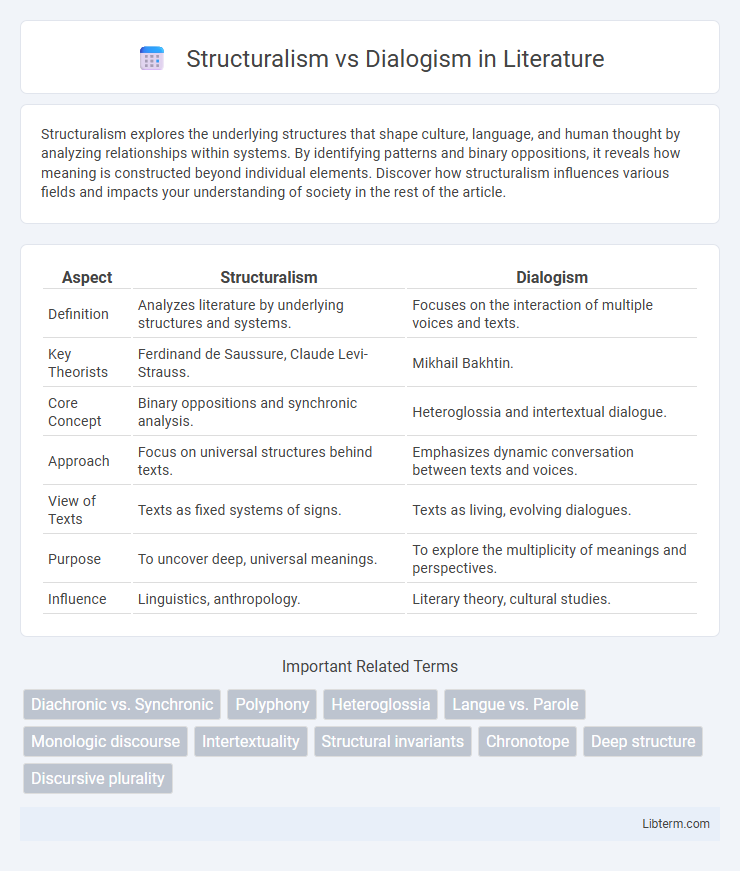
| Aspect | Structuralism | Dialogism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes literature by underlying structures and systems. | Focuses on the interaction of multiple voices and texts. |
| Key Theorists | Ferdinand de Saussure, Claude Levi-Strauss. | Mikhail Bakhtin. |
| Core Concept | Binary oppositions and synchronic analysis. | Heteroglossia and intertextual dialogue. |
| Approach | Focus on universal structures behind texts. | Emphasizes dynamic conversation between texts and voices. |
| View of Texts | Texts as fixed systems of signs. | Texts as living, evolving dialogues. |
| Purpose | To uncover deep, universal meanings. | To explore the multiplicity of meanings and perspectives. |
| Influence | Linguistics, anthropology. | Literary theory, cultural studies. |
Introduction to Structuralism and Dialogism
Structuralism emphasizes the underlying systems and structures that shape language, culture, and thought, focusing on relationships within a fixed framework. Dialogism, rooted in the work of Mikhail Bakhtin, centers on the dynamic and interactive nature of meaning, highlighting the ongoing dialogue between multiple voices and perspectives. These contrasting approaches reveal Structuralism's focus on stable frameworks while Dialogism prioritizes fluid, evolving communication processes.
Historical Background and Origins
Structuralism emerged in the early 20th century, heavily influenced by the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, emphasizing underlying structures in language and culture. Dialogism, rooted in the writings of Russian philosopher Mikhail Bakhtin in the mid-20th century, centers on the interactive and dynamic nature of language, highlighting the ongoing dialogue between voices and perspectives. Both theories grew as reactions to earlier literary and linguistic paradigms, with structuralism focusing on fixed systems and dialogism on fluid, evolving communication.
Key Theorists: Saussure vs. Bakhtin
Ferdinand de Saussure, a foundational figure in Structuralism, emphasized the study of language as a structured system of signs, where meaning arises from the differential relationships between linguistic elements. Contrarily, Mikhail Bakhtin, central to Dialogism, argued that meaning is inherently social and dynamic, shaped through continuous interaction and dialogue between diverse voices and contexts. Saussure's synchronic analysis focuses on language structure at a given time, while Bakhtin highlights the heteroglossia and the evolving nature of meaning through discourse over time.
Core Principles of Structuralism
Structuralism centers on the idea that human culture and language can be understood through underlying structures, such as binary oppositions and deep grammar rules that shape meaning. Core principles include the belief that elements gain significance only in relation to one another within a system, and that these structures operate independently of individual consciousness. This approach contrasts with dialogism, which emphasizes the dynamic, interactive nature of meaning as constantly shaped through dialogue and context.
Fundamental Concepts of Dialogism
Dialogism centers on the fundamental concept that meaning arises from the interaction and interplay of multiple voices, contrasting with Structuralism's focus on underlying, static structures. It emphasizes heteroglossia, or the coexistence of diverse perspectives and languages within a single text, reflecting dynamic social and cultural dialogues. Mikhail Bakhtin's theory of dialogism highlights how texts are polyphonic, involving constant negotiation between competing meanings rather than fixed, universal truths.
Language, Meaning, and Communication
Structuralism analyzes language as a system of signs where meaning arises from the relationships between elements within the structure, emphasizing fixed codes and binary oppositions. Dialogism views language as dynamic and inherently interactive, where meaning emerges through ongoing dialogues shaped by social context and multiple voices. Communication is seen structurally as transmission of stable messages, whereas dialogism highlights negotiation and transformation of meaning in real-time exchanges.
Intertextuality in Structuralism and Dialogism
Structuralism views intertextuality as a system of signs governed by underlying rules and codes that create meaning within a text, emphasizing fixed structures and relationships between texts. Dialogism, developed by Mikhail Bakhtin, perceives intertextuality as dynamic and interactive, where texts engage in ongoing dialogues, incorporating multiple voices and perspectives that challenge singular meanings. The contrast highlights Structuralism's focus on stable patterns, while Dialogism emphasizes fluidity and the creative interplay of diverse textual voices.
Application in Literary Criticism
Structuralism in literary criticism analyzes texts through underlying structures such as language, narrative patterns, and cultural codes, emphasizing the universality of meaning across various texts. Dialogism, as proposed by Mikhail Bakhtin, focuses on the interaction and multiplicity of voices within a text, highlighting the dynamic and context-dependent nature of meaning. Application of structuralism identifies fixed systems within literature, whereas dialogism uncovers heteroglossia and the interplay of diverse perspectives shaping the reader's interpretation.
Structuralism and Dialogism in Contemporary Thought
Structuralism in contemporary thought emphasizes underlying systems and fixed structures that determine meaning and social phenomena, positioning language and culture as interrelated composants of a broader structure. Dialogism challenges this by highlighting the dynamic, interactive, and evolving nature of meaning through multiple voices, emphasizing social context and the interplay of diverse perspectives. This debate influences disciplines such as linguistics, literary theory, and cultural studies by shaping methodologies that oscillate between fixed systems and fluid dialogues.
Conclusion: Comparing Strengths and Limitations
Structuralism offers a clear framework for analyzing underlying systems and patterns within language, culture, and literature, but it often overlooks the fluidity and dynamic nature of meaning. Dialogism emphasizes the interactive, evolving nature of texts and social interactions, highlighting multiple voices and perspectives, yet it may lack the systematic rigor that structuralism provides. Combining both approaches allows deeper understanding by balancing structural stability with interpretive flexibility, though challenges remain in integrating their distinct methodologies.
Structuralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com