Assimilation is the process by which individuals or groups absorb and integrate cultural traits, languages, or behaviors from a dominant society, often leading to a loss of original identity. Understanding assimilation helps reveal how societies evolve and how cultural diversity is maintained or diminished over time. Explore the rest of this article to discover how assimilation impacts your social experiences and cultural connections.
Table of Comparison
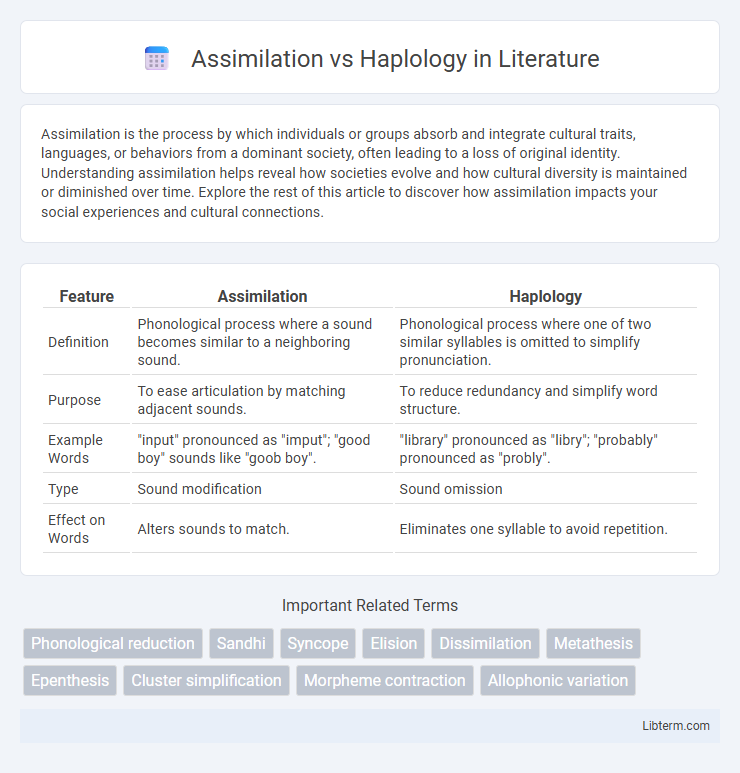
| Feature | Assimilation | Haplology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Phonological process where a sound becomes similar to a neighboring sound. | Phonological process where one of two similar syllables is omitted to simplify pronunciation. |
| Purpose | To ease articulation by matching adjacent sounds. | To reduce redundancy and simplify word structure. |
| Example Words | "input" pronounced as "imput"; "good boy" sounds like "goob boy". | "library" pronounced as "libry"; "probably" pronounced as "probly". |
| Type | Sound modification | Sound omission |
| Effect on Words | Alters sounds to match. | Eliminates one syllable to avoid repetition. |
Introduction to Assimilation and Haplology
Assimilation is a phonological process where a sound changes to become more like a nearby sound, enhancing speech fluency by reducing articulatory effort. Haplology involves the omission of one syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively, streamlining pronunciation in rapid speech. Both processes demonstrate natural tendencies in language evolution to simplify and optimize spoken communication.
Defining Assimilation in Linguistics
Assimilation in linguistics refers to a phonological process where a speech sound becomes similar or identical to a neighboring sound, facilitating smoother and more efficient articulation. This process can occur within words or across word boundaries and often affects consonants, leading to changes in place, manner, or voicing features. Assimilation contrasts with haplology, which involves the omission of one of two similar syllables to simplify pronunciation rather than altering sound features.
Understanding Haplology: A Linguistic Perspective
Haplology is a phonological phenomenon where one of two similar adjacent syllables is omitted to simplify pronunciation, contrasting with assimilation, which modifies sounds to become more alike without deletion. In linguistic analysis, haplology often occurs in rapid or casual speech, exemplified by the reduction of "probably" to "probly." Understanding haplology enhances comprehension of language evolution and phonetic efficiency in spoken communication.
Historical Origins of Assimilation and Haplology
Assimilation, a phonological process where a sound becomes similar to a neighboring sound, traces its historical origins to Proto-Indo-European languages, serving as a natural linguistic evolution to ease pronunciation. Haplology, characterized by the omission of one of two similar adjacent syllables, emerged in the history of English and other Germanic languages as a simplification mechanism in rapid speech. Both processes reflect historical phonetic changes that contribute to language economy and fluency across different linguistic contexts.
Key Differences Between Assimilation and Haplology
Assimilation involves the phonological process where a sound becomes similar to a neighboring sound to ease pronunciation, such as the change of "input" to "imput." Haplology, on the other hand, is the omission of one of two similar syllables occurring consecutively, as in the word "probably" pronounced as "probly." Key differences lie in their mechanisms: assimilation alters sounds to match adjacent ones, whereas haplology removes whole syllables to simplify speech.
Examples of Assimilation in World Languages
Assimilation occurs when a sound changes to become more like a neighboring sound, enhancing phonetic harmony in speech, as seen in English with "input" pronounced as [InpUt] shifting to [ImpUt]. In Spanish, assimilation appears in "submarino" where the [b] sound assimilates to [m] before the bilabial [m], resulting in [summarino]. Japanese demonstrates progressive assimilation in rendaku, where voicing occurs within compound words, such as "te" + "kami" becoming "tegami" (letter).
Illustrative Cases of Haplology in Use
Haplology occurs when a repeated syllable is omitted during speech, such as in the word "library" often pronounced as "libry." English examples like "probably" shortened to "probly" or "February" to "Febuary" illustrate haplology's tendency to simplify phonetic complexity. These cases highlight how natural speech patterns favor efficiency by reducing redundant segments, contrasting with assimilation, which involves sounds changing to become more similar within a word.
Linguistic Significance of Both Phenomena
Assimilation and haplology are crucial phonological processes that enhance speech efficiency by simplifying pronunciation patterns. Assimilation involves the alteration of sounds to become more like adjacent phonemes, facilitating smoother transitions in fluent speech. Haplology reduces complexity by omitting one of two similar or identical syllables, streamlining word forms and contributing to natural language evolution.
Assimilation and Haplology in Language Evolution
Assimilation accelerates language evolution by altering sounds to become more similar within words, enhancing phonetic harmony and speech efficiency across generations. Haplology simplifies pronunciation by omitting repeated syllables, contributing to streamlined word forms and faster verbal communication. Together, assimilation and haplology shape linguistic change by promoting ease of articulation and influencing phonological patterns in evolving languages.
Conclusion: Implications for Linguistic Studies
Assimilation and haplology reveal essential patterns in phonological evolution, influencing language change and variation. Understanding these processes aids linguistic studies in identifying systematic sound alterations and predicting morphological shifts. Their implications extend to historical linguistics, language acquisition, and speech recognition technologies, enhancing both theoretical analysis and practical applications.
Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com