Consonance is a poetic device characterized by the repetition of consonant sounds, often found at the end or middle of words, enhancing the musicality and rhythm of a line. This technique subtly reinforces mood and tone without overwhelming the reader, making it a favorite among poets and writers aiming for lyrical effects. Dive deeper into this article to explore how consonance can enrich your writing and capture your audience's attention.
Table of Comparison
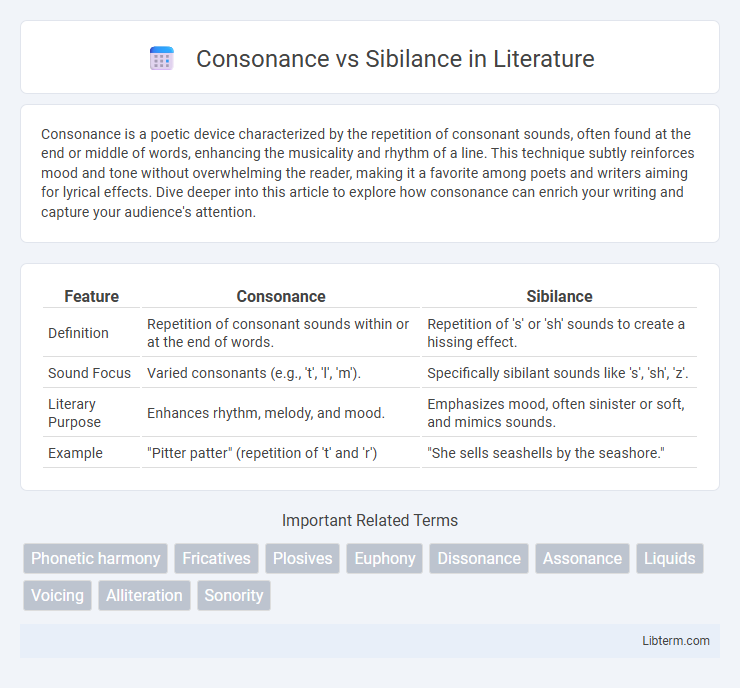
| Feature | Consonance | Sibilance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of consonant sounds within or at the end of words. | Repetition of 's' or 'sh' sounds to create a hissing effect. |
| Sound Focus | Varied consonants (e.g., 't', 'l', 'm'). | Specifically sibilant sounds like 's', 'sh', 'z'. |
| Literary Purpose | Enhances rhythm, melody, and mood. | Emphasizes mood, often sinister or soft, and mimics sounds. |
| Example | "Pitter patter" (repetition of 't' and 'r') | "She sells seashells by the seashore." |
Understanding Consonance: Definition and Characteristics
Consonance is a literary device characterized by the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words, enhancing rhythm and mood within a text. Unlike sibilance, which specifically involves the repetition of hissing "s" sounds, consonance encompasses a broader range of consonant repetitions, such as "t," "k," or "m" sounds. This technique is widely utilized in poetry and prose to create harmony, emphasize particular phrases, and reinforce thematic elements.
Exploring Sibilance: Meaning and Key Features
Sibilance is a specific type of consonance characterized by the repetition of hissing sounds such as "s," "sh," and "ch" within words or phrases, often used to create a whispering or soothing effect in poetry and prose. Key features of sibilance include its ability to evoke auditory imagery that enhances mood, tone, and rhythm, making it a powerful stylistic device in literary and linguistic contexts. This technique frequently appears in tongue twisters, slogans, and poetry to emphasize softness, secrecy, or tension through sound patterns.
Consonance vs Sibilance: Core Differences
Consonance refers to the repetition of consonant sounds anywhere in words, enhancing rhythm and cohesion in poetry or prose, while sibilance specifically involves the repetition of hissing sounds like "s," "sh," or "z," creating a soft or sharp auditory effect. The core difference lies in consonance encompassing a broader range of consonant sounds, whereas sibilance targets only sibilant sounds for emphasis. Understanding this distinction helps writers manipulate sound patterns to evoke mood and tone effectively.
Phonetic Elements: How Consonance and Sibilance Work
Consonance involves the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the beginning or middle of words, creating a harmonious and rhythmic effect in poetry and prose. Sibilance is a specific type of consonance characterized by the repetition of soft hissing sounds like "s," "sh," or "z," enhancing auditory imagery and emphasis. Both phonetic elements manipulate sound patterns to evoke mood and texture, with consonance offering broad sonic unity and sibilance providing sharp, whispering, or soothing effects.
Literary Effects of Consonance
Consonance enhances literary works by creating a harmonious repetition of consonant sounds, which intensifies mood and emphasizes key themes or emotions within the text. This phonetic device fosters a rhythmic cohesion that deepens reader engagement and aids memorability, especially in poetry and prose. Consonance often highlights subtle emotional undercurrents, adding layers of meaning without disrupting the flow of the narrative.
The Impact of Sibilance in Writing
Sibilance enhances writing by creating a hissing or whispering sound, often evoked through repeated "s," "sh," or "z" consonants, which heightens sensory engagement and emotional intensity. This technique can convey moods such as tension, softness, or eeriness, making descriptions more vivid and immersive for readers. Effective use of sibilance sharpens imagery and reinforces thematic elements, contributing to a memorable and impactful literary style.
Examples of Consonance in Literature
Consonance in literature involves the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the middle or end of words, enhancing the musicality and mood of a passage; for example, Edgar Allan Poe's "The Raven" features consonance with the repetition of the "r" sound in "Once upon a midnight dreary, while I pondered, weak and weary." Unlike sibilance, which specifically emphasizes hissing sounds like "s" and "sh," consonance encompasses a broader range of consonant repetitions, such as the "l" sounds in Samuel Taylor Coleridge's "The Rime of the Ancient Mariner" with "Lonely as a cloud." This stylistic device enriches the text's auditory appeal and helps establish rhythm and emphasis in poetry and prose.
Sibilance in Poetry and Prose: Notable Instances
Sibilance, characterized by the repetition of soft 's' or 'sh' sounds, creates a soothing or sinister atmosphere in poetry and prose, enhancing mood and rhythm. Notable instances include Edgar Allan Poe's "The Raven," where sibilance intensifies the eerie tone, and Sylvia Plath's works, where it underscores emotional tension. This sound device subtly influences the reader's experience by emphasizing particular words and evoking sensory responses through auditory imagery.
Practical Tips: Using Consonance and Sibilance Effectively
Consonance enhances rhythm and unity by repeating consonant sounds, making phrases more memorable and reinforcing key ideas in poetry or prose. Sibilance, characterized by the repetition of hissing sounds like "s" and "sh," creates a soothing or sinister tone depending on context, ideal for evoking emotion or mood. Use consonance to build cohesion and emphasis, while applying sibilance selectively to intensify atmosphere without overwhelming the reader.
Common Misconceptions about Consonance and Sibilance
Consonance and sibilance are often confused, but consonance refers to the repetition of consonant sounds anywhere in words, while sibilance specifically involves the hissing sounds of "s," "sh," and "z." A common misconception is that all sibilance is consonance, yet sibilance is a subset characterized by its distinct sharp or hissing effect. Understanding these differences clarifies their unique roles in poetry and prose sound patterns.
Consonance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com