Apocope is the linguistic process where the final sound or syllable of a word is omitted, often to create a more casual or poetic effect. This morphological phenomenon can be observed in many languages and frequently affects verbs, nouns, and adjectives, enhancing speech efficiency and fluidity. Discover how apocope shapes language and influences everyday communication in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
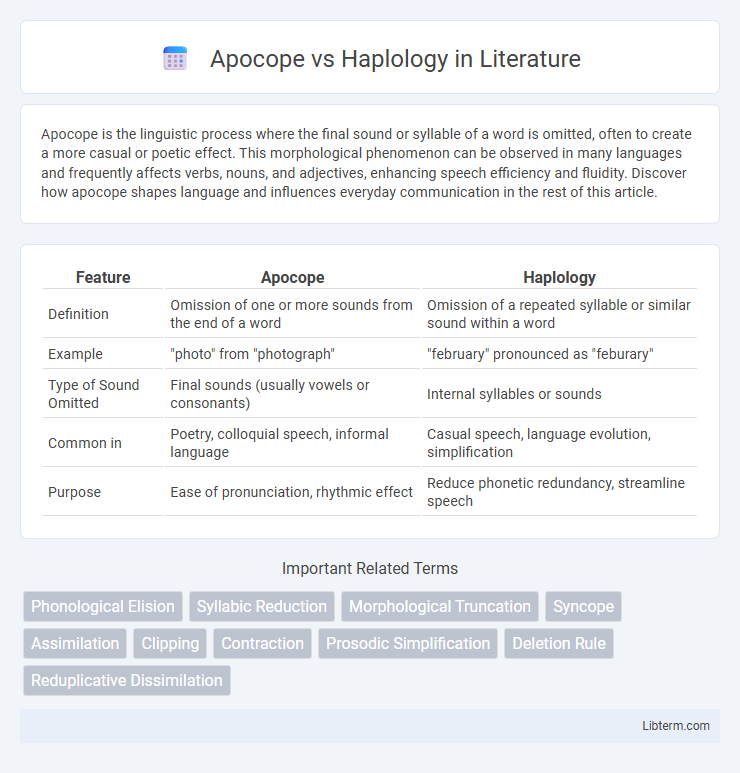
| Feature | Apocope | Haplology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of one or more sounds from the end of a word | Omission of a repeated syllable or similar sound within a word |
| Example | "photo" from "photograph" | "february" pronounced as "feburary" |
| Type of Sound Omitted | Final sounds (usually vowels or consonants) | Internal syllables or sounds |
| Common in | Poetry, colloquial speech, informal language | Casual speech, language evolution, simplification |
| Purpose | Ease of pronunciation, rhythmic effect | Reduce phonetic redundancy, streamline speech |
Introduction to Apocope and Haplology
Apocope is the phonological process where the final sound or syllable of a word is omitted, often observed in casual speech and various language evolutions. Haplology refers to the omission of one of two similar adjacent syllables within a word, streamlining pronunciation and enhancing linguistic efficiency. Both phenomena illustrate common patterns of sound simplification that influence language development and morphology.
Defining Apocope: Meaning and Examples
Apocope is the linguistic phenomenon involving the omission of one or more sounds or syllables at the end of a word, commonly seen in informal speech and poetry. Examples include "info" from "information" and "photo" from "photograph," illustrating how apocope simplifies pronunciation while retaining meaning. This process contrasts with haplology, which involves the deletion of a repeated syllable within a word rather than at its end.
Understanding Haplology: Definition and Instances
Haplology is a linguistic phenomenon where a repeated syllable or similar sounds in a word are omitted to simplify pronunciation, such as "probly" for "probably." It differs from apocope, which involves the omission of sounds or syllables specifically at the end of a word, like "info" derived from "information." Understanding haplology helps in analyzing language evolution, phonetic simplifications, and colloquial speech patterns.
Key Differences Between Apocope and Haplology
Apocope involves the omission of one or more sounds or syllables at the end of a word, commonly seen in casual speech or poetic forms, such as "info" from "information." Haplology differs by the deletion of a repeated or similar syllable within a word, exemplified by "probly" from "probably." Key differences lie in their positional impact within a word: apocope removes endings, while haplology simplifies internal duplication.
Linguistic Significance of Apocope
Apocope, the phonological process involving the loss of a sound or syllable at the end of a word, plays a critical role in linguistic evolution and morphological simplification. It facilitates smoother articulation and can signal language change, often reflecting patterns of stress and rhythm within a language. This phenomenon contrasts with haplology, which involves the omission of a syllable in the middle of a word, highlighting different mechanisms of phonological reduction in natural speech.
Linguistic Impact of Haplology
Haplology, the omission of a syllable when two similar syllables occur in sequence, significantly influences linguistic evolution by streamlining complex word forms for easier pronunciation and faster communication. Unlike apocope, which involves the loss of sounds at the end of words, haplology affects internal word structure, often leading to permanent morphological changes and affecting language rhythm and fluency. This phonological simplification shapes language acquisition, dialect formation, and lexical innovation, highlighting haplology's role in dynamic linguistic adaptation.
Historical Development of Apocope and Haplology
Apocope, the historical loss of word-final sounds, originated prominently in Latin and evolved through Romance languages, shaping noun and verb endings by dropping unstressed vowels or consonants. Haplology, the omission of a syllable when two similar syllables appear sequentially, emerged as a phonological process in the evolution of languages like Old English and Greek, streamlining pronunciation and word forms. Both processes reflect natural tendencies in language change driven by ease of articulation and accelerated speech patterns over centuries.
Apocope and Haplology in English Language
Apocope in English involves the omission of one or more sounds or syllables at the end of a word, such as "photograph" shortened to "photo." Haplology occurs when a word reduces repeated syllables for ease of pronunciation, exemplified by "probably" becoming "probly." Both processes reflect natural tendencies in English language evolution to simplify speech patterns.
Comparison of Usage Across Languages
Apocope and haplology exhibit distinct patterns of usage across languages, with apocope commonly appearing in Romance languages such as Spanish and Italian where final vowel or consonant sounds are frequently dropped to streamline speech. Haplology, the process of omitting one of two similar adjacent syllables, is prevalent in Germanic languages like English and German, often simplifying word forms for ease of pronunciation. The comparative linguistic analysis reveals that while both phenomena contribute to phonological economy, apocope tends to affect word endings whereas haplology alters internal syllabic structure.
Conclusion: Apocope vs Haplology
Apocope involves the loss of one or more sounds from the end of a word, commonly found in casual or rapid speech, whereas haplology is the omission of a syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively within a word. Both processes simplify pronunciation but target different segments of words--apocope affects word endings while haplology occurs within words. Understanding the distinction clarifies phonological patterns and aids in interpreting language evolution and dialectal variations.
Apocope Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com