An elegy is a mournful poem or song expressing sorrow for someone who has passed away, often reflecting on loss and remembrance. It captures deep emotions and provides solace by honoring the memory of the deceased through carefully chosen language and imagery. Discover more about how elegies shape our understanding of grief and healing in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
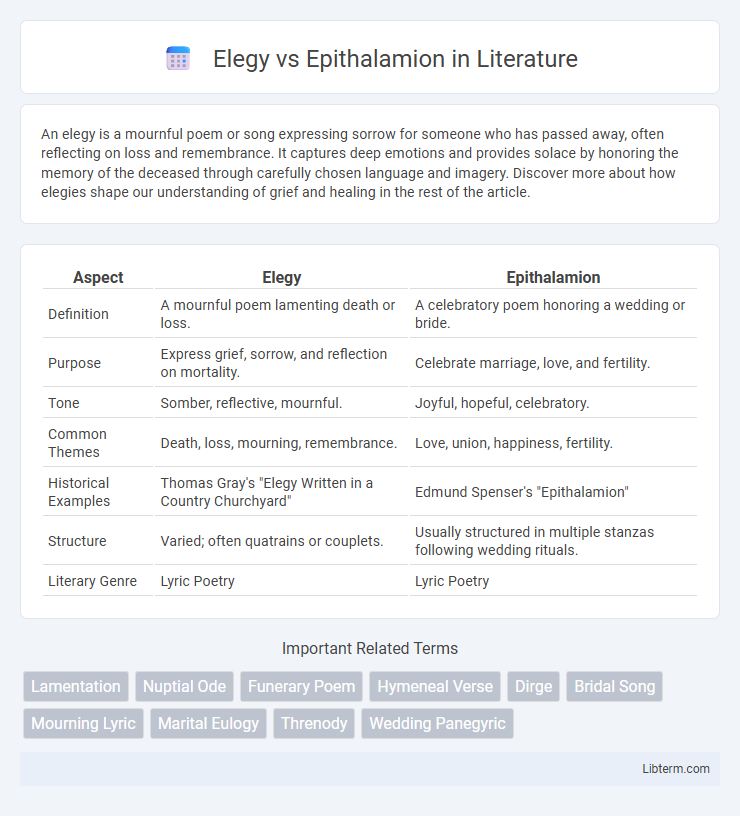
| Aspect | Elegy | Epithalamion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mournful poem lamenting death or loss. | A celebratory poem honoring a wedding or bride. |
| Purpose | Express grief, sorrow, and reflection on mortality. | Celebrate marriage, love, and fertility. |
| Tone | Somber, reflective, mournful. | Joyful, hopeful, celebratory. |
| Common Themes | Death, loss, mourning, remembrance. | Love, union, happiness, fertility. |
| Historical Examples | Thomas Gray's "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard" | Edmund Spenser's "Epithalamion" |
| Structure | Varied; often quatrains or couplets. | Usually structured in multiple stanzas following wedding rituals. |
| Literary Genre | Lyric Poetry | Lyric Poetry |
Introduction to Elegy and Epithalamion
Elegy, a poetic form rooted in ancient Greek tradition, typically conveys themes of mourning, loss, and reflection on death or sorrow. Epithalamion, originating from classical antiquity, is a poetic hymn celebrating marriage, often praising the bride and groom and invoking blessings for their union. Both forms serve distinct ceremonial purposes: elegy memorializes and consoles, while epithalamion exalts love and nuptial joy.
Defining Elegy: Themes and Purpose
Elegy is a poetic form traditionally centered on themes of mourning, loss, and reflection, often commemorating the deceased or expressing deep sorrow. Its purpose is to convey grief and provide solace through a contemplative tone, frequently addressing themes like death, fate, and the transient nature of life. Unlike epithalamion, which celebrates marriage, elegies emphasize melancholy and remembrance, making them pivotal in exploring human mortality and emotional depth.
Understanding Epithalamion: Themes and Purpose
Epithalamion, a poetic genre rooted in ancient Greek tradition, centers on themes of marriage, love, and celebration, often composed to honor a bride and groom on their wedding day. Unlike elegies, which typically express mourning or lamentation, epithalamia emphasize joy, hope, and the auspicious beginning of married life, highlighting communal blessings and the sanctity of union. This genre serves both a ceremonial purpose and a literary one, capturing cultural values around matrimony and reinforcing social bonds through its vivid, optimistic imagery.
Historical Origins of Elegy and Epithalamion
Elegies originated in ancient Greece as poetic expressions of mourning and lamentation, often performed with a musical accompaniment to convey deep sorrow. Epithalamia trace back to classical antiquity, specifically linked to wedding celebrations in ancient Rome and Greece, where they functioned as joyous hymns honoring the bride and groom. Both forms evolved through classical literature, with elegies emphasizing themes of loss and reflection, while epithalamia celebrated nuptial union and fertility.
Structural Differences Between Elegy and Epithalamion
Elegy traditionally follows a mournful and contemplative structure, often composed of quatrains or couplets with a steady meter that emphasizes loss or reflection. Epithalamion, by contrast, features a celebratory and lyrical format with a more varied stanza arrangement designed to honor marriage and joy. The structural shift from elegy's somber rhythm to epithalamion's lively, episodic verses underlines their distinct emotional and thematic purposes.
Emotional Tone: Mourning vs Celebration
Elegies convey a somber and reflective emotional tone centered on mourning loss, grief, and sorrow, often invoking a sense of melancholy and remembrance. In contrast, epithalamions express joyous celebration, commonly used in weddings to honor love, happiness, and the union of two people, evoking festive and uplifting emotions. The stark contrast between elegy's solemn lamentation and epithalamion's exuberant praise highlights the distinct purposes and moods within these poetic forms.
Famous Examples in Literary Tradition
Elegies, such as John Milton's "Lycidas" and W.H. Auden's "Musee des Beaux Arts," traditionally mourn loss and reflect on death, emphasizing themes of grief and remembrance. Epithalamions, exemplified by Edmund Spenser's "Epithalamion" and Catullus' "Carmen 61," celebrate marriage and joyous union, often featuring vivid imagery of love and nuptial celebration. These genres highlight contrasting literary functions: elegies as solemn tributes to the departed and epithalamions as festive odes to matrimonial bonds.
Cultural Contexts and Symbolism
Elegies traditionally serve as solemn poetic laments for the deceased, deeply rooted in mourning rituals across various cultures, symbolizing loss and reflection on mortality. Epithalamions, by contrast, celebrate marriage and union, often invoking divine blessings and fertility symbols within cultural wedding ceremonies. Both forms use rich symbolic language to reinforce societal values: elegies emphasize grief and remembrance, while epithalamions highlight joy, prosperity, and the continuity of life.
Influence on Modern Poetry
Elegy and epithalamion distinctly influence modern poetry through their thematic and structural elements; elegies shape contemporary expressions of grief and loss, often adopting a reflective and somber tone, while epithalamions contribute to celebratory and romantic verse forms centered on marriage and union. Modern poets integrate elegiac motifs to explore personal and collective trauma, enhancing emotional depth and resonant imagery. Epithalamion's revival in modern poetry underscores the enduring tradition of lyrical celebration, blending classical elegance with contemporary cultural contexts.
Comparing the Lasting Impact of Elegy and Epithalamion
Elegies have a lasting impact through their profound exploration of grief, loss, and mortality, resonating deeply across cultures and historical periods due to their universal themes. Epithalamions, by celebrating marriage and romantic union, influence cultural traditions and ceremonies, embedding themselves within social rituals and promoting ideals of love and fidelity. The enduring relevance of elegies is often seen in their adaptation in modern literature and memorial practices, while epithalamions persist primarily within the context of weddings and communal celebrations.
Elegy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com