Satire employs humor, irony, and exaggeration to critique social, political, or cultural issues, often revealing underlying truths and prompting reflection. This literary technique challenges norms and exposes hypocrisy by using wit to engage and entertain readers. Explore the rest of the article to discover how satire shapes perspectives and influences societal change.
Table of Comparison
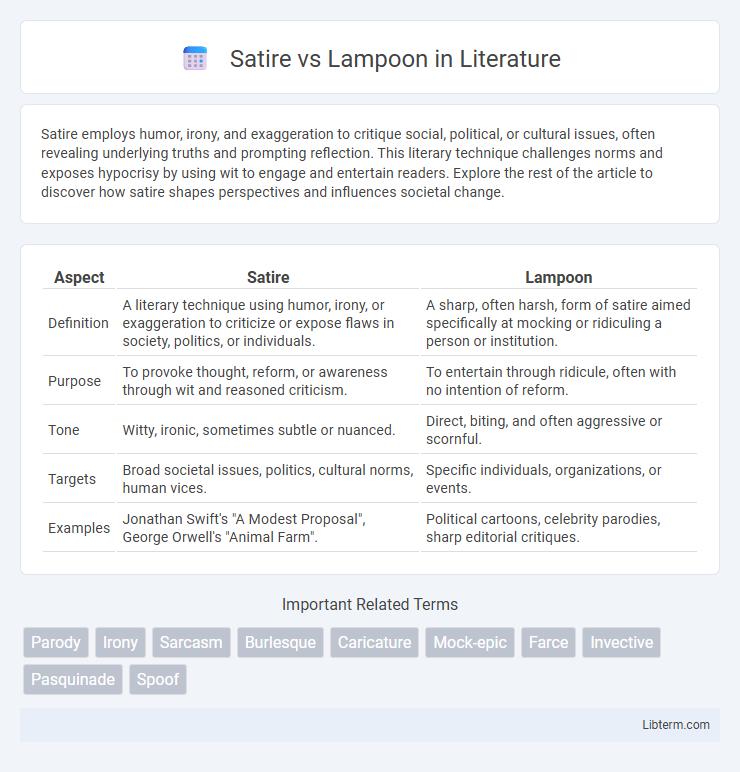
| Aspect | Satire | Lampoon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A literary technique using humor, irony, or exaggeration to criticize or expose flaws in society, politics, or individuals. | A sharp, often harsh, form of satire aimed specifically at mocking or ridiculing a person or institution. |
| Purpose | To provoke thought, reform, or awareness through wit and reasoned criticism. | To entertain through ridicule, often with no intention of reform. |
| Tone | Witty, ironic, sometimes subtle or nuanced. | Direct, biting, and often aggressive or scornful. |
| Targets | Broad societal issues, politics, cultural norms, human vices. | Specific individuals, organizations, or events. |
| Examples | Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal", George Orwell's "Animal Farm". | Political cartoons, celebrity parodies, sharp editorial critiques. |
Understanding Satire: Definition and Origins
Satire is a literary technique that uses humor, irony, and exaggeration to criticize and expose human vices or societal issues, often aiming to provoke thought and reform. Originating in ancient Rome with works like those of Horace and Juvenal, satire blends wit and moral commentary to engage audiences in reflection on political, social, and cultural shortcomings. Understanding satire involves recognizing its nuanced intent to entertain while encouraging critical awareness and change.
What is a Lampoon? Key Characteristics
A lampoon is a sharp, often harsh form of satire aimed at ridiculing an individual, group, or institution through exaggerated mockery and humor. Key characteristics include direct personal attacks, biting sarcasm, and a focus on exposing flaws or absurdities with the intent to humiliate rather than just entertain. Lampoons are typically concise, pointed, and aimed at provoking a strong reaction or criticism.
Historical Evolution of Satire and Lampoon
Satire has evolved since ancient times, originating with Greek playwrights like Aristophanes who used humor and irony to criticize societal flaws and political corruption. Lampoon emerged in the 17th century as a sharper, more direct form of satire often found in printed media and caricatures targeting specific individuals or institutions. Both genres have significantly influenced literary and cultural criticism by adapting to changing social contexts while maintaining their core purpose of exposing folly and vice through wit.
Core Differences: Satire vs Lampoon
Satire employs humor, irony, and exaggeration to expose and criticize societal flaws or human vices, often aiming for constructive change. Lampoon specifically targets individuals or institutions with sharp, mocking ridicule intended to demean or discredit. While satire seeks broader social commentary, lampoon narrows its focus to personalized, biting attacks.
Purpose and Intent: Satirical Works
Satirical works aim to expose societal flaws and human vices through humor, irony, and exaggeration, encouraging reflection and reform. Their purpose is to provoke thought and highlight issues without necessarily attacking specific individuals, promoting broader social awareness. Lampoons, by contrast, target particular people or entities with sharp ridicule and personal criticism, often intended to humiliate.
The Target of Lampooning: Individuals or Institutions
Lampoon targets individuals or institutions with sharp, often humorous criticism, aiming to expose flaws or absurdities through exaggerated mockery. Unlike general satire, which critiques broader societal issues or human behavior, lampoon zeroes in on specific public figures, political entities, or organizations as primary subjects. Its focus on identifiable targets intensifies the personal nature of the ridicule, making lampoon a potent tool for social and political commentary.
Techniques Used in Satire and Lampoon
Satire employs irony, exaggeration, and parody to expose societal flaws and provoke thought, often using humor to underline its critique. Lampoon focuses on sharp, direct ridicule through sarcasm and mockery, targeting specific individuals or groups with scathing humor to invoke public embarrassment. Both techniques leverage wit, but satire adopts a broader, more indirect approach while lampoon delivers concise, pointed attacks.
Impact on Society and Public Perception
Satire uses humor, irony, and exaggeration to challenge societal norms and provoke critical thinking, fostering social reform by encouraging reflection on human flaws and institutional shortcomings. Lampoon delivers sharp, often personal attacks through ridicule, shaping public perception by exposing and undermining specific individuals or entities. Both forms influence society by promoting awareness, yet satire tends to inspire constructive dialogue while lampoon can polarize audiences through its biting tone.
Famous Examples: Satire vs Lampoon
Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal" exemplifies satire by using irony to criticize social issues, while "The Onion" lampoons current events through exaggerated parody. Mark Twain's works often employ satire to highlight human follies, contrasting with Mad Magazine's lampoon-style humorous imitations of popular culture. These examples distinguish satire's broader social critique from lampoon's sharp, targeted ridicule.
Choosing the Right Approach: Satire or Lampoon
Choosing the right approach between satire and lampoon depends on the target's sensitivity and the message's intent, as satire uses humor and irony to provoke thought and promote change, while lampoon employs sharp ridicule to expose and mock flaws directly. Satire often maintains a subtle tone that encourages reflection, whereas lampoon delivers exaggerated criticism to shock or entertain. Understanding the audience's tolerance and the desired impact ensures the effectiveness of either method in social or political commentary.
Satire Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com