Exemplar companies set the standard for excellence by consistently achieving outstanding results and driving innovation in their industries. Their commitment to quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement creates benchmarks that others strive to reach. Discover how you can apply these principles to elevate your own business performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
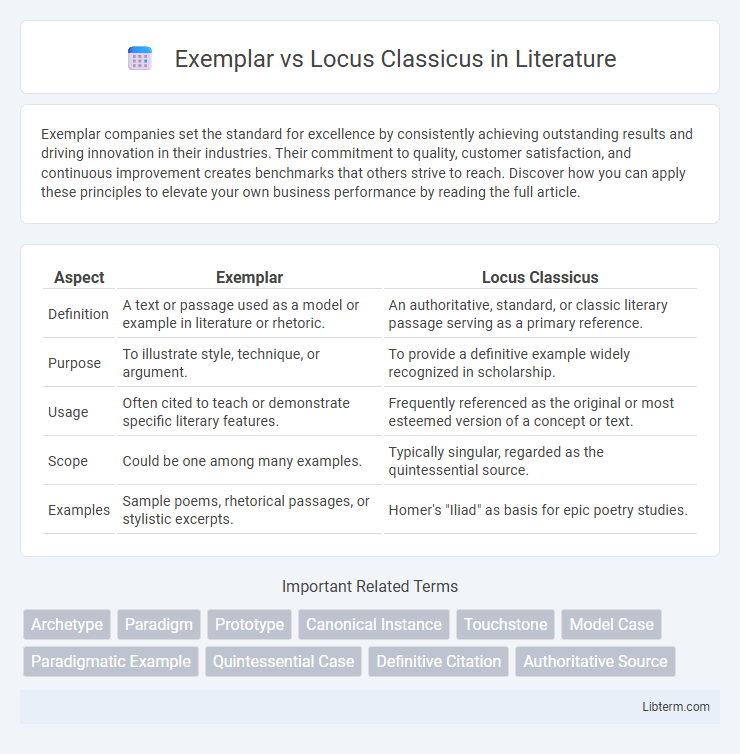
| Aspect | Exemplar | Locus Classicus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A text or passage used as a model or example in literature or rhetoric. | An authoritative, standard, or classic literary passage serving as a primary reference. |
| Purpose | To illustrate style, technique, or argument. | To provide a definitive example widely recognized in scholarship. |
| Usage | Often cited to teach or demonstrate specific literary features. | Frequently referenced as the original or most esteemed version of a concept or text. |
| Scope | Could be one among many examples. | Typically singular, regarded as the quintessential source. |
| Examples | Sample poems, rhetorical passages, or stylistic excerpts. | Homer's "Iliad" as basis for epic poetry studies. |
Introduction to Exemplar and Locus Classicus
Exemplar refers to a specific, often ideal example used to explain a concept or serve as a model in literature and rhetoric. Locus classicus denotes the original or most authoritative source or passage that exemplifies a particular idea, frequently cited to support arguments. Both terms highlight reference points in textual analysis, with exemplars illustrating concepts and locus classicus acting as definitive citations.
Defining Exemplar in Literary and Academic Contexts
Exemplar in literary and academic contexts serves as a model or standard text that illustrates ideal qualities or thematic elements for analysis and comparison. It functions as an authoritative reference that guides interpretation, supporting scholarly arguments and textual criticism. Unlike locus classicus, which identifies the original or most notable instance of a concept or phrase, exemplar emphasizes the role of a text as a pedagogical or exemplary benchmark.
Understanding Locus Classicus: Meaning and Origins
Locus classicus refers to a passage or text considered the definitive example of a particular idea or concept in classical literature, serving as the authoritative reference point for scholars and interpreters. Originating from Latin meaning "classical place," the term emphasizes the text's role as a foundational source often cited to illustrate or support specific arguments. Understanding locus classicus involves recognizing its function in maintaining textual authority and guiding interpretative frameworks within academic disciplines.
Key Differences Between Exemplar and Locus Classicus
Exemplar refers to a specific instance or model used for comparison or illustration, often serving as a representative example in research or analysis. Locus classicus, on the other hand, denotes the authoritative or standard reference point in literature or scholarly work that is widely recognized as the original or most reliable source. The key differences lie in their usage: exemplars function as practical illustrations or case studies, whereas locus classicus embodies the definitive citation establishing a concept or principle.
Historical Evolution of Both Terms
Exemplar originated in Latin, initially meaning a model or pattern to be imitated, evolving through Renaissance humanism as a key concept in rhetoric and education. Locus classicus, also derived from Latin, traditionally refers to a "classical passage" or authoritative example in ancient texts, establishing a standard reference over time in scholarly discourse. The historical evolution of both terms highlights their roles in shaping interpretative benchmarks within literary criticism and pedagogical methods.
Usage of Exemplar in Research and Literature
Exemplar serves as a key reference point in research and literature by providing concrete examples that illustrate theoretical concepts or support arguments, often enhancing the clarity and persuasiveness of scholarly work. Unlike locus classicus, which denotes a single authoritative source, exemplars function as representative models drawn from varied contexts to demonstrate broader principles or patterns. Their use enables researchers to connect abstract ideas with tangible instances, facilitating deeper understanding and comparative analysis across disciplines.
Role of Locus Classicus in Argumentation and Citation
Locus classicus serves as a foundational reference point in argumentation, providing authoritative evidence that strengthens claims by invoking well-established examples or texts. It functions as a benchmark citation, often used to validate arguments through widely recognized and historically accepted sources. This role enhances the persuasiveness and credibility of discourse by connecting contemporary arguments to seminal works or original instances.
Examples Illustrating Exemplar vs Locus Classicus
Exemplar refers to a typical or ideal example that serves as a model for understanding a concept, such as the raven in discussions of black birds representing an exemplar of the category. Locus classicus, on the other hand, denotes a classical or authoritative passage in literature or scholarship that is the primary source or citation for a particular idea, like Aristotle's *Poetics* serving as the locus classicus for tragedy in Western literary theory. Examples illustrating the difference include using a well-known novel as an exemplar of realism versus citing Aristotle's original text as the locus classicus for defining tragic elements.
Common Misconceptions and Overlaps
Exemplar and locus classicus often overlap as both serve as authoritative references, but exemplars represent typical or ideal examples while locus classicus denotes the original or most influential source of a concept. A common misconception is treating them interchangeably, ignoring that exemplars highlight prototypical instances across contexts whereas locus classicus anchors meaning to a specific foundational text or usage. Understanding this distinction clarifies debates in semantics, legal citations, and literary studies where precise reference versus model representation matters.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Term
Selecting between exemplar and locus classicus depends on context and clarity; an exemplar highlights a typical, illustrative example, whereas a locus classicus refers to an authoritative, original source. For precise academic or legal references, locus classicus is preferred to emphasize foundational texts. Exemplar suits broader usage when illustrating concepts without implying canonical authority.
Exemplar Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com