Enhance your home's curb appeal and market value by choosing the perfect exterior paint color that complements your architectural style and surroundings. Consider factors such as lighting, climate, and neighborhood trends to ensure your selection not only beautifies but also protects your property effectively. Explore the full article to discover expert tips and color palettes tailored to transform Your home's exterior with lasting impact.
Table of Comparison
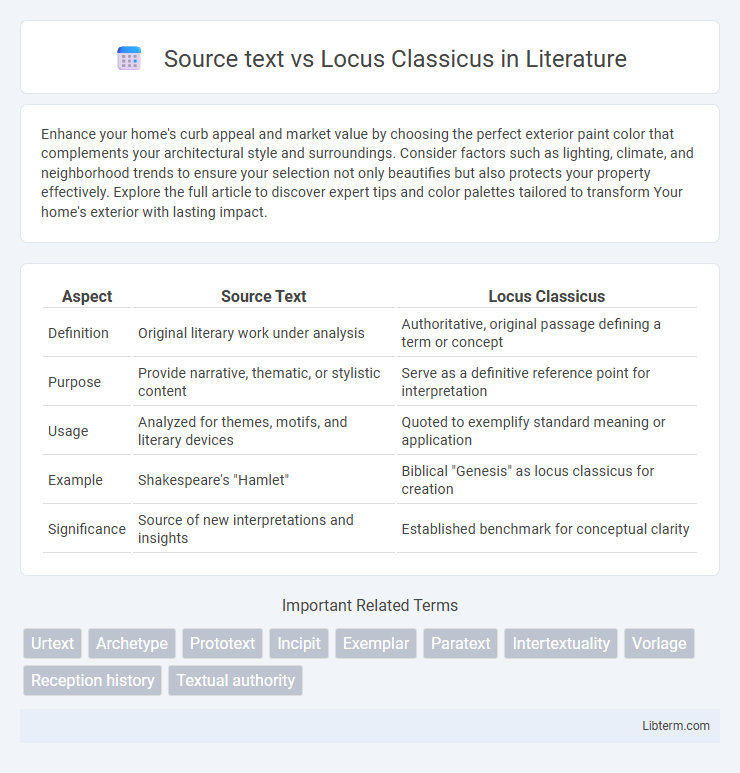
| Aspect | Source Text | Locus Classicus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Original literary work under analysis | Authoritative, original passage defining a term or concept |
| Purpose | Provide narrative, thematic, or stylistic content | Serve as a definitive reference point for interpretation |
| Usage | Analyzed for themes, motifs, and literary devices | Quoted to exemplify standard meaning or application |
| Example | Shakespeare's "Hamlet" | Biblical "Genesis" as locus classicus for creation |
| Significance | Source of new interpretations and insights | Established benchmark for conceptual clarity |
Understanding Source Text: Definition and Importance
Understanding the source text is essential for accurate interpretation and analysis of classical works, as it represents the original material from which knowledge or references are derived. A source text provides the foundational content, ensuring fidelity to the author's intent and preventing misrepresentation in secondary interpretations. Recognizing the difference between source text and locus classicus allows scholars to trace ideas back to their authentic origins while appreciating the authoritative passages that exemplify key concepts.
Locus Classicus: Meaning and Historical Context
Locus classicus refers to an authoritative or standard passage in classical literature that serves as a definitive reference for a particular concept, phrase, or argument. Originating from Latin, its historical context lies in ancient Roman and Greek texts where scholars and rhetoricians identified key excerpts to illustrate or support scholarly discourse. This concept remains pivotal in literary analysis, helping scholars anchor modern interpretations to foundational classical sources.
Differences Between Source Text and Locus Classicus
A source text is the original document or manuscript from which information is derived, while a locus classicus refers to a specific, authoritative passage or citation within classical literature that serves as a definitive example or reference point. The source text encompasses the entire work, providing broader context, whereas the locus classicus is a pinpointed excerpt often cited for its exemplary or foundational significance. Understanding the differences enhances textual analysis by distinguishing between comprehensive content and key authoritative references.
Role of Source Text in Academic Research
The source text serves as the original material from which scholars extract primary information, ensuring the authenticity and accuracy of academic research. In contrast, the locus classicus functions as the authoritative reference point, often cited to validate theories or arguments. Relying on the source text allows researchers to engage directly with foundational data, fostering critical analysis and preventing misinterpretation prevalent in secondary citations.
Significance of Locus Classicus in Literature
Locus classicus refers to the most authoritative and often-cited passage in classical literature that establishes the original meaning or usage of a concept, serving as a foundational reference for scholars and critics. Its significance in literature lies in providing a definitive textual source that anchors interpretation, ensuring that subsequent analyses remain grounded in the authentic context of the work. By contrast, a source text may encompass any original material, but the locus classicus holds unique prestige as the benchmark for textual authenticity and critical study.
Examples of Source Texts Across Disciplines
Source texts serve as foundational documents or original works that provide primary evidence across disciplines, such as ancient manuscripts in history, seminal research articles in science, or original case law in legal studies. Locus classicus refers to a definitive, authoritative passage within a source text, exemplified by Darwin's "On the Origin of Species" in biology or Plato's "Republic" in philosophy. Examples of source texts include Shakespeare's plays in literature, Newton's "Principia Mathematica" in physics, and the Dead Sea Scrolls in religious studies.
Notable Loci Classici in Classic and Modern Works
Notable loci classici serve as definitive reference points in both classic and modern literary and scholarly works, anchoring key themes and arguments within a recognized authoritative context. These exemplary passages often function as source texts, providing foundational evidence or exemplars that shape subsequent interpretations in fields such as philosophy, literature, and law. Recognition of loci classici enhances understanding by linking contemporary discourse with time-tested textual authorities, ensuring continuity and depth in academic inquiry.
Source Text vs. Locus Classicus: Common Misconceptions
Source text and locus classicus are often misunderstood as synonymous, yet they hold distinct roles in literary and scholarly studies. A source text refers to the original document or material from which information is derived, while a locus classicus denotes a canonical passage widely recognized for exemplifying a particular idea or phrase. Misconceptions arise when locus classicus passages are mistaken as the sole source text, overlooking broader original contexts and diverse textual origins.
How to Identify a Source Text and a Locus Classicus
A source text can be identified by its original authorship and status as the earliest or primary document from which later works derive, often featuring firsthand accounts or foundational ideas. A locus classicus is recognized as the definitive or most authoritative passage within a text that exemplifies a concept, typically cited repeatedly in scholarly literature. Distinguishing between the two involves assessing the source text's originality and the locus classicus's emblematic significance within interpretative traditions.
The Impact of Accurate Attribution on Scholarship
Accurate attribution in scholarship hinges on distinguishing source texts from loci classici, as source texts provide original content while loci classici serve as authoritative references shaping interpretation and transmission. Precision in identifying a locus classicus enhances the reliability and credibility of academic arguments by anchoring claims to widely recognized foundational evidence. Misattribution can lead to scholarly misunderstandings, affecting the integrity of research and the evolution of knowledge within a discipline.
Source text Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com