Diglossic situations occur when two dialects or languages are used by a community under different circumstances, often with one regarded as more prestigious. Understanding the dynamics of diglossia can shed light on language evolution, identity, and social structure within a culture. Explore this article to delve deeper into how diglossic patterns influence communication and society.
Table of Comparison
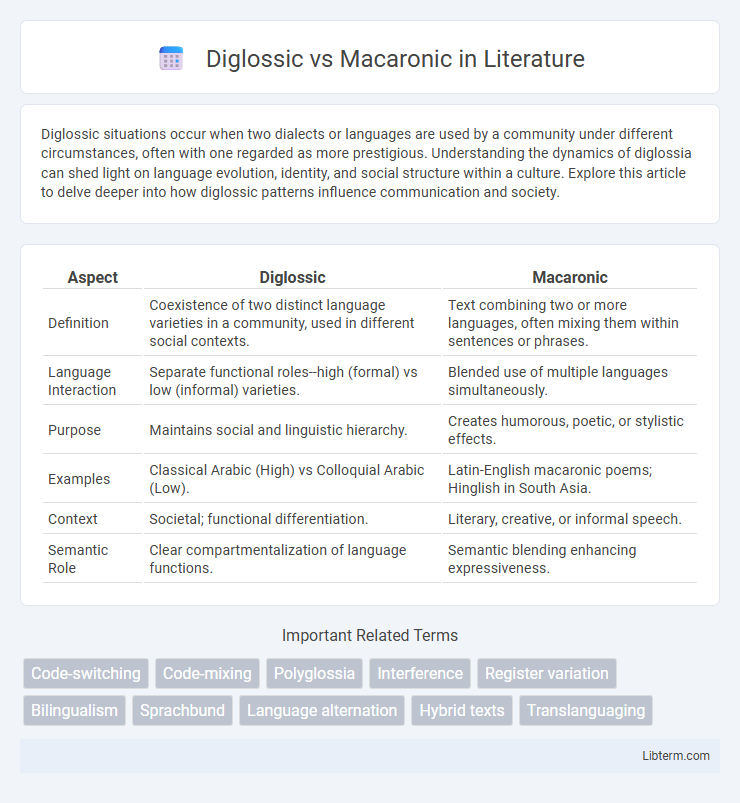
| Aspect | Diglossic | Macaronic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of two distinct language varieties in a community, used in different social contexts. | Text combining two or more languages, often mixing them within sentences or phrases. |
| Language Interaction | Separate functional roles--high (formal) vs low (informal) varieties. | Blended use of multiple languages simultaneously. |
| Purpose | Maintains social and linguistic hierarchy. | Creates humorous, poetic, or stylistic effects. |
| Examples | Classical Arabic (High) vs Colloquial Arabic (Low). | Latin-English macaronic poems; Hinglish in South Asia. |
| Context | Societal; functional differentiation. | Literary, creative, or informal speech. |
| Semantic Role | Clear compartmentalization of language functions. | Semantic blending enhancing expressiveness. |
Introduction to Diglossic and Macaronic Language
Diglossic language situations involve the use of two distinct varieties of the same language, typically a high (formal) and a low (informal) variety, coexisting within a community for different social functions. Macaronic language, on the other hand, blends elements from two or more languages within a single utterance or text, often mixing words and grammatical structures. Understanding diglossia highlights linguistic function and social context, while macaronic language emphasizes linguistic mixing and hybridity.
Defining Diglossia: Key Features
Diglossia is a linguistic situation where two distinct varieties of the same language coexist within a community, each serving specific social functions. The "high" variety is used in formal settings such as literature, education, and official communication, while the "low" variety appears in everyday conversation and informal contexts. This functional compartmentalization distinguishes diglossia from macaronic language use, which blends languages or dialects within the same discourse.
Understanding Macaronic Language
Macaronic language blends elements from two or more languages within the same text or speech, often mixing vocabulary, grammar, and syntax to create a hybrid form. This linguistic phenomenon commonly appears in literature, music, and informal conversation, serving as a playful or expressive tool that reflects bilingual or multilingual communities. Unlike diglossia, where distinct languages have separate social functions, macaronic language operates within single communicative acts.
Historical Development of Diglossic Societies
Diglossic societies historically emerged in regions where distinct language varieties coexisted with defined social functions, such as Classical Arabic alongside colloquial dialects in the Arab world dating back to the early Islamic period. This structured linguistic hierarchy evolved to manage administrative, religious, and everyday communication, maintaining high (formal) and low (vernacular) language forms. Over centuries, diglossia shaped literary traditions and social identity, distinguishing formal education and official discourse from colloquial interactions.
Origins and Uses of Macaronic Texts
Macaronic texts originated in medieval Europe as a linguistic blend of Latin with vernacular languages, primarily used by scholars and poets to parody classical forms or to create humorous, satirical content. These texts combine elements from different languages within a single work, enabling rich cultural interplay and reflecting social dynamics of bilingual or multilingual communities. Unlike diglossia, which involves functional language variation in society, macaronic language deliberately mixes languages within sentences or phrases for artistic effect.
Sociolinguistic Impact of Diglossia
Diglossia significantly influences social identity and group cohesion by reinforcing language hierarchies and functional differentiation between high (formal) and low (informal) varieties. This sociolinguistic phenomenon often leads to restricted access to education and socioeconomic mobility for speakers of the low variety, perpetuating social stratification. Unlike macaronic language mixing, diglossia maintains strict compartmentalization of language use, deeply embedding linguistic roles within cultural and institutional frameworks.
Artistic and Literary Role of Macaronic Language
Macaronic language plays a significant artistic and literary role by blending elements of multiple languages within a single text, often for humorous or satirical effect, enriching cultural expression and linguistic creativity. Unlike diglossic situations where two language varieties function in separate social contexts, macaronic texts intentionally interweave languages to challenge linguistic boundaries and engage readers in unique interpretive experiences. This stylistic device is prominent in medieval poetry and modern experimental literature, highlighting the fluidity of language identity and cultural hybridity.
Linguistic Structure: Diglossic vs. Macaronic
Diglossic linguistic structure involves the use of two distinct language varieties within a single speech community, where each variety serves specific social functions, such as a formal high variety versus an informal low variety. Macaronic language blends elements from two or more languages within a single utterance or text, often mixing syntax, vocabulary, and grammar to create a hybrid form. The key distinction lies in diglossia's clear functional separation between language varieties, while macaronic language exhibits simultaneous intermingling and code-switching at the structural level.
Practical Examples in Modern Culture
Diglossic situations appear in societies like Switzerland, where Swiss German is used in informal speech while Standard German dominates formal settings, illustrating clear functional language separation. Macaronic language is evident in popular music and social media, often blending English with regional languages, such as Spanglish in American Latino communities, creating a hybrid linguistic style. These examples highlight diglossia's structured bilingualism versus macaronic's fluid code-switching in everyday communication.
Conclusion: Comparing Diglossic and Macaronic Phenomena
Diglossic situations involve the systematic use of two distinct language varieties within a speech community, typically separating formal and informal contexts, while macaronic language blends elements of multiple languages within the same utterance or text. Diglossia reflects stable bilingualism with clear functional separation, whereas macaronic forms indicate code-switching or linguistic creativity without strict compartmentalization. Understanding these differences aids in analyzing sociolinguistic patterns and language contact dynamics across multilingual environments.
Diglossic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com