Discourse shapes how ideas are communicated and understood within various social contexts, influencing perceptions and interactions. Examining the structures and functions of discourse helps unravel the underlying power dynamics and cultural norms embedded in language use. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how discourse impacts communication in everyday life.
Table of Comparison
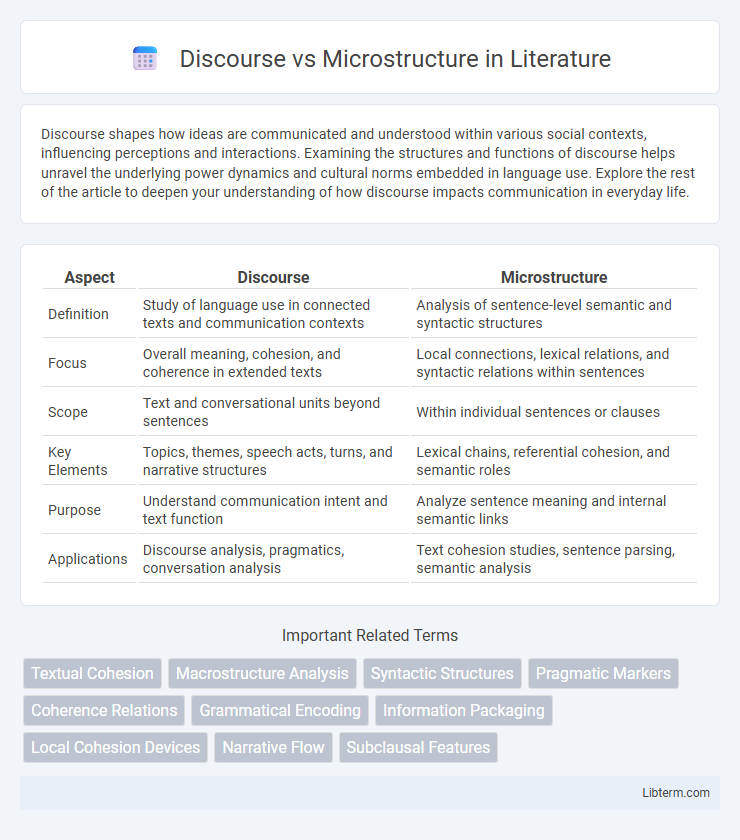
| Aspect | Discourse | Microstructure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of language use in connected texts and communication contexts | Analysis of sentence-level semantic and syntactic structures |
| Focus | Overall meaning, cohesion, and coherence in extended texts | Local connections, lexical relations, and syntactic relations within sentences |
| Scope | Text and conversational units beyond sentences | Within individual sentences or clauses |
| Key Elements | Topics, themes, speech acts, turns, and narrative structures | Lexical chains, referential cohesion, and semantic roles |
| Purpose | Understand communication intent and text function | Analyze sentence meaning and internal semantic links |
| Applications | Discourse analysis, pragmatics, conversation analysis | Text cohesion studies, sentence parsing, semantic analysis |
Introduction to Discourse and Microstructure
Discourse refers to the larger units of language beyond the sentence, encompassing how ideas are organized and connected to convey meaning in spoken or written communication. Microstructure focuses on the detailed organization within sentences, such as syntax, morphology, and local coherence, providing the building blocks for coherent discourse. Understanding both discourse and microstructure is essential for analyzing language comprehensively, as discourse reveals the broader communicative intent while microstructure ensures clarity and precision at the sentence level.
Defining Discourse in Linguistics
Discourse in linguistics refers to structured sequences of language beyond the sentence level, encompassing spoken or written communication that conveys meaning within context. It involves the analysis of larger units such as conversations, narratives, and texts, focusing on coherence, cohesion, and the relationship between sentences. Discourse contrasts with microstructure, which examines linguistic elements at the sentence or phrase level, including syntax, morphology, and phonology.
Understanding Microstructure: A Detailed Overview
Microstructure refers to the internal organization and arrangement of elements within a text, including syntax, morphology, and phonology, which contribute to meaning at the sentence or phrase level. Understanding microstructure involves analyzing how these linguistic components function together to create coherence and clarity within smaller units of language. This detailed examination contrasts with discourse analysis, which focuses on larger structures like paragraph or conversational flow.
Key Differences Between Discourse and Microstructure
Discourse refers to the broader structure and organization of spoken or written communication, encompassing sentences and larger units that convey meaning in context. Microstructure focuses on the detailed linguistic elements within a text, such as syntax, morphology, and semantics at the sentence or phrase level. Key differences include discourse's emphasis on coherence, topic development, and pragmatic context, whereas microstructure centers on grammatical accuracy, word choice, and semantic relationships within individual sentences.
Role of Context in Discourse and Microstructure
Discourse involves the broader context that shapes meaning across sentences and interactions, integrating cultural, social, and situational factors to facilitate effective communication. Microstructure focuses on the finer linguistic elements such as syntax, morphology, and lexical choices within sentences, where context influences word meaning and grammatical relations. Understanding context in discourse enables interpretation of speaker intent and coherence, while in microstructure, it guides the selection of appropriate syntactic forms and semantic nuances at the sentence level.
Analyzing Language at the Discourse Level
Analyzing language at the discourse level involves examining larger units of text or conversation beyond individual sentences to understand how meaning is constructed through context, coherence, and interaction. Discourse analysis focuses on the relationship between utterances, the intentions of speakers or writers, and the social or cultural factors shaping communication. In contrast, microstructure analysis targets sentence-level features like syntax, morphology, and lexical choice, making discourse analysis essential for interpreting pragmatic meaning and real-world communication patterns.
Exploring Microstructure Features in Texts
Microstructure features in texts include cohesion, lexical choice, and syntactic complexity, which contribute to the clarity and flow of individual sentences and their immediate connections. Discourse analysis examines larger units of language, focusing on how these microstructures combine to create coherence and overall meaning across paragraphs or entire texts. Exploring microstructure elements enables detailed assessment of linguistic devices that shape reader comprehension and engagement within the text.
Applications in Linguistics and Communication Studies
Discourse analysis examines language use across larger units such as conversations or written texts, focusing on coherence, context, and social interaction, making it essential in communication studies for understanding how meaning is constructed and negotiated. Microstructure analysis, by contrast, deals with the finer-grained elements of language such as syntax, morphology, and phonology, serving linguistics by revealing detailed structural patterns and language rules. Both approaches complement each other in applied linguistics, where discourse provides insight into pragmatic functions and microstructure supports the precise description of language form.
Challenges in Differentiating Discourse and Microstructure
Differentiating discourse and microstructure presents challenges due to their overlapping features in language analysis, where discourse encompasses broader thematic and contextual elements, while microstructure focuses on sentence-level cohesion and coherence. The subtle interplay between macro-level pragmatics and micro-level syntax often leads to ambiguity in delineating boundaries, complicating tasks such as text segmentation and discourse parsing. Advances in computational linguistics and natural language processing aim to address these challenges by developing algorithms capable of simultaneously analyzing discourse patterns and microstructural elements for improved text understanding.
Conclusion: Balancing Macro and Micro Linguistic Perspectives
Balancing macro and micro linguistic perspectives is essential for comprehensive language analysis, as discourse examines the broader context and communicative functions while microstructure focuses on sentence-level syntax and semantics. Integrating both approaches enriches understanding by linking global coherence with local linguistic features, improving insights into meaning construction and language use. This synergy enhances applications in linguistics, cognitive science, and natural language processing by addressing multiple layers of language simultaneously.
Discourse Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com