Genre classification helps organize and categorize creative works, making it easier for audiences to find content that matches their interests. Understanding different genres allows you to set accurate expectations and appreciate the unique stylistic elements within films, books, music, or games. Explore the article to discover how genre influences storytelling and enhances your entertainment experience.
Table of Comparison
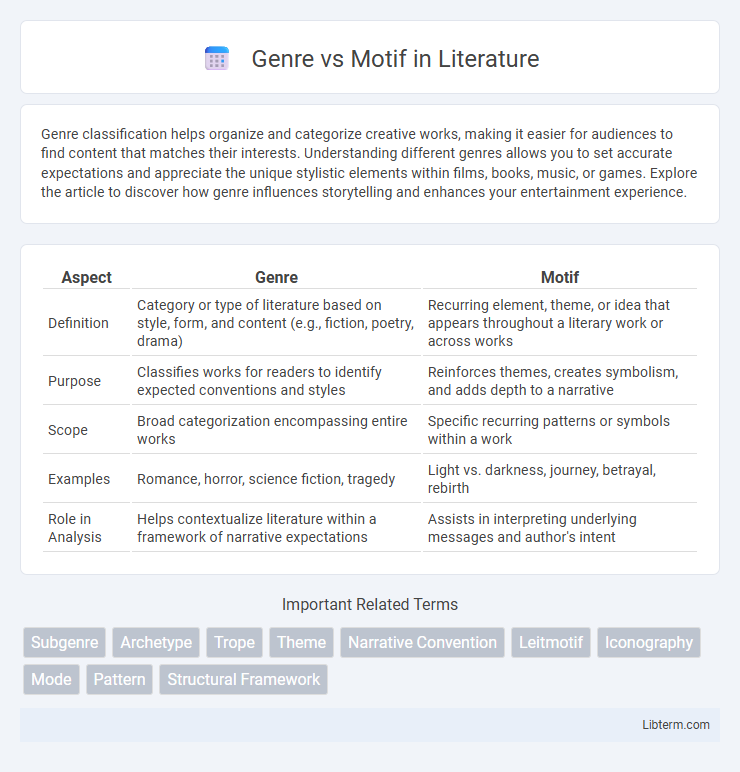
| Aspect | Genre | Motif |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Category or type of literature based on style, form, and content (e.g., fiction, poetry, drama) | Recurring element, theme, or idea that appears throughout a literary work or across works |
| Purpose | Classifies works for readers to identify expected conventions and styles | Reinforces themes, creates symbolism, and adds depth to a narrative |
| Scope | Broad categorization encompassing entire works | Specific recurring patterns or symbols within a work |
| Examples | Romance, horror, science fiction, tragedy | Light vs. darkness, journey, betrayal, rebirth |
| Role in Analysis | Helps contextualize literature within a framework of narrative expectations | Assists in interpreting underlying messages and author's intent |
Understanding Genre: Definition and Scope
Genre defines a category of artistic composition characterized by similarities in form, style, or subject matter, guiding audience expectations and industry classification. It encompasses broad classifications such as fiction, non-fiction, fantasy, horror, and romance, each with distinctive thematic and structural conventions. Understanding genre allows creators and consumers to navigate content effectively, influencing narrative techniques and thematic focus within various media forms.
What Is a Motif? A Clear Explanation
A motif is a recurring element, symbol, or idea that appears throughout a literary work, reinforcing the theme and deepening the narrative's meaning. Unlike genre, which classifies the overall category of a story such as thriller, romance, or fantasy, motifs operate within the text to create connections and evoke emotions. Common motifs include objects, colors, phrases, or concepts that gain significance through repetition and contribute to the story's underlying message.
Key Differences Between Genre and Motif
Genre defines the overall category of a narrative, such as fiction, horror, or romance, shaping the story's structure and audience expectations. Motif refers to recurring elements, symbols, or themes within a work that reinforce its central message or mood, like the use of darkness to symbolize fear. Key differences include genre being a broad classification guiding the story's format, while motif is a specific, repeated detail that supports thematic development.
The Role of Genre in Literature and Media
Genre in literature and media serves as a structural framework that categorizes works based on shared conventions, themes, and stylistic elements, guiding audience expectations and interpretations. It influences narrative techniques, character development, and plot structures, establishing a familiar context that enhances engagement and comprehension. While motifs are recurring thematic elements or symbols within a work, genre defines the broader classification, shaping the overall storytelling approach and cultural resonance.
How Motifs Enhance Storytelling
Motifs enhance storytelling by reinforcing central themes and creating symbolic resonance throughout a narrative, allowing audiences to connect deeper with the plot and characters. Unlike genre, which defines the overall category and style of a story, motifs are recurring elements such as images, sounds, or phrases that add layers of meaning and cohesion. By weaving motifs consistently into various story components, writers enrich emotional impact and highlight key messages organically within the genre framework.
Common Genres and Their Characteristics
Common genres like mystery, romance, and science fiction each possess distinct characteristics that shape the narrative structure and reader expectations. Mystery genre often features suspense, clues, and a resolution centered on solving a puzzle or crime, while romance emphasizes emotional relationships and character development. Science fiction typically explores futuristic settings, advanced technology, and speculative scientific concepts, allowing a blend of imaginative storytelling and social commentary.
Popular Motifs Across Different Genres
Popular motifs such as the hero's journey, love triangles, and the battle between good and evil frequently appear across diverse genres including fantasy, romance, and thriller, creating recognizable narrative patterns that resonate with audiences. While genres categorize stories by structural and stylistic conventions, motifs are recurring thematic elements that transcend genre boundaries and enrich storytelling depth. Understanding the interplay between genre and motif allows creators to innovate within traditional frameworks and engage viewers through familiar yet dynamic storytelling elements.
Why Genre Matters in Audience Expectation
Genre establishes a framework that guides audience expectations by signaling themes, narrative structures, and emotional tones typical to specific categories like horror, romance, or science fiction. This predictability helps viewers or readers anticipate story progression and character development, facilitating engagement and satisfaction. Understanding genre conventions also aids creators in innovating within or subverting audience assumptions to enhance impact.
The Impact of Motifs on Narrative Depth
Motifs significantly enhance narrative depth by reinforcing themes and creating symbolic connections that resonate throughout a story, distinguishing them from genres that merely categorize the work's overall style or content. Recurring motifs contribute layers of meaning, enabling readers to uncover subtle emotional or conceptual undercurrents within a narrative. This thematic repetition deepens character development and plot complexity, elevating the storytelling experience beyond the bounds of its genre classification.
Blending Genre and Motif for Powerful Stories
Blending genre and motif creates powerful stories by combining distinct narrative frameworks with recurring thematic elements, enhancing emotional resonance and thematic depth. For example, a science fiction genre infused with the motif of isolation can amplify tension and character development, while a romance genre featuring motifs of transformation enriches the emotional journey. Integrating genre and motif strategically allows storytellers to craft multilayered narratives that engage audiences through familiar structures and meaningful symbolism.
Genre Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com