Lexis, the complete set of words in a language, forms the foundation of effective communication and expression. Understanding your lexis enhances vocabulary acquisition and improves language comprehension, enabling clearer and more precise communication. Explore the rest of this article to discover how mastering lexis can transform your language skills.
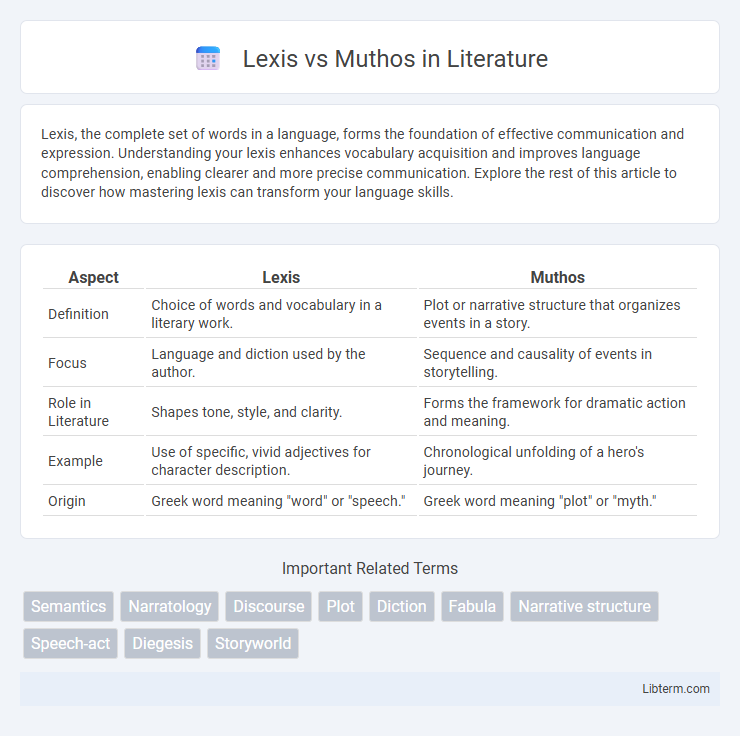
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lexis | Muthos |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Choice of words and vocabulary in a literary work. | Plot or narrative structure that organizes events in a story. |
| Focus | Language and diction used by the author. | Sequence and causality of events in storytelling. |
| Role in Literature | Shapes tone, style, and clarity. | Forms the framework for dramatic action and meaning. |
| Example | Use of specific, vivid adjectives for character description. | Chronological unfolding of a hero's journey. |
| Origin | Greek word meaning "word" or "speech." | Greek word meaning "plot" or "myth." |
Understanding Lexis: Definition and Significance
Lexis refers to the specific choice of words and vocabulary within a language, crucial for conveying precise meaning and tone in communication. It encompasses not only individual words but also phrases and collocations that shape the semantic landscape of a text. Understanding lexis is essential for analyzing language patterns, enhancing vocabulary acquisition, and improving overall language proficiency.
What is Muthos? A Comprehensive Overview
Muthos refers to the traditional narrative or mythic story that conveys cultural beliefs, values, and existential truths within ancient societies, often rooted in oral tradition. It serves as a foundational element in understanding human experience by embodying symbolic meaning rather than factual accuracy, distinct from lexis, which prioritizes precise language and logical structure. Emphasizing archetypal themes and moral lessons, muthos functions as a collective repository of wisdom passed through generations.
Lexis vs Muthos: Key Differences
Lexis and Muthos represent two fundamental elements in classical storytelling, with Lexis referring to the choice of words or diction used by characters, while Muthos denotes the structured plot or sequence of events in a narrative. Lexis contributes to character development and dialogue, emphasizing language style and expression, whereas Muthos focuses on the thematic framework and causality within the story. The key difference lies in Lexis shaping *how* the story is told through language, whereas Muthos defines *what* happens in the story's progression.
The Role of Lexis in Rhetoric and Literature
Lexis, referring to word choice and style, plays a crucial role in rhetoric and literature by shaping meaning and influencing audience interpretation. It enhances persuasive power through precise vocabulary, nuanced diction, and effective metaphors, differentiating it from Muthos, which centers on plot and narrative structure. Mastery of Lexis allows writers and speakers to evoke emotions, reinforce themes, and craft memorable expressions that resonate deeply with their audiences.
Muthos in Classical Narratives: Function and Impact
Muthos in classical narratives serves as the foundational mythic framework that shapes cultural identity and imparts moral lessons through symbolic storytelling. Unlike lexis, which pertains to the specific language and style, muthos structures the plot and thematic essence, driving the narrative's emotional and philosophical resonance. Its function extends beyond mere entertainment, fostering communal values and influencing the collective imagination across generations.
Historical Evolution of Lexis and Muthos
The historical evolution of lexis and muthos traces back to Ancient Greek literature, where lexis refers to the precise use of language or diction, while muthos denotes the structured narrative or plot within a story. Classical philosophers like Aristotle distinguished muthos as the foundational element of tragedy, emphasizing its priority over lexis in creating emotional impact and thematic coherence. Over time, literary theory evolved to explore the dynamic interplay between lexis as the artistic expression of language and muthos as the underlying mythic framework that drives storytelling across cultures.
Lexis and Muthos in Aristotle’s Poetics
In Aristotle's Poetics, Lexis refers to the style of expression or diction, encompassing word choice, phrasing, and tone that shapes the audience's perception and emotional response. Muthos signifies the plot or the sequence of events, which Aristotle considers the foundation of tragedy, responsible for structure and coherence in the narrative. The interplay between Lexis and Muthos demonstrates how effective storytelling relies on both compelling content and the skilled delivery of language.
Modern Interpretations of Lexis and Muthos
Modern interpretations of lexis and muthos emphasize the distinction between language and narrative structure in literary theory. Lexis refers to the specific choice of words and style, which crafts the emotional tone and rhythm of a text, while muthos denotes the plot or sequence of events that shapes the story's meaning. Contemporary scholars analyze how lexis enhances the thematic depth and psychological impact of muthos, highlighting the interplay between language use and storytelling in shaping audience experience.
Practical Applications: Lexis and Muthos in Storytelling
Lexis in storytelling emphasizes the choice of words and language style to shape the audience's perception and emotional engagement, enhancing clarity and impact in communication. Muthos, referring to the plot or narrative structure, drives the sequence of events and character actions to create meaning and coherence within the story. Effective storytelling combines precise lexis with a compelling muthos, ensuring that both language and plot work together to captivate and influence the audience.
Conclusion: The Interplay Between Lexis and Muthos
Lexis and muthos function as integral components within narrative construction, where lexis pertains to the style and diction of language, and muthos represents the plot or sequence of events. The effective interplay between these elements shapes the audience's emotional engagement and comprehension of dramatic works, with lexis enhancing the thematic depth and muthos providing structural coherence. Together, they forge a cohesive storytelling experience that balances linguistic expression with narrative progression.
Lexis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com