Essence captures the fundamental nature or core quality of something, often defining its true identity beyond superficial attributes. Understanding the essence of a concept or product helps you appreciate its deeper significance and value. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how essence influences perception and meaning.
Table of Comparison
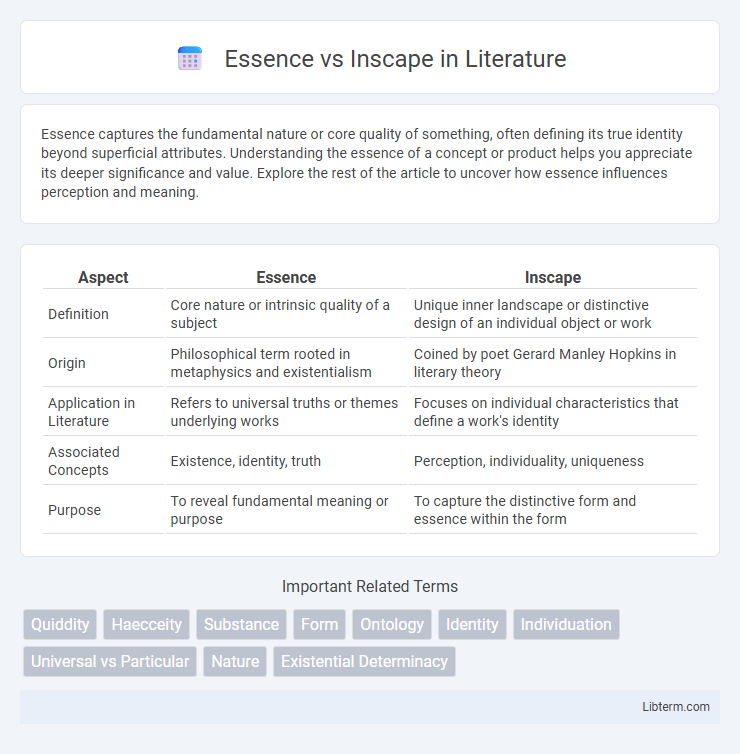
| Aspect | Essence | Inscape |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core nature or intrinsic quality of a subject | Unique inner landscape or distinctive design of an individual object or work |
| Origin | Philosophical term rooted in metaphysics and existentialism | Coined by poet Gerard Manley Hopkins in literary theory |
| Application in Literature | Refers to universal truths or themes underlying works | Focuses on individual characteristics that define a work's identity |
| Associated Concepts | Existence, identity, truth | Perception, individuality, uniqueness |
| Purpose | To reveal fundamental meaning or purpose | To capture the distinctive form and essence within the form |
Understanding Essence: A Philosophical Overview
Understanding essence involves grasping the fundamental nature or intrinsic properties that define an entity's identity, distinguishing it from other beings. Essence refers to what makes a thing what it is, often contrasted with appearance or accident, emphasizing the core attributes that persist through change. Philosophers like Aristotle and Heidegger explored essence to explain being and existence, highlighting its role in metaphysics and ontology.
Defining Inscape: Gerard Manley Hopkins’ Concept
Inscape, a key concept developed by Gerard Manley Hopkins, refers to the unique, intrinsic design that constitutes the individual identity of a thing or being, capturing its essential pattern and distinctiveness. Unlike essence, which implies a universal or abstract core common to a category, inscape emphasizes the particular details that make each entity uniquely itself, presenting a dynamic and vivid perception of reality. Hopkins' notion of inscape is pivotal in his poetry, illustrating the interplay between form and meaning, and offering a profound way to appreciate nature's diversity through the lens of individual uniqueness.
Essence vs Inscape: Key Differences
Essence refers to the intrinsic nature or indispensable quality that defines an entity, while inscape denotes the unique inner landscape or individual characteristics that shape its identity. Essence captures universal attributes that remain constant, whereas inscape emphasizes personal, subjective features distinguishing one being or object from another. Understanding the key differences between essence and inscape is crucial in philosophy, art, and literary analysis to distinguish between fundamental nature and particular individuality.
Historical Origins and Development
Essence and Inscape have roots in medieval philosophy, where essence referred to the fundamental nature defining a thing's identity, prominently discussed by Aristotle and later Scholastic thinkers. Inscape, coined by poet Gerard Manley Hopkins in the 19th century, emphasizes the unique, distinctive pattern or inner landscape of an individual object or being, reflecting its individuality. The historical development of essence centers on metaphysical inquiry, while inscape evolved through literary and aesthetic contexts, highlighting a shift from abstract universals to concrete particularities.
Essence in Classical Philosophy
Essence in Classical Philosophy refers to the fundamental nature or intrinsic qualities that define an entity, distinguishing it from accidental properties. Rooted in Aristotelian metaphysics, essence represents what makes a substance what it fundamentally is, often contrasted with existence or appearance. Unlike Inscape, which emphasizes individual uniqueness and internal structure, essence highlights universal characteristics shared across instances of a species or category.
Inscape and Its Role in Poetry
Inscape, a term coined by poet Gerard Manley Hopkins, refers to the unique inner nature or distinctive design that defines individual entities in poetry, emphasizing their intrinsic characteristics and essence. It plays a crucial role in poetry by enabling poets to capture and convey the profound, often intangible qualities that make each subject singular, thus enriching the reader's experiential understanding. Through the vivid articulation of inscape, poetry transcends mere description, delivering a resonant, immersive encounter with the subject's authentic being.
Modern Interpretations of Essence and Inscape
Modern interpretations of essence emphasize the core attributes or fundamental nature that define an entity's identity across various contexts, including philosophy and ontology. Inscape, originally coined by poet Gerard Manley Hopkins, is reinterpreted in contemporary aesthetics as the unique inner landscape or distinctive pattern that gives an individual object or experience its particular character. The growing interdisciplinary dialogue integrates essence as the universal foundation while inscape captures the subjective, perceptual qualities that differentiate and personalize existence.
Practical Applications in Literature and Art
Essence in literature and art captures the fundamental nature or intrinsic qualities of a subject, guiding writers and artists to portray universal truths and core characteristics. Inscape emphasizes the unique, individual inner landscape or distinct arrangement of features within a work, inspiring creative expression focused on personal perception and imaginative details. Practical applications in literature involve authors revealing characters' essences to evoke empathy, while artists use inscape to convey subjective experiences and create richly textured visual narratives.
Essence and Inscape in Contemporary Thought
Essence and Inscape in contemporary thought represent crucial philosophical concepts where essence refers to the fundamental nature or intrinsic properties that define an entity, while inscape denotes the unique inner characteristics that distinguish one individual or object from another. Modern philosophers and theorists emphasize essence as the universal attributes shared across instances, and inscape as the particular, subjective qualities that contribute to identity and individuality. This distinction influences diverse fields including metaphysics, aesthetics, and identity theory by highlighting the interplay between shared essence and unique inscape in understanding reality.
Comparing Essence and Inscape: A Semantic Analysis
Essence captures the fundamental nature or intrinsic qualities that define an entity, while inscape refers to the unique inner landscape or distinctive individuality of a subject. Semantic analysis reveals essence as a universal, abstract concept key to ontology and metaphysics, whereas inscape emphasizes subjective, visual, and poetic dimensions, often used in literary criticism and art theory. The comparison highlights essence as static and essential, with inscape dynamic and perceptual, bridging philosophical substance and experiential identity.
Essence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com