Redundancy in systems or communication refers to the duplication of critical components or functions to increase reliability and prevent failure. It reduces the risk of downtime by ensuring that backup resources are available when primary ones fail. Explore the rest of the article to understand how redundancy can enhance your system's efficiency and resilience.
Table of Comparison
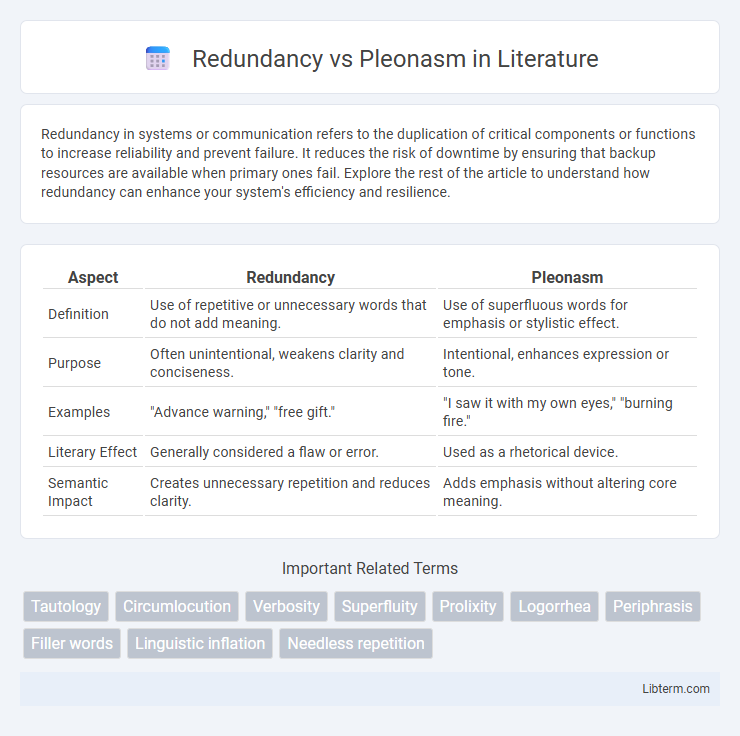
| Aspect | Redundancy | Pleonasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of repetitive or unnecessary words that do not add meaning. | Use of superfluous words for emphasis or stylistic effect. |
| Purpose | Often unintentional, weakens clarity and conciseness. | Intentional, enhances expression or tone. |
| Examples | "Advance warning," "free gift." | "I saw it with my own eyes," "burning fire." |
| Literary Effect | Generally considered a flaw or error. | Used as a rhetorical device. |
| Semantic Impact | Creates unnecessary repetition and reduces clarity. | Adds emphasis without altering core meaning. |
Understanding Redundancy in Language
Redundancy in language occurs when extra words repeat the same idea unnecessarily, such as "free gift" or "advance planning," leading to inefficiency in communication. This contrasts with pleonasm, which involves the use of more words than needed for emphasis or clarification, like "burning fire." Understanding redundancy helps improve clarity and conciseness by eliminating repetitive expressions that clutter sentences.
Defining Pleonasm: What Does It Mean?
Pleonasm is a linguistic term referring to the use of more words than necessary to convey meaning, often resulting in redundancy within a phrase. Unlike general redundancy, which can be unintentional repetition or excess, pleonasm involves deliberate or stylistic choices that emphasize or clarify a statement. Examples include phrases like "free gift" or "true fact," where the additional words add emphasis but are logically superfluous.
Key Differences Between Redundancy and Pleonasm
Redundancy involves the unnecessary repetition of information that does not add meaning, such as "free gift," while pleonasm refers to the use of more words than needed to express an idea, often for emphasis or stylistic reasons, like "burning fire." Redundancy typically weakens communication clarity by repeating identical content, whereas pleonasm can enhance expression or provide poetic effect despite excess wording. Understanding these distinctions helps improve language precision by avoiding superfluous repetition and recognizing purposeful elaboration.
Historical Origins of Redundancy and Pleonasm
Redundancy and pleonasm both stem from ancient linguistic practices aimed at emphasis and clarity in communication, with redundancy often tracing back to Latin rhetoric where repetition reinforced meaning. Pleonasm originates from Greek rhetorical traditions, emphasizing excess wording to amplify or clarify ideas beyond their necessary expression. Historical usage in classical literature reveals how both devices evolved as stylistic tools to enhance persuasive and poetic speech.
Common Examples of Redundant Phrases
Common examples of redundant phrases include "free gift," "advance warning," and "true fact," where the modifier adds no new meaning to the noun. In contrast, pleonasm involves the use of more words than necessary to convey meaning, often resulting in repetitive or unnecessarily elaborate expressions, such as "tuna fish" or "hot water heater." Understanding the distinction between redundancy and pleonasm helps improve clarity and precision in writing by eliminating superfluous language.
Notable Instances of Pleonasm in Everyday Speech
Notable instances of pleonasm in everyday speech include phrases like "free gift," "true fact," and "advance planning," where redundant words add emphasis without altering the meaning. These expressions illustrate how pleonasm functions as a linguistic tool to reinforce clarity or style, despite being logically superfluous. Understanding pleonasm enhances communication awareness by distinguishing it from redundancy, which often implies unnecessary repetition rather than deliberate emphasis.
The Impact of Redundancy on Effective Communication
Redundancy in communication involves repetitive or unnecessary information that can dilute the clarity and effectiveness of the message, whereas pleonasm refers to the use of more words than necessary, often for emphasis or style. Excessive redundancy can overwhelm the receiver, causing confusion and reducing the overall impact of the communication. By eliminating redundant elements, speakers and writers enhance message precision, improve audience engagement, and ensure successful knowledge transfer.
When Is Pleonasm Acceptable or Useful?
Pleonasm is acceptable or useful when it enhances clarity, emphasis, or style in communication by deliberately repeating words or ideas for effect. Poets and writers often use pleonasm to create rhythm or highlight important concepts, while redundancy typically degrades concise writing and should be avoided in technical or academic contexts. Understanding the distinction between pleonasm as a rhetorical device and redundancy as unnecessary repetition helps writers choose when to employ each appropriately.
Tips to Avoid Unnecessary Redundancy and Pleonasm
To avoid unnecessary redundancy and pleonasm, carefully review sentences for repeated meanings, such as "free gift" or "true fact," and eliminate one word that conveys the same idea. Use precise vocabulary and rely on context to convey emphasis without duplicating information. Employ tools like style guides or grammar checkers to identify common pleonasms and improve sentence clarity.
Redundancy vs Pleonasm: Why It Matters in Writing
Redundancy involves unnecessary repetition that adds no value to writing, while pleonasm uses extra words for emphasis or clarity, sometimes enhancing style. Understanding the difference is crucial for effective communication, as excessive redundancy can clutter text, decreasing readability and reader engagement. Writers must balance clarity and conciseness to maintain impactful, polished prose that respects the reader's time.
Redundancy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com