Idioms are expressions whose meanings cannot be deduced from the literal definitions of the words they contain, making them essential for mastering fluent communication. Understanding idioms enriches your vocabulary and helps convey complex ideas succinctly in everyday conversations and writing. Explore the rest of this article to unlock the secrets behind popular idioms and how they can enhance your language skills.
Table of Comparison
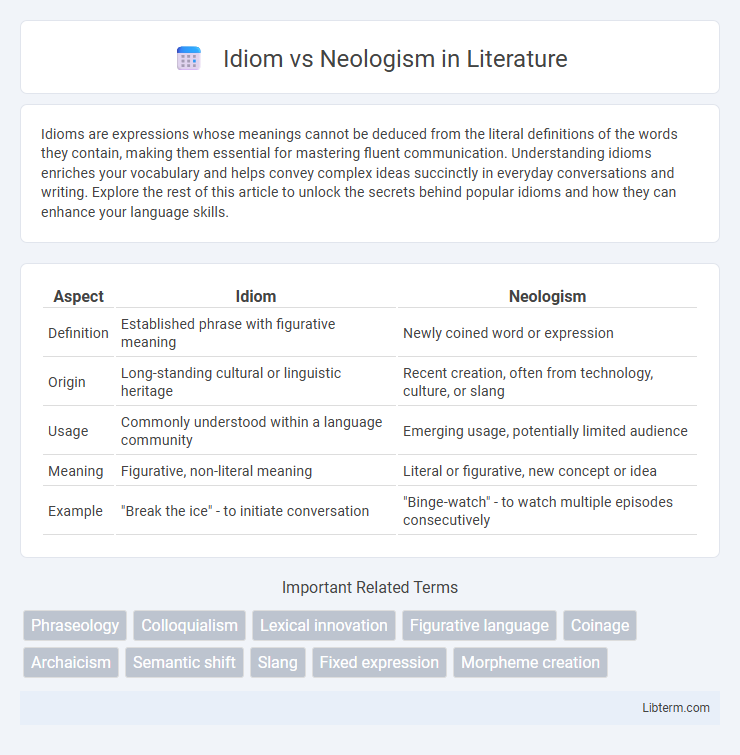
| Aspect | Idiom | Neologism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Established phrase with figurative meaning | Newly coined word or expression |
| Origin | Long-standing cultural or linguistic heritage | Recent creation, often from technology, culture, or slang |
| Usage | Commonly understood within a language community | Emerging usage, potentially limited audience |
| Meaning | Figurative, non-literal meaning | Literal or figurative, new concept or idea |
| Example | "Break the ice" - to initiate conversation | "Binge-watch" - to watch multiple episodes consecutively |
Introduction to Idioms and Neologisms
Idioms are fixed expressions with meanings that cannot be deduced from the individual words, such as "kick the bucket," which means to die. Neologisms are newly coined terms or phrases, often created to describe emerging concepts or technologies, like "selfie." Understanding idioms involves grasping cultural context and figurative language, while neologisms require awareness of evolving vocabulary and innovation in language use.
Defining Idioms: Meaning and Usage
Idioms are fixed expressions with meanings that cannot be deduced from the individual words, such as "spill the beans" meaning to reveal a secret. They are deeply ingrained in language and culture, often used to convey figurative meanings that add color and emphasis to communication. Unlike neologisms, which are newly coined terms, idioms have a long-standing usage and are recognized as established phrases within the language.
Understanding Neologisms: Creation and Adoption
Neologisms emerge through creative processes such as blending, borrowing, and compounding, driven by cultural shifts and technological advancements. Unlike idioms, which are fixed expressions with figurative meanings rooted in tradition, neologisms offer novel terms that fill lexical gaps or express new concepts. Linguistic communities adopt neologisms through media exposure, social interaction, and cognitive ease of use, accelerating their integration into everyday language.
Historical Development of Idioms
Idioms have evolved over centuries, rooted in cultural traditions and historical events that shape their meanings beyond literal interpretations. These fixed expressions often originate from folklore, religion, and ancient practices, preserving linguistic heritage across generations. Unlike neologisms, which emerge spontaneously to describe new concepts or technologies, idioms reflect long-term societal values and collective experiences.
How Neologisms Emerge in Language
Neologisms emerge in language through cultural shifts, technological advancements, and social innovation, often filling lexical gaps or expressing new concepts. Unlike idioms, which are fixed expressions with established meanings, neologisms are newly coined terms that can quickly gain popularity via media, internet platforms, and scientific communities. The rapid evolution of digital communication accelerates the creation and adoption of neologisms, reflecting contemporary societal changes and expanding linguistic diversity.
Cultural Significance of Idioms
Idioms carry deep cultural significance as they encapsulate unique historical contexts, social values, and collective experiences of a community, making them rich linguistic artifacts. Unlike neologisms, which are newly coined terms often driven by technological or social changes, idioms offer insight into traditions and shared meanings passed down through generations. Their figurative nature and cultural rootedness make idioms essential for understanding and preserving cultural identity within language.
The Role of Neologisms in Modern Communication
Neologisms play a crucial role in modern communication by introducing new words or expressions that capture emerging concepts and technologies better than traditional idioms. Unlike idioms, which are fixed phrases with established meanings, neologisms evolve rapidly and allow language to adapt to cultural changes and innovations. This dynamic quality helps facilitate clearer and more precise communication in digital media, science, and social discourse.
Idiom vs Neologism: Key Differences
Idioms are established phrases with figurative meanings that often cannot be deduced from the individual words, such as "break the ice," whereas neologisms are newly coined terms or expressions emerging from cultural, technological, or social changes, like "selfie." Idioms have a long history and are widely recognized within a language community, while neologisms often require explanation and gain acceptance over time. The key difference lies in idioms representing idiomatic expressions embedded in language tradition, contrasted with neologisms reflecting linguistic innovation and evolving vocabulary.
Impact on Language Evolution
Idioms preserve cultural heritage by encapsulating traditional meanings in figurative expressions, enriching language with historical depth. Neologisms drive language evolution through rapid incorporation of new concepts and technological advancements, reflecting societal changes and innovation. The interplay between idioms and neologisms balances linguistic continuity with dynamic adaptation, shaping contemporary communication.
Conclusion: The Dynamic Nature of Language
Idioms and neologisms both illustrate the adaptive and evolving nature of language as society and culture change. While idioms preserve historical and cultural meanings in fixed expressions, neologisms introduce novel terms to address emerging concepts and innovations. This dynamic interplay ensures language remains vibrant and relevant in communication.
Idiom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com